Surgery Videos
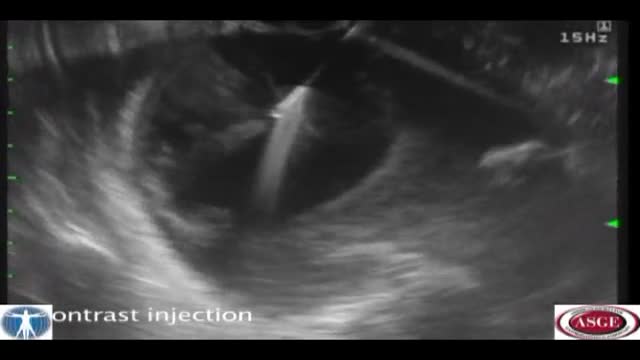
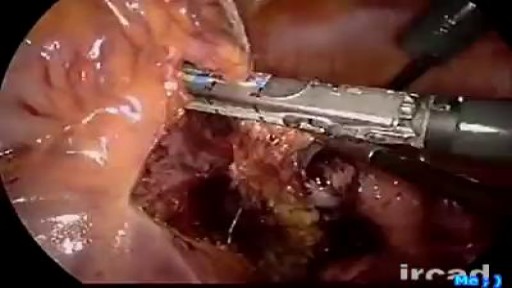
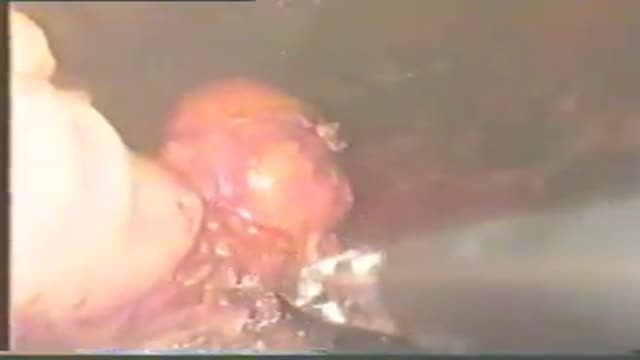
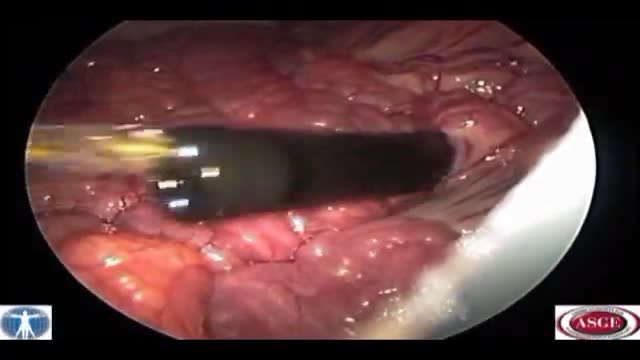
Pancreatic pseudocyst drainage was the first therapeutic application of EUS. The cyst is punctured under ultrasound guidance, contrast injected, and a guidewire inserted. Initial dilation to 8mm is performed over the wire The EUS scope is then exchanged over the wire for a forward viewing endoscope.... A second dilation to 18mm is performed. This enables entry of the endoscope into the cyst perform cystoscopy, debridement if necessary, and insertion of multiple large bore double pigtail stents. The curved linear array-or CLA—echoendoscope has oblique viewing optics located proximal to an oblique scanning transducer. The accessory exits from the shaft of the echoendoscope at an ablique angle, adjustable between 15 and 30 degrees. There are several technical limitations using this echoendoscope. The oblique angle of exit results in a weekend transfer of force when advancing the accessory, difficult deployment of larger bore accessories, and in instrument tunneling effect relative to the bowel wall. There is the potential loss of access during endoscope exchange. A novel CLA echoendoscope was developed by the Olympus Corporation that shifts the orientation of endoscopic and ultrasound views from oblique to forward viewing. The channel is therapeutic at 3.7mm Note that the working channel is located adjacent to the ultrasound transducer at the endoscope tip. The accessory exits the working channel in the axis of the shaft. Shown here are balloon inflation and deployment of a Dormia basket. We report on the use of the prototype forward viewing echoendoscope in six consecutive patients who were referred for pancreatic cyst drainage. Here you see endoscopic view-indistinguisable from that of a gastroscope-showing a bulge where the cyst impinges against the posterior gastric wall. Power Doppler is switched on and highlights multiple vessels interposed in the wall This allows selection of a safe vessel-free window for a cyst puncture A 19 G needle is advanced into the cyst lumen. A sample of contents is aspirated for fluid analysis. A guidewire under ultrasound guidance into the cyst. An 18mm balloon is coaxially thread over the wire and advanced across the cyst wall, Note that resistance is encountered, but the forward transfer of force overcome this. The dilation is performed under forward viewing endoscopuc and ultrasound guidance. As the balloon is maximally inflated we see the cystgastrostomy open up. The balloon is then deflated while simultaneously advancing the scope into the cyst cavity. Cystoscopy isnow performed showing the cyst contents to be filled with pasty wall-adherent necroses. Pulsed power Doppler is switched on we can see and hear arterial flow vessels within the wall of the cyst. This identifies sensitive areas at bleeding risk when performing debridement In this case vigorous water jet irrigation is performed through an accessory water irrigation channel built into the echoendoscope. This issued to clear nonadherent debris. Our