M_Nabil
|Subscribers
Latest videos
A prenatal ultrasound (also called a sonogram) is a noninvasive diagnostic test that uses sound waves to create a visual image of your baby, placenta, and uterus, as well as other pelvic organs. It allows your healthcare practitioner to gather valuable information about the progress of your pregnancy and your baby's health. During the test, an ultrasound technician (sonographer) transmits high-frequency sound waves through your uterus that bounce off your baby. A computer then translates the echoing sounds into video images that reveal your baby's shape, position, and movements. (Ultrasound waves are also used in the handheld instrument called a Doppler that your practitioner uses during your prenatal visits to listen to your baby's heartbeat.) You may have an early ultrasound at your practitioner's office at 6 to 10 weeks to confirm and date the pregnancy. Or you may not have one until the standard midpregnancy ultrasound between 16 and 20 weeks. That's when you may learn your baby's sex, if you like. (The technician will probably present you with a grainy printout of the sonogram as a keepsake.) You may also have a sonogram as part of a genetic test, such as the nuchal translucency test, chorionic villus sampling, or amniocentesis, or at any other time if there are signs of a problem with your baby. You'll have more frequent ultrasounds if you have diabetes, hypertension, or other medical complications.
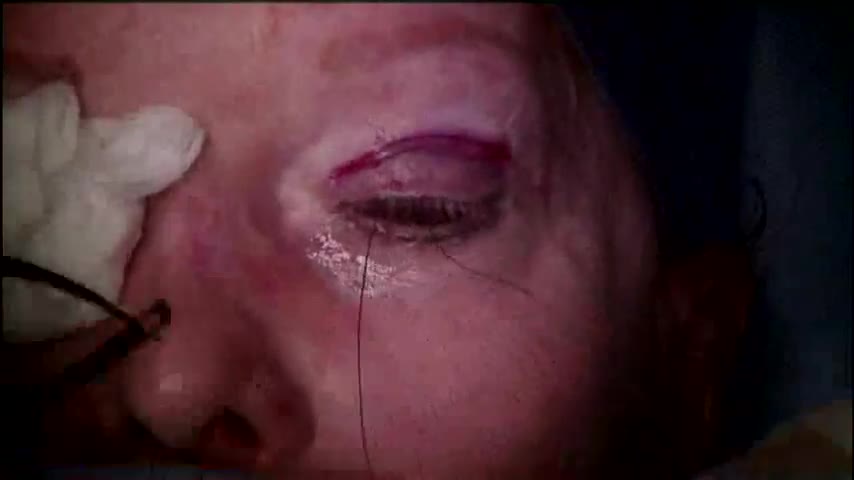
Performed by Kami Parsa M.D. Patient is a 55 year old with a history of previous upper eyelid blepharoplasty with excessive skin removed from both upper eyelids which resulted in bilateral lagophthalmos. Patient could not close her eyes and had problems with severe dry eyes.
Retrograde Laparoscopic Appendectomy: Subhepatic Appendix
This animated video will run you through the process of nuclear stress test.
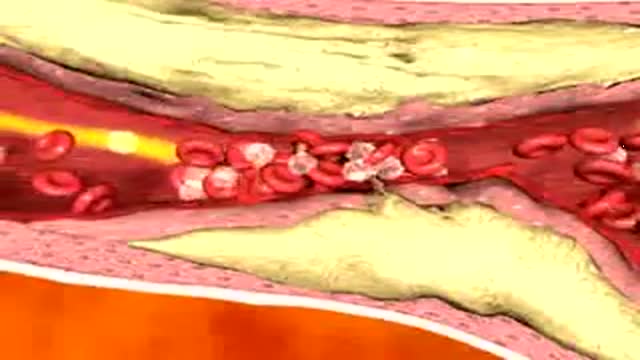
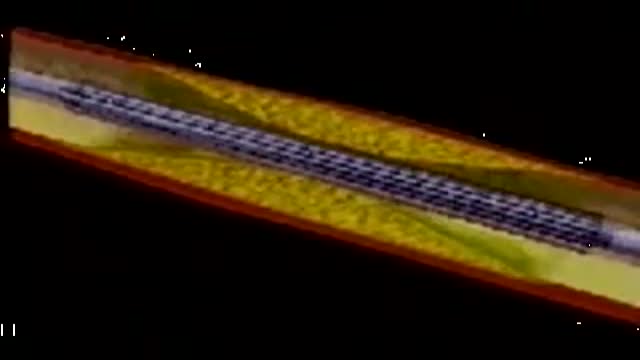
In this animation it depicts an artery with cholesterol plaque (the yellowish area) which is blocking most of the inside of this artery. Then small cells called platelets become clumped together and cause the red blood cells to form a clot. This is what causes a HEART ATTACK.
