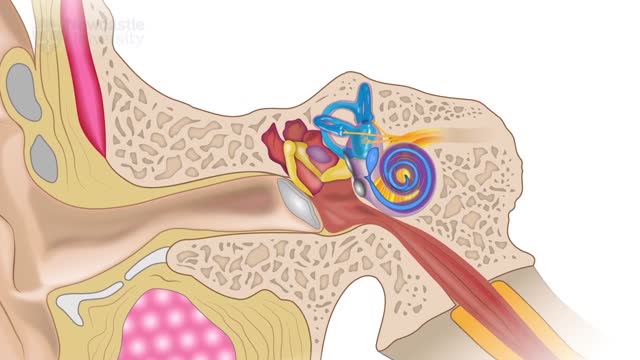
Otorhinolaryngology
Nose cautery can help prevent nosebleeds. The doctor uses a chemical swab or an electric current to cauterize the inside of the nose. This seals the blood vessels and builds scar tissue to help prevent more bleeding. For this procedure, your doctor made the inside of your nose numb.
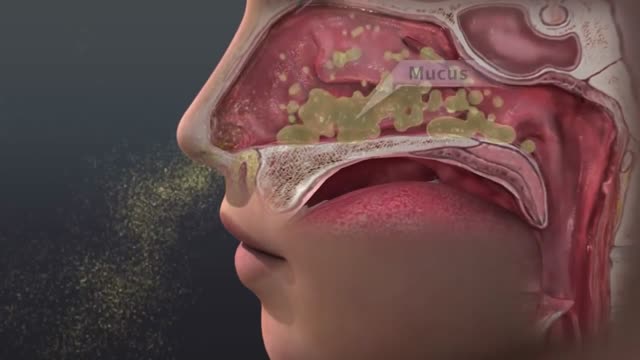
Got a stuffy nose from allergies or a cold? Nasal irrigation may help. You pour a saltwater (saline) solution into one nostril. As it flows through your nasal cavity into the other nostril, it washes out mucus and allergens. For nasal irrigation, you'll need a container and saline solution. You can buy prefilled containers, or use a bulb syringe or neti pot. All are available at drugstores.
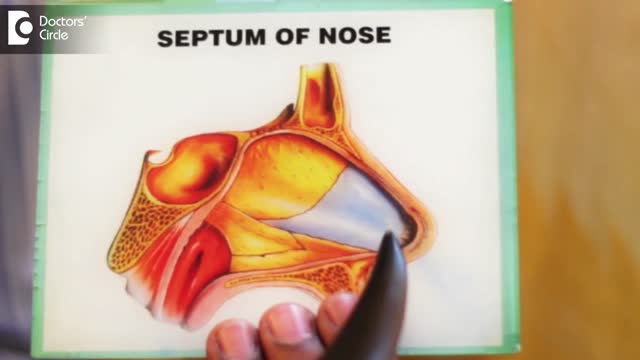
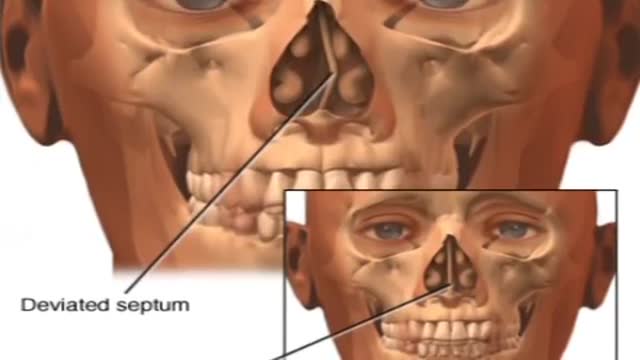
Septoplasty (SEP-toe-plas-tee) is a surgical procedure to correct a deviated septum — a displacement of the bone and cartilage that divides your two nostrils. During septoplasty, your nasal septum is straightened and repositioned in the middle of your nose.
