Pediatrics

This is a Video in Clinical Medicine from the New England Journal of Medicine. Tympanocentesis in Children with Acute Otitis Media Overview Tympanocentesis is defined as needle aspiration of fluid from the middle ear. In children with acute otitis media, drainage of pus from the middle ear results in a rapid and marked improvement in symptoms and enables the clinician to prescribe tailored antimicrobial therapy. This video will demonstrate the technique of tympanocentesis. Indications Tympanocentesis is recommended in children with refractory acute otitis media, in immunocompromised children with otitis media, and in children with suppurative complications of acute otitis media, . . . .

Uncomplicated acute otitis media (AOM) should be treated empirically with amoxicillin. Recurrent AOM should raise concern for beta-lactamase resistance and warrants treatment with amoxicillin-clavulanic acid. Ototopical medications are unnecessary, even if there is tympanic membrane perforation.

-Intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis for mothers colonized with group B Streptococcus can prevent early-onset neonatal disease. Adequate prophylaxis consists of ampicillin, penicillin, or cefazolin for ;::4 hours before delivery. Regardless of intrapartum treatment, all high-risk infants must be observed for ;::49 hours. A complete blood count with differential and blood culture are indicated if the infant is preterm <37 weeks or was exposed to prolonged rupture of membranes.>18 hrs.
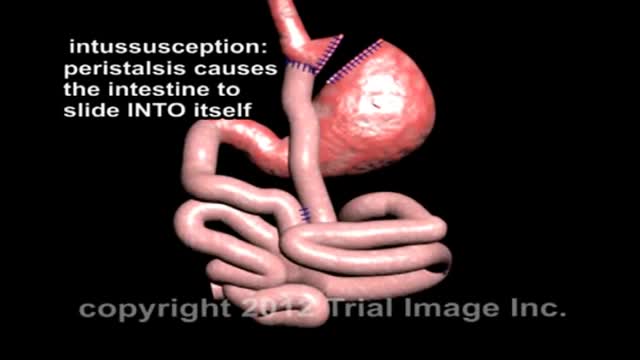
In cases when the presentation is unclear, ultrasonography is the imaging methodology of choice. The characteristic finding is the presence of a "target sign". Ultrasonography is not required in patients with obvious clinical diagnosis (as seen in this patient). Such patients can proceed directly to treatment with diagnostic and therapeutic air (pneumatic) or water-soluble (hydrostatic contrast) enema.

Hemolytic-uremic syndrome (or haemolytic-uraemic syndrome), abbreviated HUS, is a disease characterized by hemolytic anemia (anemia caused by destruction of red blood cells), acute kidney failure (uremia), and a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia).

An antecedent upper respiratory infection is present in 50% of patients. Abdominal pain is a presenting symptom in 1 0-15% of patients. The skin lesions are symmetric, involve dependent parts of the body, and classically progress from an erythematous, macular rash to papular purpura. The joints and kidneys are also commonly involved

The word enuresis is derived from a Greek word (enourein) that means “to void urine.” It can occur either during the day or at night (though some restrict the term to bedwetting that occurs at night). Enuresis can be divided into primary and secondary forms.
Encopresis is a problem that children age four or older can develop due to chronic (long-term) constipation. With constipation, children have fewer bowel movements than normal, and the bowel movements they do have can be hard, dry, and difficult to pass. The child may avoid using the bathroom to avoid discomfort.

A febrile seizure is a convulsion in a child that may be caused by a spike in body temperature, often from an infection. Your child's having a febrile seizure can be alarming, and the few minutes it lasts can seem like an eternity. Febrile seizures represent a unique response of a child's brain to fever, usually the first day of a fever. Fortunately, they're usually harmless and typically don't indicate an ongoing problem. You can help by keeping your child safe during a febrile seizure and by comforting him or her afterward.