Electrical Cardioversion
This video depicts how a stent is placed in the coronary artieries. We first place a guiding wire in the heart artery through a catheter, usually from the groin. Then the stent is inflated by a balloon in the artery, which is then removed. The stent remains permanently. Blood thinners, aspirin and plavix, are both required after a stent is placed in your heart artery.
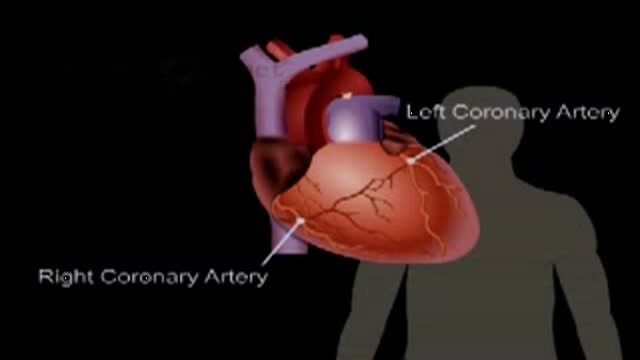
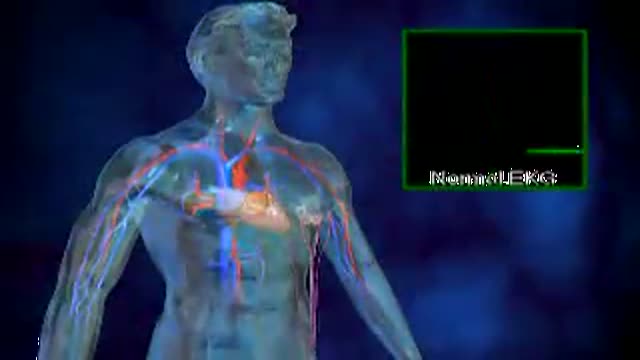
The anatomy and function of the heart
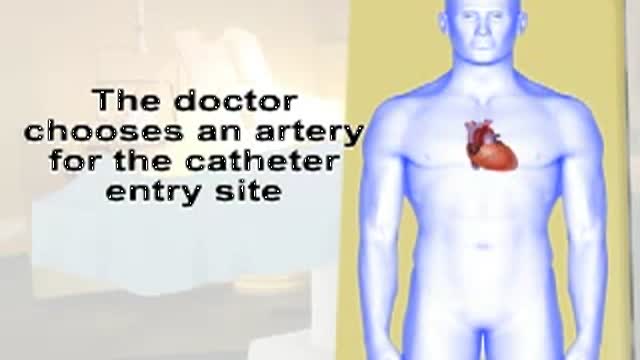
This video gives you an overview of how a cardiac catheterization is performed.
cardiac catheterization in the work up of heart disease.
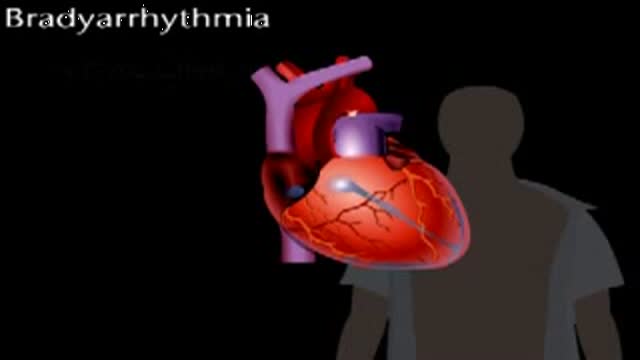
Bradyarrythmias
Atrial Fibrillation is the most common heart rythmn abnormatlity and is very common as you age. Atrial fibrillation is a condition in which the top chambers of the heart, the Atrium are fibrillating, rather than having a regular synchronized contraction. One of the worst complications of Atrial Fibrillation can be Stroke. There are very good treatments of Atrial Fibrillation. This animated video is an overview of Atrial Fibrillation.
Blocked coronary arteries.
