Urology
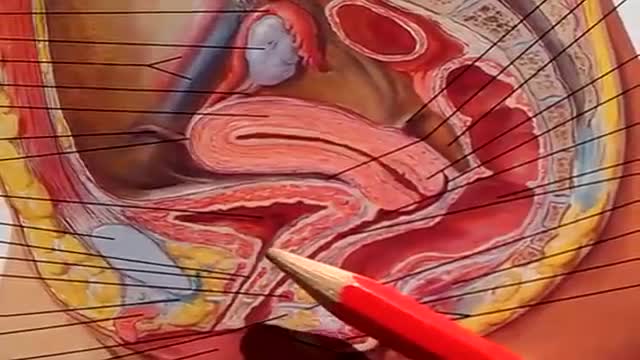
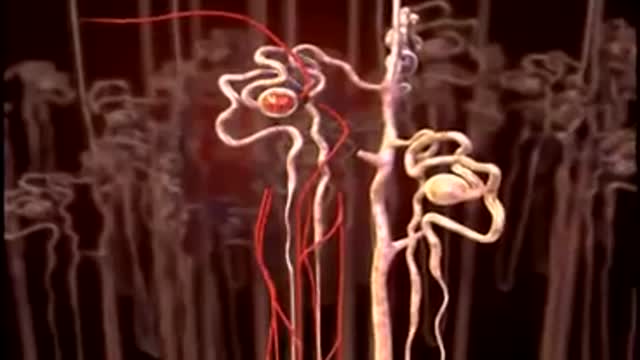
The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular organ that collects urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible (or elastic) organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra.
Pelvic ureter. The ureter enters the pelvis, where it crosses anteriorly to the iliac vessels, which usually occurs at the bifurcation of the common iliac artery into the internal and external iliac arteries. Here, the ureters are within 5 cm of one another before they diverge laterally.
To remove a smaller stone in your ureter or kidney, your doctor may pass a thin lighted tube (ureteroscope) equipped with a camera through your urethra and bladder to your ureter. Once the stone is located, special tools can snare the stone or break it into pieces that will pass in your urine.
A ureteral stent is a thin, hollow tube that is placed in the ureter to help urine pass from the kidney into the bladder. Ureters are the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. You may have a small amount of blood in your urine for 1 to 3 days after the procedure.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are infections of the urethra, bladder, ureters, or the kidneys, which comprise the urinary tract. E. coli bacteria cause the majority of UTIs, but many other bacteria, fungi, and parasites may also cause UTIs. Females have a higher risk for UTIs than most males, probably because of their anatomy; other risk factors for UTIs include any condition that may impede urine flow (e.g., enlarged prostate, kidney stones, congenital urinary tract abnormalities, and inflammation). Patients with catheters or those who undergo urinary surgery and men with enlarged prostates are at higher risk for UTIs.
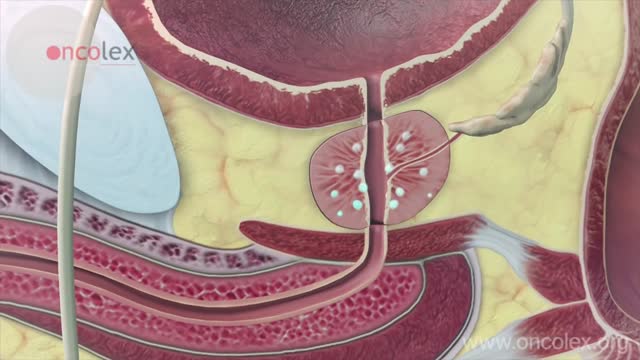
A prostate gland biopsy is a test to remove small samples of prostate tissue to be looked at under a microscope. ... For a prostate biopsy, a thin needle is inserted through the rectum (transrectal biopsy), through the urethra, or through the area between the anus and scrotum (perineum).
our uterus (or womb) is normally held in place inside your pelvis with various muscles, tissue, and ligaments. Because of pregnancy, childbirth or difficult labor and delivery, in some women these muscles weaken. Also, as a woman ages and with a natural loss of the hormone estrogen, her uterus can drop into the vaginal canal, causing the condition known as a prolapsed uterus.
