Pharmacology
Gastrointestinal GI Drug Delivery
OPAXIO Mechanism of Action
AZT Mechanism of Antiviral Activity
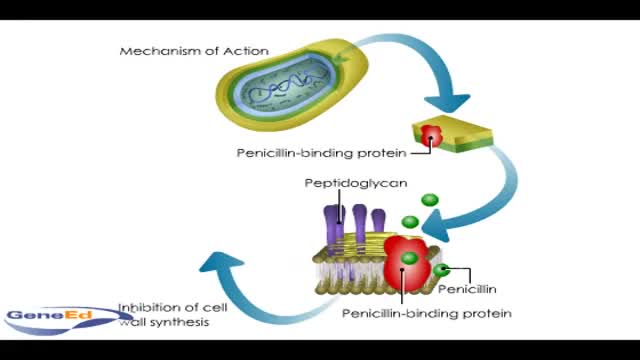
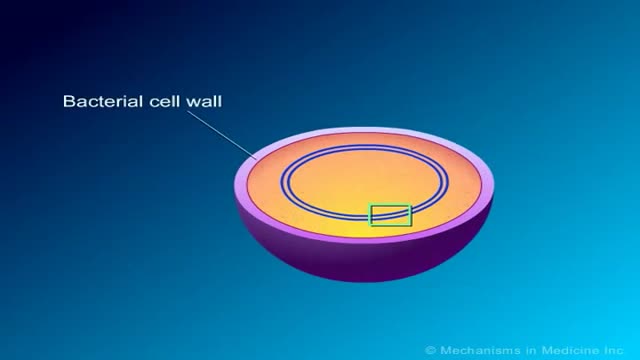
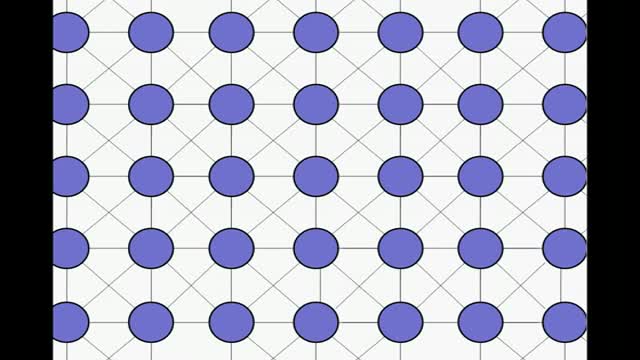
Penicllin mechanism of action
Macrolides Mechanisms of Action and Resistance
Cocaine in human brain
Mode of action of NNRTIs
Mechanism of Addiction
Gleevecs mechanism of Action
Mechanism of action of a novel HIV drug called Tipranavir
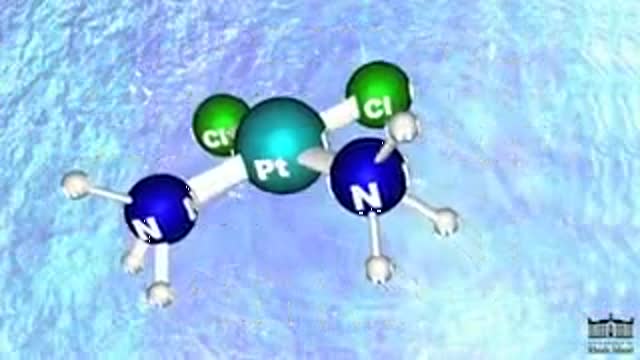
Cisplatin is in a class of drugs known as platinum-containing compounds used to treat various types of cancers including metastatic testicular and ovarian tumors. The molecule was first discovered in 1845, but did not receive FDA approval until 1978. Today it is known as the "penicillin of cancer drugs," because it is so effective for many different cancers. There are three key players involved in Cisplatin's mechanism: (1) Cisplatin, (2) DNA (3) and an HMG Protein. Most Cisplatin enters the body through active transport, but some molecules are passively defused through the cell membrane. Once in the nucleus, Cisplatin can form an adduct with two consecutive guanine bases within a strand of DNA. The molecule loses its chlorine atoms in exchange for the nitrogen atoms of the target guanines. Cisplatin can bond more tightly with nitrogen because nitrogen balances the platinum charge more effectively than chlorine. It is this adduct-induced DNA bend that allows binding of proteins which contain the high mobility group, HMG domain. Once the protein is bound to the DNA, it inserts a wedge-like phenyl group of phenylalanine 37 into the widened minor groove created by the bend. The tightly bound HMG protein causes destacking of the nucleotide bases, resulting in the DNA helix becoming kinked. In this way, Cisplatin can be thought of as a monkey wrench in the DNA repair system. With the HMG protein bound to the DNA, the modified strand is not repaired properly and so the cell dies. The success of Cisplatin depends on its ratio of efficacy between cancerous and healthy cells.
jhhbhhhbjhb j jh jhjh
8 year old girl treated by quacks with severe high dose of steroids for 5 years
A video showing the process of Oral Medications Absorption