experience has shown that it is not necessary to actively remove wall-adherent debris using extraction tools as such Dormia or Roth net basket to achieve cyst resolution. Three large bore 10 Fr double pigtail stents are now inserted into the cyst under direct endoscopic guidance. The first stent is delivered over a guide catheter. The second stent. And the third stent All three stents are deployed. Finally, a nasocystic catheter is inserted for maintenance irrigation. In another patient we used the Cook Cystome to perform cystgastrostomy. We have found the Cystotome easy to delivery through the forward viewing echoendoscope. As shown, we advance the Cystotome into the cyst while applying diathermy. This is performed under and endoscopic guidance, entering the cyst at a near perpendicular orientation. After entry, the Cystotome is removed and cyst fluid gushes from the cystagastrotomy site.
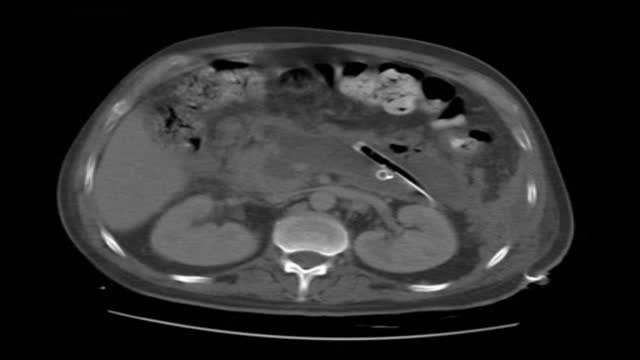
This is the CT of a 43 year old male patiënt with infected necrotizing pancreatitis that will undergo a VARD procedure; Videoscopic Assisted Retroperitoneal Debridment. Two weeks before this procedure two large bore percutaneous drains were placed in the peripancreatic collection. The patient i...s placed in supine position with the left side 30 degrees elevated. A 5-7 cm subcostal incision is made in the left flank. With help of CT images and by following the percutaneous drain, the subcutaneous tissue and the fascia are dissected and we enter the retroperitoneal peripancreatic collection. First, with a regular suction device any pus encountered is removed. Two long sympathectomy hooks are inserted in order to keep in the incision open. We than insert the zero degree laparoscope. The first necrosis encountered is removed under direct sight with the use of long grasping forceps. Following the percutaneous drain deeper into the cavity, parts of loosely adherent necrotic material are removed. Gently pulling we remove the necrotic tissue. The suction device is helpful in removing any fluid obstructing the view. Complete necrosectomy is not the ultimate aim of this procedure. Only loosely adherent pieces of necrosis are removed thereby keeping the risk of tearing underlying blood vessels to a minimum. In the rare case of extensive bleeding, the retroperitoneal cavity can be easily packed, either awaiting the bleeding to definitely stop or to act as a bridge to angiographic coiling. This patient is now 6 weeks after onset of disease. We always try to postpone surgical intervention, if possible up to 30 days. On the left side of the collection is the percutaneous drain. In this patient the drain had worked well for 2 weeks. When the patient deteriorated again it was decided to perform the VARD procedure. Large pieces of necrotic pancreas can be removed with VARD. This is a big advantage ov VARD over pure endosopic or percutaneous techniques. When all the necrotic tissue is removed we clean the cavity. Two drains are left in situ as a postoperative lavage system. The VARD procedure is performed via a 6 cm incision, which is closed and continuous postoperative lavage started immediately.