Initial treatment of a deviated septum may be directed at managing the symptoms of the tissues lining the nose, which may then contribute to symptoms of nasal obstruction and drainage. Your doctor may prescribe: Decongestants. Decongestants are medications that reduce nasal tissue swelling, helping to keep the airways on both sides of your nose open. Decongestants are available as a pill or as a nasal spray. Use nasal sprays with caution, however. Frequent and continued use can create dependency and cause symptoms to be worse (rebound) after you stop using them. Decongestants have a stimulant effect and may cause you to be jittery as well as elevate your blood pressure and heart rate. Antihistamines. Antihistamines are medications that help prevent allergy symptoms, including obstruction and runny nose. They can also sometimes help nonallergic conditions such as those occurring with a cold. Some antihistamines cause drowsiness and can affect your ability to perform tasks that require physical coordination, such as driving. Nasal steroid sprays. Prescription nasal corticosteroid sprays can reduce inflammation in your nasal passage and help with obstruction or drainage. It usually takes from one to three weeks for steroid sprays to reach their maximal effect, so it is important to follow your doctor's directions in using them. Medications only treat the swollen mucus membranes and won't correct a deviated septum.
A deviated septum occurs when the thin wall (nasal septum) between your nasal passages is displaced to one side. In many people, the nasal septum is displaced — or deviated — making one nasal passage smaller. When a deviated septum is severe, it can block one side of your nose and reduce airflow, causing difficulty breathing. The additional exposure of a deviated septum to the drying effect of airflow through the nose may sometimes contribute to crusting or bleeding in certain individuals. Nasal obstruction can occur from a deviated nasal septum, from swelling of the tissues lining the nose, or from both. Treatment of nasal obstruction may include medications to reduce the swelling or nasal dilators that help open the nasal passages. To correct a deviated septum, surgery is necessary.
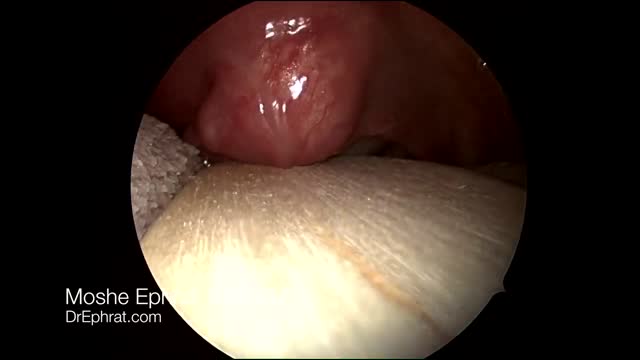
Nasal polyps are soft, painless, noncancerous growths on the lining of your nasal passages or sinuses. They hang down like teardrops or grapes. They result from chronic inflammation due to asthma, recurring infection, allergies, drug sensitivity or certain immune disorders. Nasal polyps are polypoidal masses arising mainly from the mucous membranes of the nose and paranasal sinuses. They are overgrowths of the mucosa that frequently accompany allergic rhinitis, and are freely movable and nontender.
Nasal polyps are soft, painless, noncancerous growths on the lining of your nasal passages or sinuses. They hang down like teardrops or grapes. They result from chronic inflammation due to asthma, recurring infection, allergies, drug sensitivity or certain immune disorders.
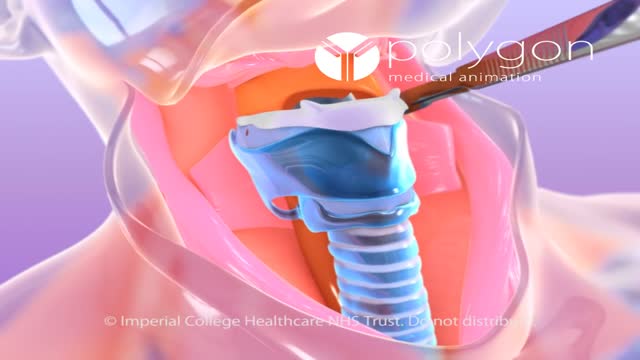
Laryngectomy is the removal of the larynx and separation of the airway from the mouth, nose and esophagus. In a total laryngectomy the entire larynx is removed and in a partial laryngectomy only a portion is taken out. The laryngectomee breathes through an opening in the neck known as a stoma.