During the examination, the doctor gently puts a lubricated, gloved finger of one hand into the rectum. He or she may use the other hand to press on the lower belly or pelvic area. A digital rectal exam is done for men as part of a complete physical examination to check the prostate gland .
Testicular Self Exam
Testicle pain (testicular pain) is pain that occurs in or around one or both testicles. Sometimes testicle pain actually originates from somewhere else in the groin or abdomen, and is felt in one or both testicles (referred pain).
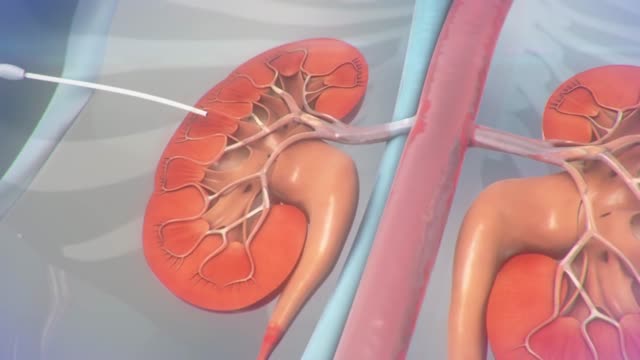
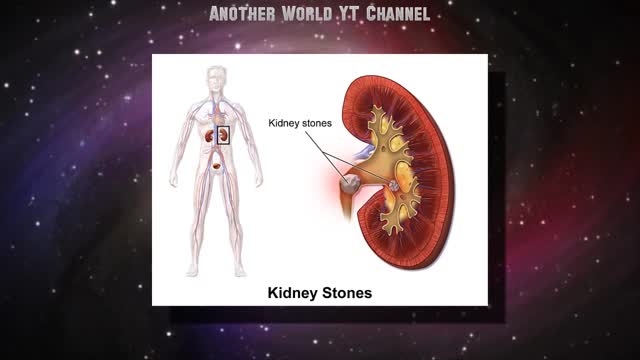
A kidney stone may not cause symptoms until it moves around within your kidney or passes into your ureter — the tube connecting the kidney and bladder. At that point, you may experience these signs and symptoms: Severe pain in the side and back, below the ribs Pain that spreads to the lower abdomen and groin Pain that comes in waves and fluctuates in intensity Pain on urination Pink, red or brown urine Cloudy or foul-smelling urine Nausea and vomiting Persistent need to urinate Urinating more often than usual Fever and chills if an infection is present Urinating small amounts of urine Pain caused by a kidney stone may change — for instance, shifting to a different location or increasing in intensity — as the stone moves through your urinary tract.
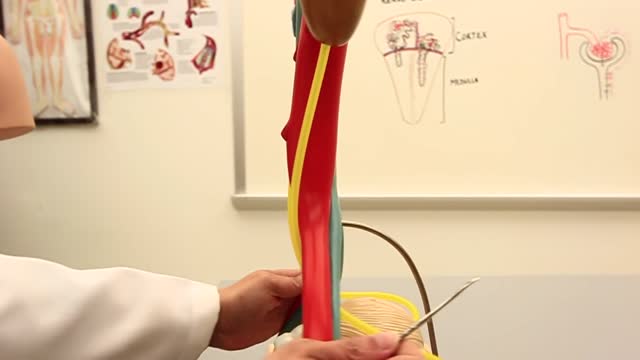
The Urinary System is a group of organs in the body concerned with filtering out excess fluid and other substances from the bloodstream. The substances are filtered out from the body in the form of urine. Urine is a liquid produced by the kidneys, collected in the bladder and excreted through the urethra.