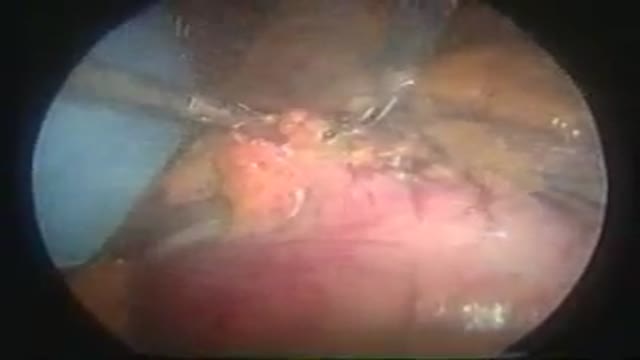
The Mini Gastric Bypass (MGB) is a short, simple, successful and inexpensive laparoscopic gastric bypass weight loss surgery. The operation usually takes only 30 min., hospitalization less than 24 hours. The Mini Gastric Bypass is low risk, has excellent long term weight loss, minimal pain and can b...e easily reversed or revised.

We herein describe endoscopic treatment of symptomatic pancreatic pseudocyst with significant necrosis and a fistula. Fifty eight year old man had presented to us with a large pseudocyst following an episode of acute pancreatitis. He was complaining of significant abdominal pain for two months. A... CT scan abdominal had revealed a large retro-gastric pseudocyst with necrosis and portal venous thrombosis. An upper GI endoscopy had revealed small linear fundal varcies. Endoscopic as well as surgical treatment for the cyst was discussed with the patient. Patient wished not to undergo surgical treatment and therefore endoscopic treatment was selected after a proper consent. EUS was performed to see for the interposed vessel prior to the pseudocyst puncture. Needle knife puncture was made and a guide wire was passed in the pseudocyst cavity. After confirming the wire placement in the cyst, the tract was dilated up to 20 mms using a CRE balloon. Fluid from the cyst was emptied out in the stomach. An ERCP scope was passed in to the cyst cavity, which revealed a significant necrotic material (much more than what the CT scan had revealed). All the free lying necrotic material was taken out with the help of a snare and a dormia basket. A lot of necrotic was stuck to the cyst wall, which was removed with the help of water jet, mechanical scooping and cutting through using a needle knife papillotome. Three 10 fr. Pigtail stents were placed at the end of the procedure. Further necrosectomy was carried out on alternate days for three more sessions. Dilation was required prior to each session three pigtail trans-gastric stents were placed at the end of each session. Single stent was kept in situ during each procedure to guide the path (the position of the stoma changed dramatically once the cyst was empty). During the last lesion (session four), a pancreatogram was taken. It revealed a mildly dilated CBD in the head, normally duct in the proximal body with a leak from the distal body, and contrast was seen going in to the pseudocyst cavity. The duct could not be opacified distally. A 7 fr. 15 cms stent was placed trans-papillary. When the cyst cavity was reentered through trans-gastric route, the trans-papillary pancreatic stent was clearly visible with soft necrotic material around it. In fact, the stent guided further necrosis removal. It also helped in diverting the pancreatic juice to the duodenum rather than in the pseudocyst cavity. Patient was discharged after this session and was followed up regularly. A CT scan was obtained after three months, which revealed a complete resolution of the necrosis and pseudocyst. There was a possibility of a persistent fistula after the removal of trans-papillary stent and a recurrence of the pseudocyst. Fistula closure with cyanoacrylate glue is well described in the literature. The procedure can have obvious complications secondary to accidental blockage of the main pancreatic duct. So, we thought it prudent to use a safer alternative to treat the condition. We removed the longer pancreatic stent and replaced it with a shorter pancreatic stent occupying only the head region. The patient was followed up after a month; sonography of the abdomen did not reveal any recurrence of the pseudocyst. All the stents were removed at this examination.