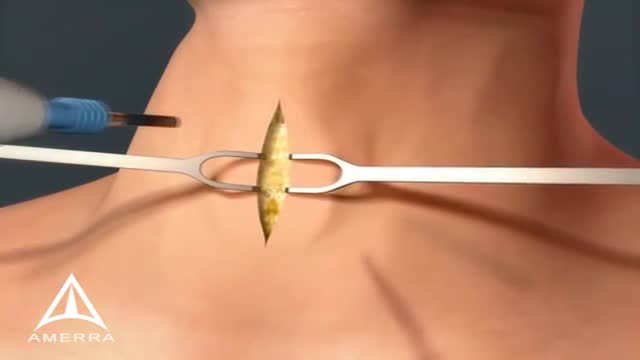
A tracheotomy or a tracheostomy is an opening surgically created through the neck into the trachea (windpipe) to allow direct access to the breathing tube and is commonly done in an operating room under general anesthesia. A tube is usually placed through this opening to provide an airway and to remove secretions from the lungs. Breathing is done through the tracheostomy tube rather than through the nose and mouth. The term “tracheotomy” refers to the incision into the trachea (windpipe) that forms a temporary or permanent opening, which is called a “tracheostomy,” however; the terms are sometimes used interchangeably.
Ear irrigation is a routine procedure used to remove excess earwax, called cerumen, or foreign materials from the ear. The ear naturally secretes earwax to protect, lubricate, keep debris out, and regulate bacterial growth. Under normal conditions, the body keeps the amount of earwax in the ears .
Acute otitis media: Inflammation of the middle ear in which there is fluid in the middle ear accompanied by signs or symptoms of ear infection: a bulging eardrum usually accompanied by pain; or a perforated eardrum, often with drainage of purulent material (pus).
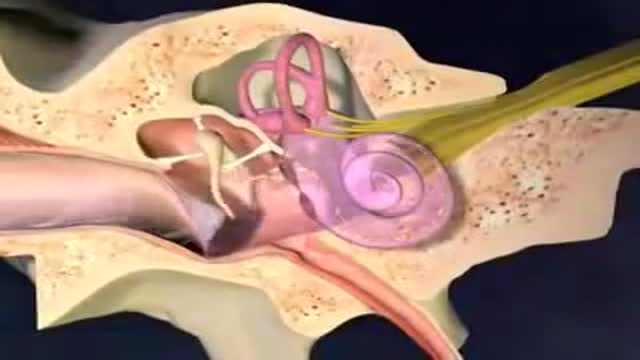
Hearing loss can affect anyone at any age, due to heredity, medical conditions or loud noise exposure. However, as we get older, we naturally become more susceptible to hearing loss because of changes to the delicate mechanics of our ears.
With inner ear disorders, your brain receives signals from the inner ear that aren't consistent with what your eyes and sensory nerves are receiving. Vertigo is what results as your brain works to sort out the confusion. These self-help acupressure points works with meridians to help the body regain normal healing and homeostasis.
Dizziness is a word that is often used to describe two different feelings. It is important to know exactly what you mean when you say "I feel dizzy," because it can help you and your doctor narrow down the list of possible problems. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you are about to faint or "pass out." Although you may feel dizzy, you do not feel as though you or your surroundings are moving. Lightheadedness often goes away or improves when you lie down. If lightheadedness gets worse, it can lead to a feeling of almost fainting or a fainting spell (syncope). You may sometimes feel nauseated or vomit when you are lightheaded. Vertigo is a feeling that you or your surroundings are moving when there is no actual movement. You may feel as though you are off balance, spinning, whirling, falling, or tilting. When you have severe vertigo, you may feel very nauseated or vomit. You may have trouble walking or standing, and you may lose your balance and fall.
To treat your tinnitus, your doctor will first try to identify any underlying, treatable condition that may be associated with your symptoms. If tinnitus is due to a health condition, your doctor may be able to take steps that could reduce the noise. Examples include: Earwax removal.
Throat Endoscopy: This video shows the vocal cords while singing
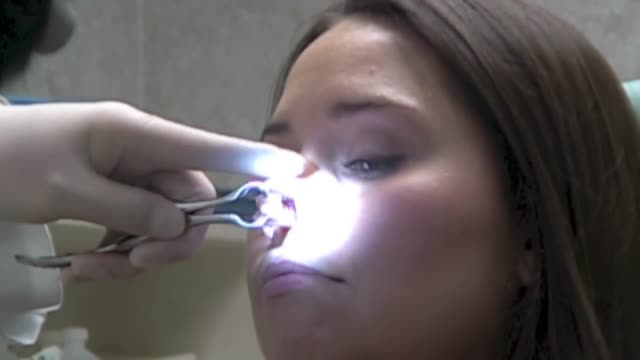
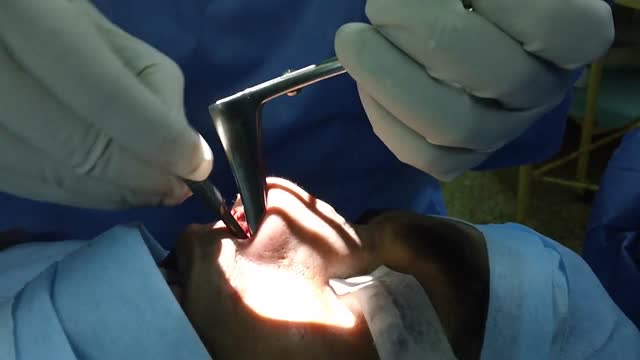
Nasal Foreign Body Removal Techniques
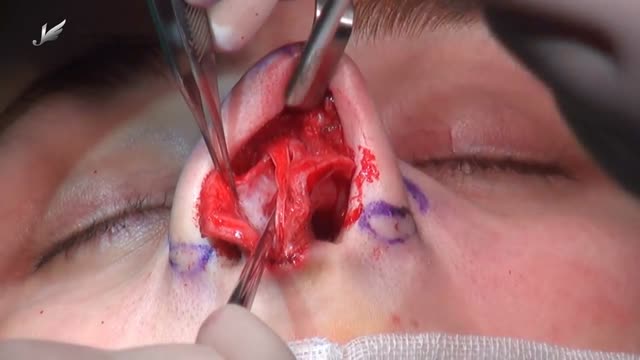
Rhinoplasty enhances facial harmony and the proportions of your nose. It can also correct impaired breathing caused by structural defects in the nose. Rhinoplasty surgery can change: Nose size in relation to facial balance Nose width at the bridge or in the size and position of the nostrils Nose profile with visible humps or depressions on the bridge Nasal tip that is enlarged or bulbous, drooping, upturned or hooked Nostrils that are large, wide, or upturned Nasal asymmetry
Instead, try these natural solutions and lifestyle changes, which may help you stop snoring. Change Your Sleep Position. ... Lose Weight. ... Avoid Alcohol. ... Practice Good Sleep Hygiene. ... Open Nasal Passages. ... Change Your Pillows. ... Stay Well Hydrated.
Nosebleeds are common. Most often they are a nuisance and not a true medical problem. But they can be both. Nosebleed care Sit upright and lean forward. By remaining upright, you reduce blood pressure in the veins of your nose. This discourages further bleeding. Sitting forward will help you avoid swallowing blood, which can irritate your stomach. Pinch your nose. Use your thumb and index finger to pinch your nostrils shut. Breathe through your mouth. Continue to pinch for five to 10 minutes. Pinching sends pressure to the bleeding point on the nasal septum and often stops the flow of blood. To prevent re-bleeding, don't pick or blow your nose and don't bend down for several hours after the bleeding episode. During this time remember to keep your head higher than the level of your heart. If re-bleeding occurs, blow out forcefully to clear your nose of blood clots and spray both sides of your nose with a decongestant nasal spray containing oxymetazoline (Afrin, Mucinex Moisture Smart, others). Pinch your nose again as described above and call your doctor. When to seek emergency care The bleeding lasts for more than 20 minutes The nosebleed follows an accident, a fall or an injury to your head, including a punch in the face that may have broken your nose