Cardiology
Surprising Facts About High Blood PressureMust
Surprising Facts About High Blood Pressure
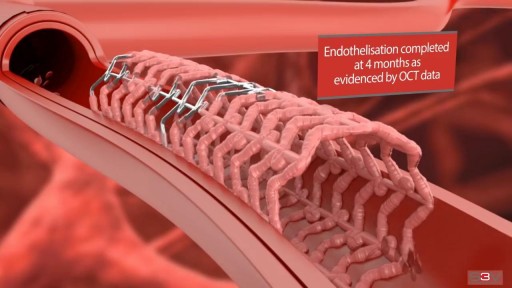
Heart Attack Angioplasty Procedure Animation Video
Angioplasty is a procedure to restore blood flow through the artery. You have angioplasty in a hospital. The doctor threads a thin tube through a blood vessel in the arm or groin up to the involved site in the artery. The tube has a tiny balloon on the end.
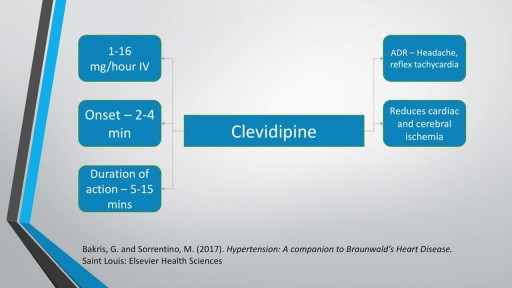
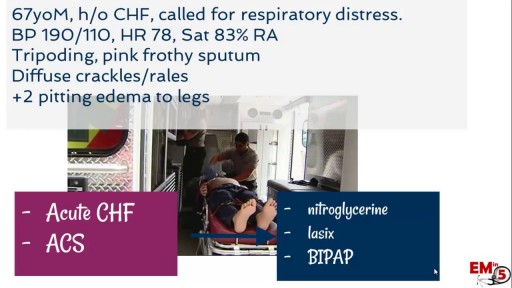
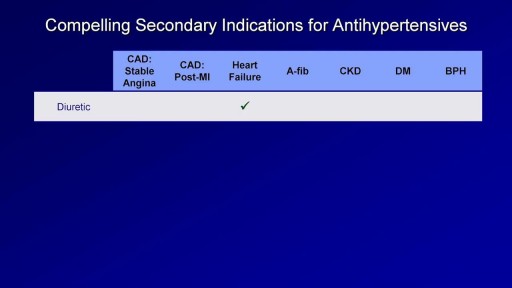
A brief description of hypertensive emergencies including its definition, risk factors, clinical manifestations and management
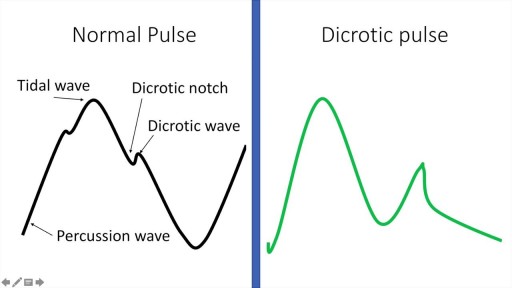
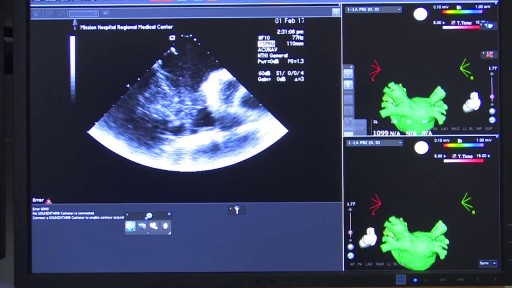
A detailed description of the Arterial Pulse including its waveform and pathological subtypes. Also discussed are the abnormal rates (tachycardia and bradycardia) and their causes, abnormal rhythm (including regularly regular and irregularly irregular pulses) and abnormal character (including pulses bisferiens, pulses parvus et tarsus, pulsus alternans, pulses paradoxus and others.) Description of pulse in various pathological states including Aortic stenosis and aortic regurgitation is also included. Finally there is also a description of the peripheral signs of aortic regurgitation.