Internal hemorrhoids and loose rectal mucosa may block the exposure during the purse string suturing in stapled hemorrhooidopexy, and this may cause some complications. To retract the prolapsing rectal mucosa we modified the purse string anoscope of the PPH01 kit (Ethicon-Endosurgery, Cincinnati, O...H, USA) and produced a special anoscope. The open part of the purse string suture anoscope is covered by transparent acrylic (Orthoacryl�, Dentaurum, Pforzheim, Germany). The covering material had complete cylindrical outer and inner surfaces and was thin enough to let the anoscope easily rotate in the anal dilator and to let the 26 mm curved, round bodied needle of the 2/0 polypropilene suture move in the anoscope. A window, 3 cm long and 3-4 mm wide, was opened at the angled part of the anoscope 2 cm to the tip of the anoscope. This special anoscope was used for the purse string suture during stapled hemorrhoidopexy procedure in five patients. No postoperative complications, early or late, were encountered, and we propose that stapled hemorrhoidopexy procedure can be applied more easily by using this special anoscope.
Liver Metastasis Resection. A Technique That Makes It Easier. Authors: de Santibañes E, Sánchez Clariá R, Palavecino M, Beskow A, Pekolj J. Background: Liver resection is the only therapeutic option that achieves long-term survival for patients with hepatic metastases. We propose a tech...nique that causes traction and counter traction on the resection area, thus easily exposing the structures to be ligated. Since the parenchyma protrudes like a cork from a bottle we named this procedure “Corkscrew Technique”. Objective: To describe an original surgical technique to resect liver metastases. Technique: We delimite the resection area at 2 cm from the tumor. We place separated stitches, in a radiate way. The needle diameter must allow passing far from the deepest margin of the tumor. The stitches must be tractioned all together to separate the tumor from the normal parenchyma. Material and Methods: Between years 1983 and 2006, we perform 1270 liver resection. We used the corkscrew technique like only procedure in 612 patients whereas in 129 patients we associated it to an anatomic resection. Results: Mortality was 1%. Morbidity was 16% with a reoperation rate of 3%. Conclusions: The Corkscrew Technique is simple and safe, it spares surgical time, avoids blood loss, ensures free tumor margins and it is easy to perform.
Natural Orifice Endoscopic Transgastric Distal Pancreatectomy, A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Natural orifice surgery may represent a paradigm shift in the area of minimally invasive surgery and therapeutic endoscopy. However, studies to date have been limited primarily to small ca...se series with small sample sizes. There has been no large rigorous randomized controlled trial of natural orifice surgery to date. Early work on procedures such as peritoneoscopy, oophorectomy and tubal ligation, while pioneering, have reproduced laparoscopic procedures with minimal morbidity and mortality. In contrast, distal pancreatectomy has a post-operative morbidity of more than 50% even in high volume tertiary care centers. As a highly morbid surgery, the post-operative event rate would allow for a significant difference to be seen in a trial of conventional versus NOTES distal pancreatectomy. We have recently completed a prospective randomized controlled trial of NOTES versus laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy in a swine model which builds on our earlier non-survival work. This video focuses on the endoscopic technique.

Maintaining sufficient blood flow to the gastric tube after a subtotal esophagectomy for esophageal cancer is crucial for decreasing the esophagogastric anastomotic leakage. After subtotal esophagectomy for esophageal cancer, to additionally revascularize the gastric tube using the splenic artery a...nd vein, external carotid artery, and internal jugular vein, the supercharge technique was performed in esophageal reconstruction patients. Operative results of these patients (supercharge group) were retrospectively compared with those of patients not receiving the technique (control group). Both operation time and operative blood loss in the supercharge group were significantly longer and larger than those of the control group. However, the incidence of anastomotic leakage was significantly lower in the supercharge group than in the control group, and a 30-day reduction in the mean postoperative hospital stay was achieved with the supercharge group. This practical supercharge technique could be a breakthrough less to reduce leakage during esophageal anastomosis.