Are Glass Sex Toys Safe? | How to Use a Glass Dildo
Body-Safe Sex Toys
Penile Injection Therapy
Orchitis (or-KIE-tis) is an inflammation of one or both testicles. It is usually caused by a bacterial infection or by the mumps virus. Bacterial orchitis can be caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs), particularly gonorrhea or chlamydia. Bacterial orchitis often results from epididymitis, an inflammation of the coiled tube (epididymis) at the back of the testicle that stores and carries sperm. In that case, it's called epididymo-orchitis. Orchitis causes pain and can affect fertility. Medication can treat the causes of bacterial orchitis and can ease some signs and symptoms of viral orchitis. But it may take several weeks for scrotal tenderness to disappear.
An undescended testicle (cryptorchidism) is a testicle that hasn't moved into its proper position in the bag of skin hanging below the penis (scrotum) before birth. Usually just one testicle is affected, but about 10 percent of the time both testicles are undescended. An undescended testicle is uncommon in general, but common among baby boys born prematurely. The vast majority of the time, the undescended testicle moves into the proper position on its own, within the first few months of life. If your son has an undescended testicle that doesn't correct itself, surgery can relocate the testicle into the scrotum.
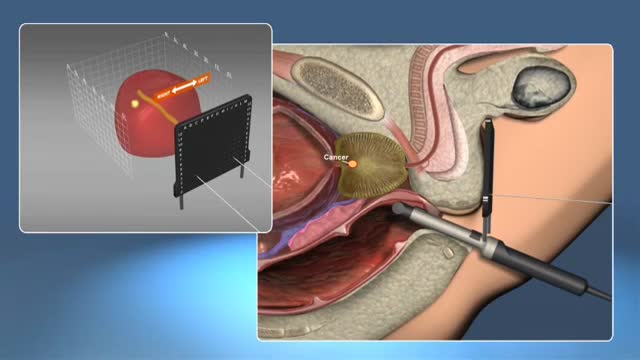
Prostate Cancer older man thinking Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men (after skin cancer), but it can often be treated successfully. More than 2 million men in the US count themselves as prostate cancer survivors.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also known as benign prostatic hypertrophy, is a histologic diagnosis characterized by proliferation of the cellular elements of the prostate. Cellular accumulation and gland enlargement may result from epithelial and stromal proliferation, impaired preprogrammed cell death (apoptosis), or both. BPH involves the stromal and epithelial elements of the prostate arising in the periurethral and transition zones of the gland (see Pathophysiology). The hyperplasia presumably results in enlargement of the prostate that may restrict the flow of urine from the bladder. BPH is considered a normal part of the aging process in men and is hormonally dependent on testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) production. An estimated 50% of men demonstrate histopathologic BPH by age 60 years. This number increases to 90% by age 85 years. The voiding dysfunction that results from prostate gland enlargement and bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) is termed lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). It has also been commonly referred to as prostatism, although this term has decreased in popularity. These entities overlap; not all men with BPH have LUTS, and likewise, not all men with LUTS have BPH. Approximately half of men diagnosed with histopathologic BPH demonstrate moderate-to-severe LUTS. Clinical manifestations of LUTS include urinary frequency, urgency, nocturia (awakening at night to urinate), decreased or intermittent force of stream, or a sensation of incomplete emptying. Complications occur less commonly but may include acute urinary retention (AUR), impaired bladder emptying, the need for corrective surgery, renal failure, recurrent urinary tract infections, bladder stones, or gross hematuria. (See Presentation.) Prostate volume may increase over time in men with BPH. In addition, peak urinary flow, voided volume, and symptoms may worsen over time in men with untreated BPH (see Workup). The risk of AUR and the need for corrective surgery increases with age.
Prostatitis is an infection or inflammation of the prostate gland that presents as several syndromes with varying clinical features. The term prostatitis is defined as microscopic inflammation of the tissue of the prostate gland and is a diagnosis that spans a broad range of clinical conditions. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has recognized and defined a classification system for prostatitis in 1999.[1] The 4 syndromes of prostatitis are as follows: I - Acute bacterial prostatitis II - Chronic bacterial prostatitis III - Chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS; further classified as inflammatory or noninflammatory) IV - Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis