Cardiology
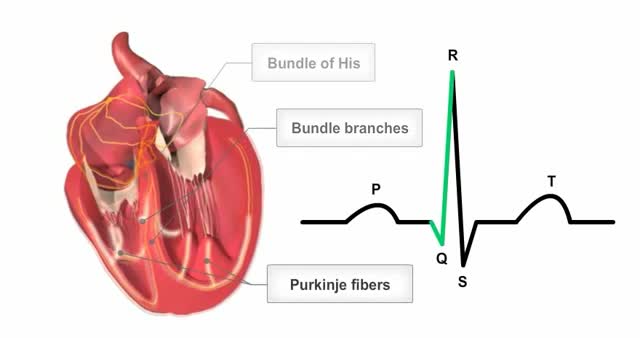
The heart's conductions system controls the generation and propagation of electric signals or action potentials causing the hearts muscles to contract and the heart to pump blood.
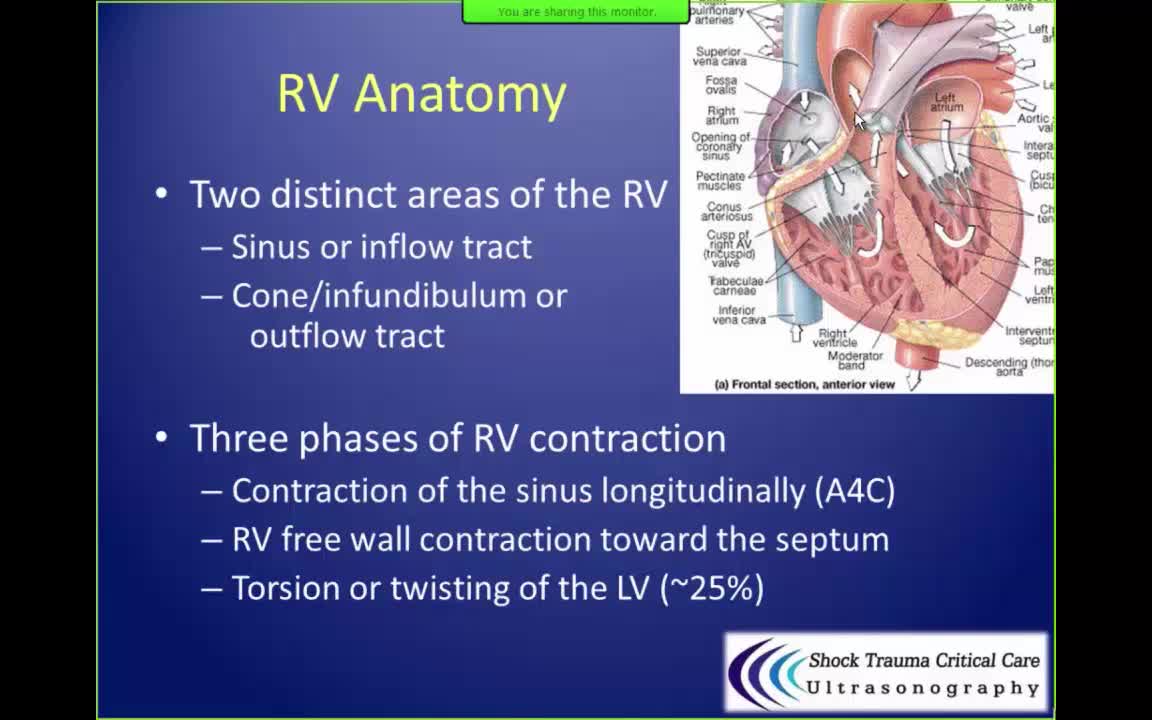
In patients with advanced congestive heart failure due to cardiomyopathy or ischemia, right ventricle shortening is the only significant independent associate of survival by multivariate analysis (as opposed to other parameters including left ventricular ejection fraction, cardiac index, and pulmonary resistance).
. In this video he offers a differential diagnosis for a 60-year-old woman with dyspnea and an episode of syncope.
Is There A Way To Know If I Have An Aortic Aneurysm Before It Ruptures?
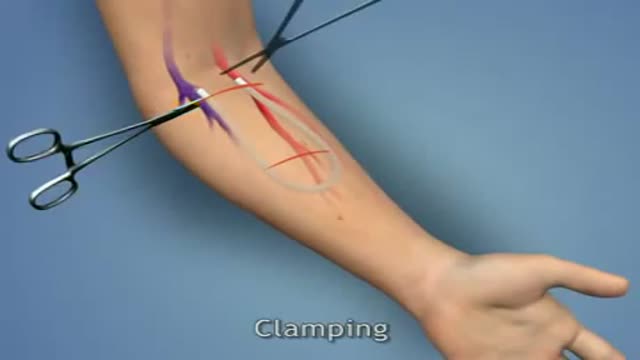
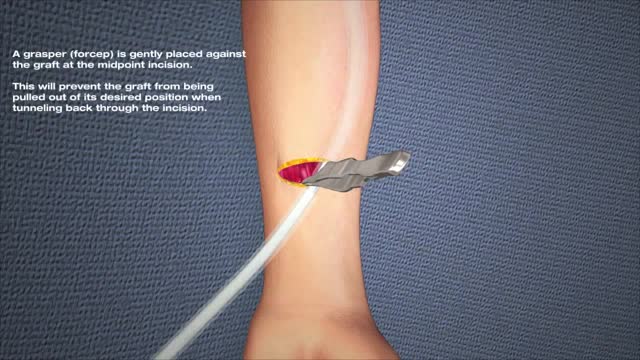
A surgeon creates an arteriovenous fistula by making a connection between an artery (which carries blood away from the heart) and a vein (which carries blood back to the heart). This artificial connection allows the vein to become larger and for the walls of the vein to thicken, a process termed maturation. A mature fistula makes it easier for the vein to be punctured repeatedly for dialysis. Maturation typically takes three to six months to occur, but in rare cases, can take up to a year. This makes advance planning for an arteriovenous fistula important. When a patient is felt to be approximately a year away from requiring dialysis, the patient should be referred for evaluation for possible creation of an arteriovenous fistula.
Hemodialysis, also called dialysis, is the most common treatment for kidney failure. A dialysis machine is an artificial kidney which cleanses the blood. During dialysis, blood is drawn from the patient into the dialysis machine, circulated through the machine, and then returned to the patient. Two needles are inserted into the patient's bloodstream to allow this process to occur. Hemodialysis is normally performed three times a week and the purpose of vascular access is to provide reliable sites where the bloodstream can be easily accessed each time. There are three major types of vascular access: arteriovenous fistula, arteriovenous graft, and venous catheter. The great majority of vascular accesses are created in the arm, but they can also be created in the leg.
Congestive Heart Failure
Symptoms range from nonspecific and constitutional to sudden cardiac death. [18] In about 20% of cases, myxomas may be asymptomatic and discovered as an incidental finding. Signs and symptoms of mitral stenosis, endocarditis, mitral regurgitation, and collagen vascular disease can simulate those of atrial myxoma. A high index of suspicion aids in diagnosis. Symptoms of left-sided heart failure include the following: Dyspnea on exertion (75%) that may progress to orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, and pulmonary edema is observed. [19, 20] Symptoms are caused by obstruction at the mitral valve orifice. Valve damage may result in mitral regurgitation.
Interrupted aortic arch (IAA) is the absence or discontinuation of a portion of the aortic arch, the section of the aorta that turns downward toward the lower half of the body. Once the diagnosis of this rare defect is suspected and confirmed, treatment and surgical intervention are vitally important. Heart models and animation were developed by the Cincinn
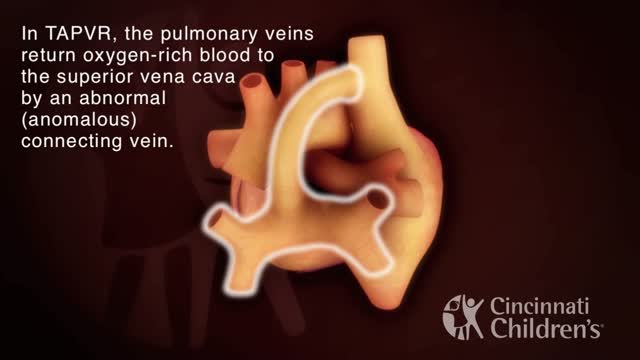
Total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR) is a rare congenital malformation in which pulmonary veins that return oxygen-rich blood from the lungs do not connect normally to the left atrium. Instead all four pulmonary veins drain abnormally to the right atrium. Heart models and animation were developed by the Cincinnati Children's Heart Institute in conjunction with Cincinnati Children's Critical Care Media Lab.
Truncus arteriosus is a rare type of heart disease that in which a single blood vessel (truncus arteriosus) comes out of the right and left ventricles, instead of the normal 2 vessels (pulmonary artery and aorta). It is present at birth (congenital heart disease)
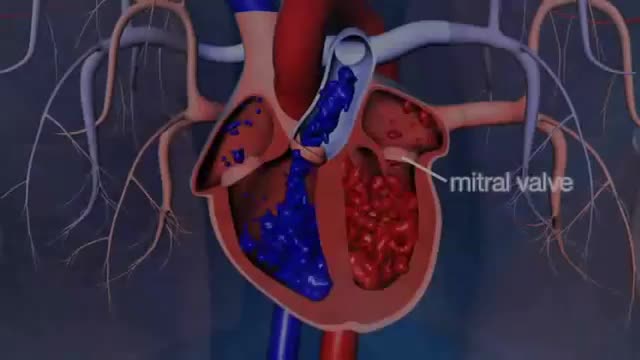
Dr. Glenn Barnhart explains the symptoms of mitral valve regurgitation such as becoming short of breath. There are five structures of the mitral valve: annulus, leaflet tissue, chordae tendineae, papillary muscles, and left ventricle. All of these are taken into consideration when the mitral valve is leaking and not working right. There are four degrees of mitral valve regurgitation: mild, moderate, moderately severe,.
Alcohol septal ablation (ASA, TASH, Sigwart procedure) is a percutaneous, minimally-invasive treatment performed by an interventional cardiologist to relieve symptoms and improve functional status in severely symptomatic patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) who meet strict clinical, anatomic and physiologic ...
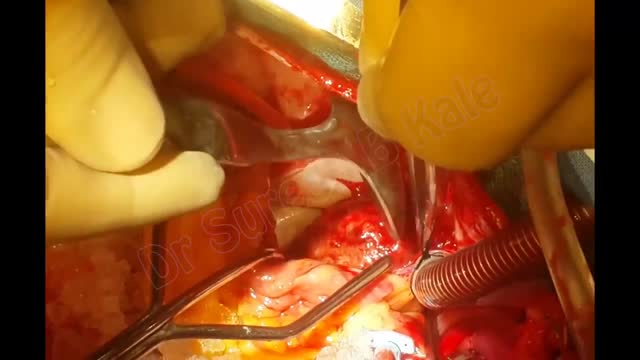
watch to see the Large Clot in the heart
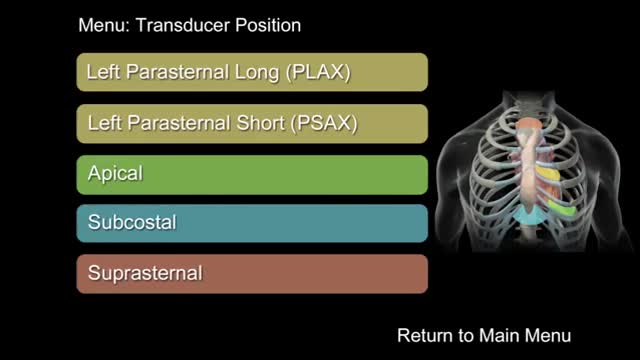
Probes, landmarks, and general windows to obtain transthoracic echo views
"How to Perform a Transthoracic Echocardiographic Study Volume 1: Transducer Position and Anatomy" is an instructional video, offered by ASE, and can be used for professional lectures and offers an interactive section for flexible presentations. The video includes an overview of relevant cardiac anatomy, a step by step presentation of all Transducer Positions, and the sequential transducer movements to acquire standard echo images needed to complete a Transthoracic Echocardiographic Study.
giant systolic pulsations, known as C-V waves, were noticeable during jugular venous examination of a 33-year-old woman who had tricuspid-valve endocarditis. In video 2, transthoracic echocardiography revealed severe tricuspid regurgitation.
Ebstein anomaly is a congenital malformation of the heart that is characterized by apical displacement of the septal and posterior tricuspid valve leaflets, leading to atrialization of the right ventricle with a variable degree of malformation and displacement of the anterior leaflet.
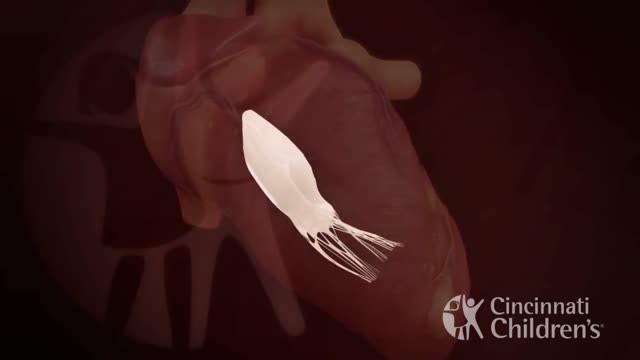
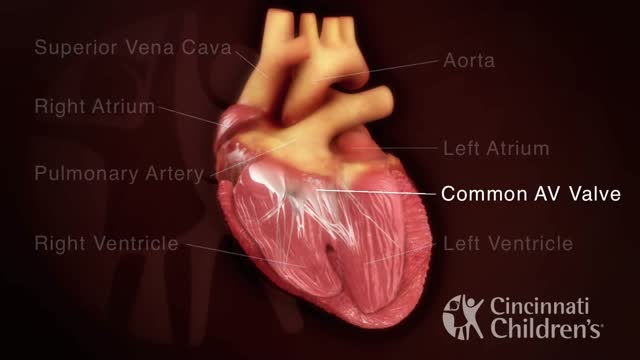
An atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) is a heart defect in which there are holes between the chambers of the right and left sides of the heart, and the valves that control the flow of blood between these chambers may not be formed correctly. This condition is also called atrioventricular canal (AV canal) defect or endocardial cushion defect. In AVSD, blood flows where it normally should not go. The blood may also have a lower than normal amount of oxygen, and extra blood can flow to the lungs. This extra blood being pumped into the lungs forces the heart and lungs to work hard and may lead to
Central catheters provide dependable intravenous access and enable hemodynamic monitoring and blood sampling [1-3]. The jugular veins are one of the most popular sites for central venous access due to accessibility and overall low complication rates, and are the preferred site for temporary hemodialysis.