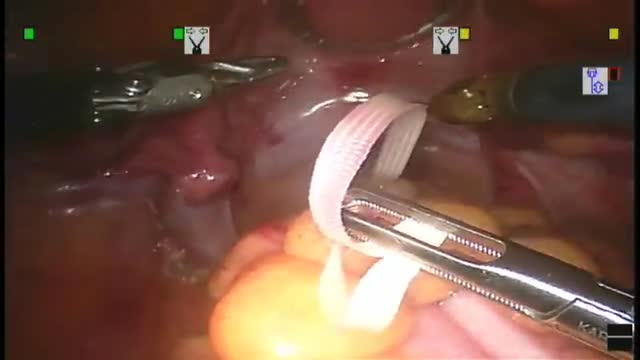
Robotic surgery was developed to facilitate endoscopic surgery and overcome its disadvantage. Thus, we performed robotic Total Mesorectal Excison (TME) in patient with rectal cancer by using the Intuitive Surgical® da Vinci surgicalTM system (Intuitive Surgical®, Sunnyvale, CA). To our knowledge, ...this is the first robotic low anterior resection base on standard TME principle with pelvic autonomic preservation. In conclusion, Robotic system is the best operative instrument for performing the standard TME procedure in rectal cancer patients.

Loop duodenal switch is an end-to-side proximal duodeno-ileal bypass with a sleeve gastrectomy. The proximal duodenal stump is anastomosed to an ileal loop, 200 cm from the ileocecal valve. The procedure is a malabsorptive operation with some theoretical advantages: only one anastomosis is performed..., and so the operative time is shorter, and there is no mesenteric opening. It is not a mini-gastric bypass, as the gastric antrum, the pylorus and the first centimeters of the duodenum are preserved. The short term outcome shows a very good weight loss curve with no metabolic disturbances.

Can bile duct injuries be prevented? A new technique in laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Over the last decade, laparoscopic cholecystectomy has gained worldwide acceptance and considered to be as "gold standard" in the surgical management of symptomatic cholecystolithiasis. However, the incidence of bile duct injury in laparoscopic cholecystectomy is still two times greater ...compared to classic open surgery. The development of bile duct injury may result in biliary cirrhosis and increase in mortality rates. The mostly blamed causitive factor is the misidentification of the anatomy, especially by a surgeon who is at the beginning of his learning curve. Biliary tree injuries may be decreased by direct coloration of the cystic duct, ductus choledochus and even the gall bladder. Methods gall bladder fundus was punctured by Veress needle and all the bile was aspirated. The same amount of fifty percent methylene blue diluted by saline solution was injected into the gall bladder for coloration of biliary tree. The dissection of Calot triangle was much more safely performed after obtention of coloration of the gall bladder, cystic duct and choledocus. Results Between October 2003 and December 2004, overall 46 patients (of which 9 males) with a mean age of 47 (between 24 and 74) underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy with methylene blue injection technique. The diagnosis of chronic cholecystitis (the thickness of the gall bladder wall was normal) confirmed by pre-operative abdominal ultrasonography in all patients. The diameters of the stones were greater than 1 centimeter in 32 patients and calcula of various sizes being smaller than 1 cm. were documented in 13 cases. One patient was operated for gall bladder polyp (our first case). Successful coloration of the gall bladder, cystic duct and ductus choledochus was possible in 43 patients, whereas only the gall bladder and proximal cystic duct were visualised in 3 cases. In these cases, ductus choledochus visibility was not possible. None of the patients developed bile duct injury. Conclusion The number of bile duct injuries related to anatomic misidentification can be decreased and even vanished by using intraoperative methylene blue injection technique into the gall bladder fundus intraoperatively.
Transoral Access in Endoscopic Thyroid Surgery Background: The number of patients demanding endoscopic neck surgery is rising. The access trauma of the axillary, breast and chest approaches is bigger than in open or video assisted surgery. We tested the feasibility of he sublingual transoral access which is in our opinion the only real minimally...-invasive extracollar endoscopic access to the thyroid gland Methods: We performed an experimental investigation in a porcine model. In 10 pigs we made 10 endoscopic transoral thyroidectomys with a modified axilloscope with the help of ultrasonic scissors and a neuro-monitoring system for identification of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Results: The average operation time from the introduction to the removal of the obturator just above the larynx was 57 seconds. The mean operation time was 43 minutes. With the help of the neuro-monitoring system we proved in all cases the function of the recurrent laryngeal nerve on both sides. The pigs were observed for another two hours after operation. During and after the operation no complications appeared. Conclusions: We could show that the endoscopic transoral thyroid resection in pigs is possible and save. Our results might be useful for using this access for endoscopic thyroid resection in humans.