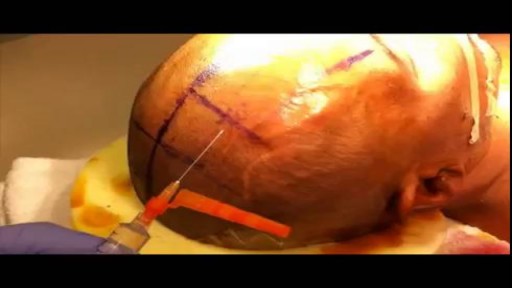
This video describes, step by step, how to place an external ventricular drain. This is a common neurosurgical procedure used to relieve intracranial pressure.
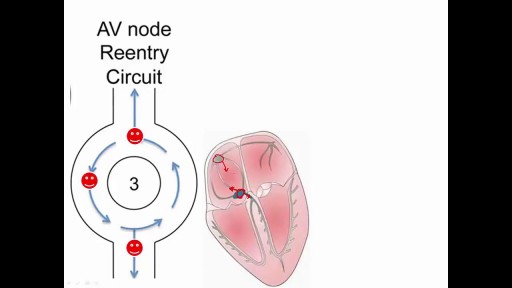
The procedure is used most often to treat a condition called supraventricular tachycardia, or SVT, which occurs because of abnormal conduction fibers in the heart. Catheter ablation is also used to help control other heart rhythm problems such as atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation.
The superior vena cava is a major vein in a person's body. It carries blood from the head, neck, upper chest, and arms to the heart. Superior vena cava syndrome (SVCS) occurs when a person's superior vena cava is partially blocked or compressed. Cancer is usually the main cause of SVCS.
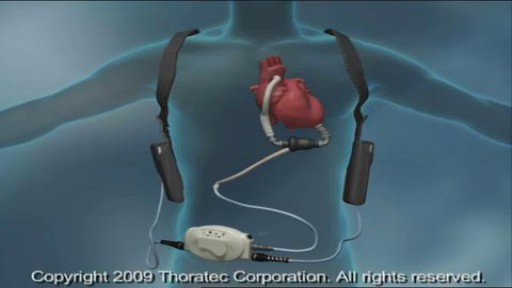
A ventricular assist device (VAD) — also known as a mechanical circulatory support device — is an implantable mechanical pump that helps pump blood from the lower chambers of your heart (the ventricles) to the rest of your body. A VAD is used in people who have weakened hearts or heart failure. Although a VAD can be placed in the left, right or both ventricles of your heart, it is most frequently used in the left ventricle. When placed in the left ventricle it is called a left ventricular assist device (LVAD). You may have a VAD implanted while you wait for a heart transplant or for your heart to become strong enough to effectively pump blood on its own. Your doctor may also recommend having a VAD implanted as a long-term treatment if you have heart failure and you're not a good candidate for a heart transplant.
Although individual surgeons and centers employ different methods to insert a left ventricular assist device (LVAD), the fundamental concepts remain true for all. That is, most devices use the apex of the left ventricle (LV) as the inflow site to the pump, which subsequently gives off an outflow graft to the aorta, thus bypassing the ailing LV. Currently available devices do not differ significantly with regard to general implantation technique. The sequence of implantation can vary also from patient to patient, depending on the particular situation. In some cases, concomitant procedures may be performed in conjunction with LVAD implantation without adversely affecting outcome.
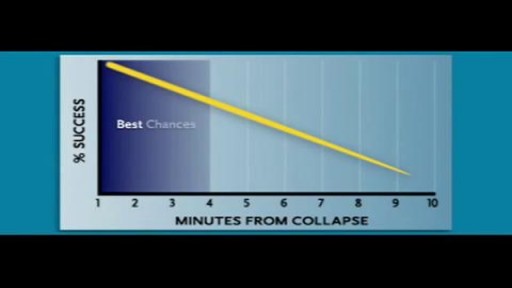
Cardiac arrest usually results from an electrical disturbance in the heart. It's not the same as a heart attack. The main symptom is loss of consciousness and unresponsiveness. This medical emergency needs immediate CPR or use of a defibrillator. Hospital care includes drugs, an implantable device, or other procedures.