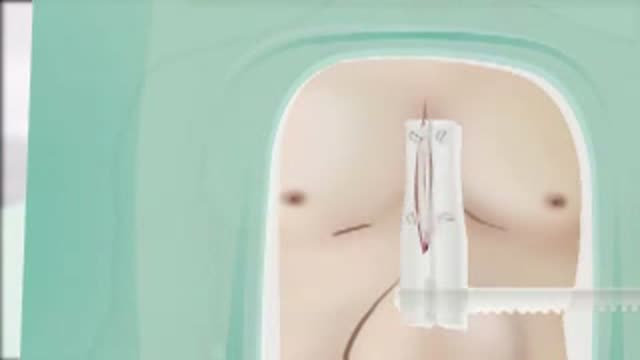
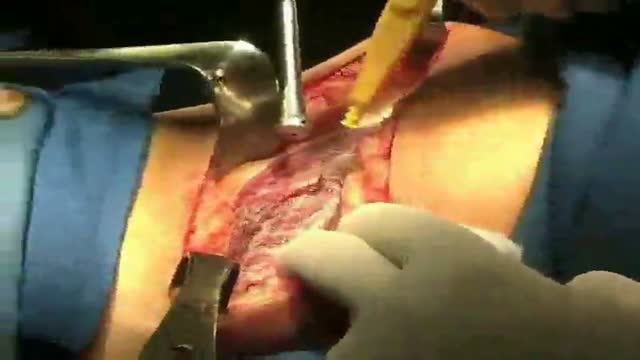
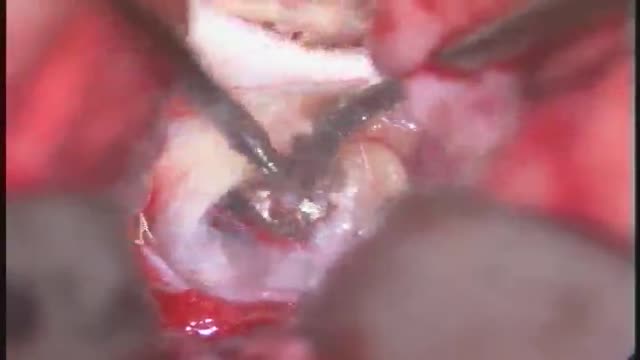
Aortic Valve Replacement Animation
51 yr old female with right flank pain and recurrent UTI. IVP showed a UPJ calculus on the right.
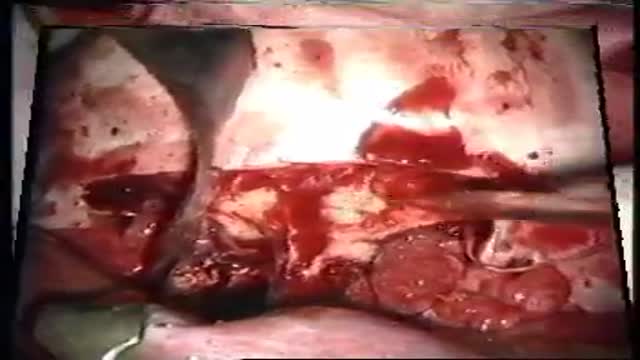
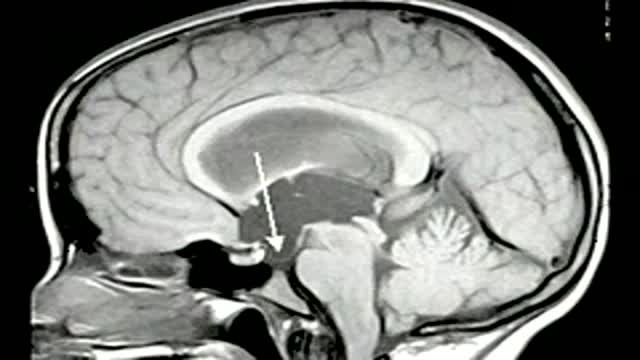
The essential steps of a translaminaterminalis approach for removal of craniopharyngiomas
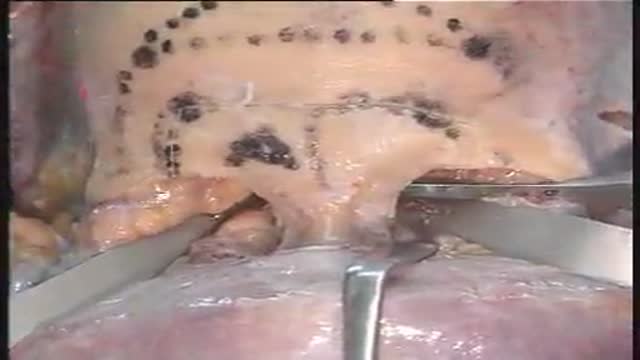
Access to processes within the skull base with lateral extension to the pterygopalatine fossa are reached by combined subfrontal osteotomy and Le Fort I osteotomy
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in a patient with obstructive hydrocephalus
lesions at the anterior skull base invading the paranasal area and the paracavernous area can be reached without brain retraction by the shown subfrontal approach. it enables to control the paranasal sinus, optic nerve, periorbital tissue, carotid artery and pituary gland. reconstruction is not easy... but cosmetically appealing. CSF leaks are rare with the use of fascia lata and tissucol ( fibrin glue). osseous reconstruction is done by microsrews and calciumpyrophosphate ( norian, synthes).
A quick look at an early stage stomach abnormality.