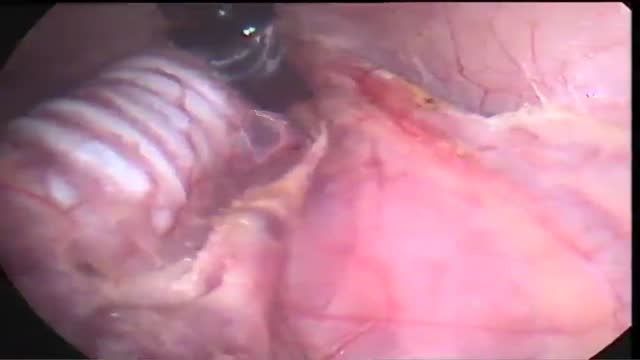
Background: The number of patients demanding endoscopic neck surgery is rising. The access trauma of the axillary, breast and chest approaches is bigger than in open or video assisted surgery. We tested the feasibility of he sublingual transoral access which is in our opinion the only real minimally...-invasive extracollar endoscopic access to the thyroid gland Methods: We performed an experimental investigation in a porcine model. In 10 pigs we made 10 endoscopic transoral thyroidectomys with a modified axilloscope with the help of ultrasonic scissors and a neuro-monitoring system for identification of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Results: The average operation time from the introduction to the removal of the obturator just above the larynx was 57 seconds. The mean operation time was 43 minutes. With the help of the neuro-monitoring system we proved in all cases the function of the recurrent laryngeal nerve on both sides. The pigs were observed for another two hours after operation. During and after the operation no complications appeared. Conclusions: We could show that the endoscopic transoral thyroid resection in pigs is possible and save. Our results might be useful for using this access for endoscopic thyroid resection in humans.
Biliary and Pancreatic Sphincterotomies for Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction
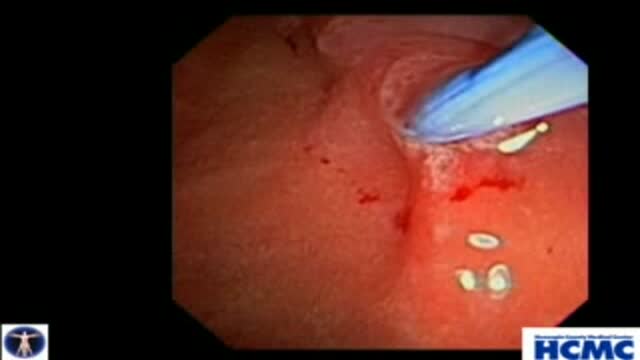
This 43 year old woman has severe recurrent RUQ pain post cholecystectomy. Liver and pancreatic chemistries and duct size are normal, but pancreatic manometry is abnormal. The plan is to perform dual biliary and pancreatic sphincterotomy. The pancreatic duct is cannulated with a 3.9 French tip tr...iple lumen papillotome loaded with a 0.025 inch Jagwire. Contrast is injected to outline the course of the duct. The wire is passed to the tail. Notice the knuckling of the wire into the tail. This provides a safety loop, but is only safe in a small duct with use of a smaller caliber wire. Then with the wire securely in PD, papillotome is used to cannulate the bile duct. Placement of the wire in PD guarantees access for pancreatic stent placement, which is mandatory in these patients to reduce risk, it also facilitates difficult biliary cannulation. Here is the fluoroscopic view as the papillotome is passed deep into bile duct. This shows wires in the CBD and PD. Now a biliary sphincterotomy is performed, with the pancreatic guidewire in place beside the papillotome. The scope is pushed into a longer position to orient up the middle of the papilla. The sphincterotomy is done in very careful stepwise fashion to avoid perforation. Now the biliary wire is removed and the papillotome passed over the pancreatic wire for pancreatic sphincterotomy. The incision is aimed back up towards the biliary sphincterotomy to ensure the septum only is cut. Note the large pancreatic orifice. Last, a 4 French 9cm unflanged soft material pancreatic stent is placed. We always use single pigtail design to avoid inward migration of the stent. The long unflanged design allows spontaneous passage within a few weeks.

A video-animation presentation about sentinel lymph node biopsies for breast cancer diagnosis. 3D graphics are used to explain the process. Topics include the lymphatic system and the methods used. This video is part of the breast cancer education series produced by CancerQuest at Emory University