Pediatric febrile seizures, which represent the most common childhood seizure disorder, exist only in association with an elevated temperature. Evidence suggests, however, that they have little connection with cognitive function, so the prognosis for normal neurologic function is excellent in children with febrile seizures. [1] Epidemiologic studies have led to the division of febrile seizures into 3 groups, as follows: Simple febrile seizures Complex febrile seizures Symptomatic febrile seizures Essential update: Starting MMR/MMRV vaccination earlier may reduce seizure risk In a case-series analysis of a cohort of 323,247 US children born from 2004 to 2008, Hambidge et al found that delaying the first dose of measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) or measles-mumps-rubella-varicella (MMRV) vaccine beyond the age of 15 months may more than double the risk of postvaccination seizures in the second year of life. [2, 3] In infants, there was no association between vaccination timing and postvaccination seizures. [3] In the second year of life, however, the incident rate ratio (IRR) for seizures within 7-10 days was 2.65 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.99-3.55) after first MMR doses at 12-15 months of age, compared with 6.53 (95% CI, 3.15-13.53) after first MMR doses at 16-23 months. For the MMRV vaccine, the IRR for seizures was 4.95 (95% CI, 3.68-6.66) after first doses at 12-15 months, compared with 9.80 (95% CI, 4.35-22.06) for first doses at 16-23 months.
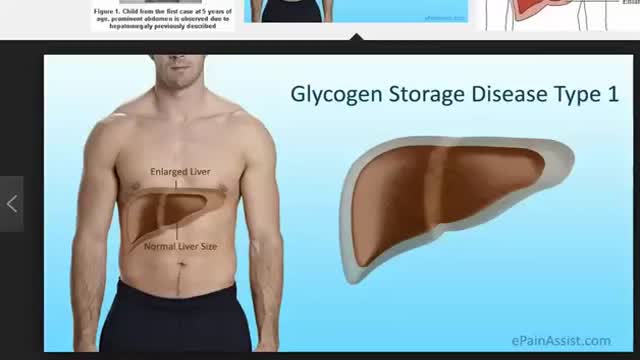
Signs and symptoms of this condition typically appear around the age of 3 or 4 months, when babies start to sleep through the night and do not eat as frequently as newborns. Affected infants may have low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), which can lead to seizures. They can also have a buildup of lactic acid in the body (lactic acidosis), high blood levels of a waste product called uric acid (hyperuricemia), and excess amounts of fats in the blood (hyperlipidemia). As they get older, children with GSDI have thin arms and legs and short stature. An enlarged liver may give the appearance of a protruding abdomen. The kidneys may also be enlarged. Affected individuals may also have diarrhea and deposits of cholesterol in the skin (xanthomas).
Pompe disease is a rare multisystem genetic disorder that is characterized by absence or deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme alpha-glucosidase (GAA). This enzyme is required to breakdown (metabolize) the complex carbohydrate glycogen and convert it into the simple sugar glucose.

Glycogen storage disease (GSD, also glycogenosis and dextrinosis) is the result of defects in the processing of glycogen synthesis or breakdown within muscles, liver, and other cell types. GSD has two classes of cause: genetic and acquired.
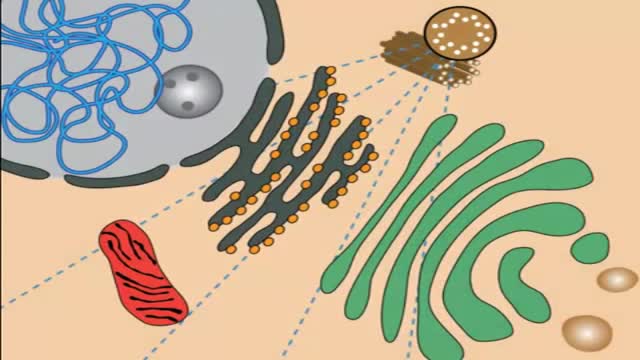
Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs; /ˌlaɪsəˈsoʊməl/) are a group of approximately 50 rare inherited metabolic disorders that result from defects in lysosomal function. Lysosomes are sacs of enzymes within cells that digest large molecules and pass the fragments on to other parts of the cell for recycling.
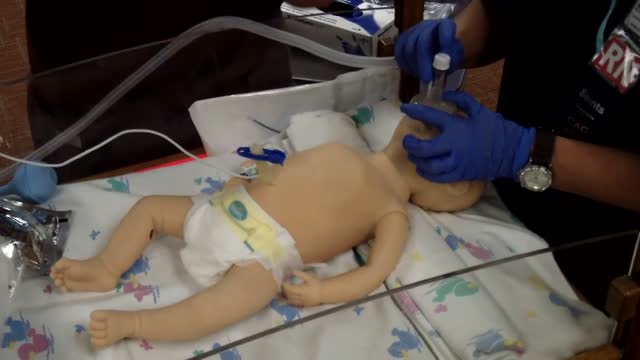
Neonatal resuscitation skills are essential for all health care providers who are involved in the delivery of newborns. The transition from fetus to newborn requires intervention by a skilled individual or team in approximately 10% of all deliveries. This figure is concerning because 81% of all babies in the United States are born in nonteaching, nonaffiliated level I or II hospitals. In such hospitals, the volume of delivery service may not be perceived as sufficient economic justification for the continuous in-hospital presence of personnel with high-risk delivery room experience, as recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). [1] Perinatal asphyxia and extreme prematurity are the 2 complications of pregnancy that most frequently necessitate complex resuscitation by skilled personnel. However, only 60% of asphyxiated newborns can be predicted ante partum. The remaining newborns are not identified until the time of birth. Additionally, approximately 80% of low-birth-weight infants require resuscitation and stabilization at delivery. Nearly one half of newborn deaths (many of which involve extremely premature infants) occur during the first 24 hours after birth. Many of these early deaths also have a component of asphyxia or respiratory depression as an etiology. For the surviving infants, effective management of asphyxia in the first few minutes of life may influence long-term outcome. Even though prenatal care can identify many potential fetal difficulties ante partum, allowing maternal transfer to the referral center for care, many women who experience preterm labor are not identified prospectively and therefore are not appropriately transferred to a tertiary perinatal center. Consequently, many deliveries of extremely premature infants occur in smaller hospitals. For this reason, all personnel involved in delivery room care of the newborn should be trained adequately in all aspects of neonatal resuscitation. Additionally, equipment that is appropriately sized to resuscitate infants of all gestational ages should be available in all delivering institutions, even if the institution does not care for preterm or intensive care infants. Along with the necessary skills, the practitioner should approach any resuscitation with a good comprehension of transitional physiology and adaptation, as well as an understanding of the infant's response to resuscitation. Resuscitation involves much more than possessing an ordered list of technical skills and having a resuscitation team; it requires excellent assessment skills and a grounded understanding of physiology.
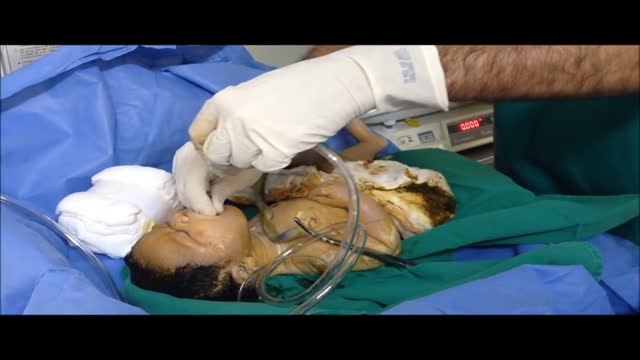
The following guidelines are an interpretation of the evidence presented in the 2010 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations1). They apply primarily to newly born infants undergoing transition from intrauterine to extrauterine life, but the recommendations are also applicable to neonates who have completed perinatal transition and require resuscitation during the first few weeks to months following birth. Practitioners who resuscitate infants at birth or at any time during the initial hospital admission should consider following these guidelines. For the purposes of these guidelines, the terms newborn and neonate are intended to apply to any infant during the initial hospitalization. The term newly born is intended to apply specifically to an infant at the time of birth.