Neurology
First aid steps to help stop or shorten a seizure or prevent an emergency situation. This may involve giving a rescue treatment (often called "as needed" medicine or treatment) that has been recommended by your health care team. The rescue treatments described here can be given by non-medical people who are not in a hospital setting. They are intended for use by anyone (the person with seizures, family member or other observer) who has been trained in their use. These therapies can be given anywhere in the community
Early symptoms of MS include blurred vision, numbness, dizziness, and muscle weakness.
Have you ever seen Alzheimer's Brain Vs. Normal Brain?
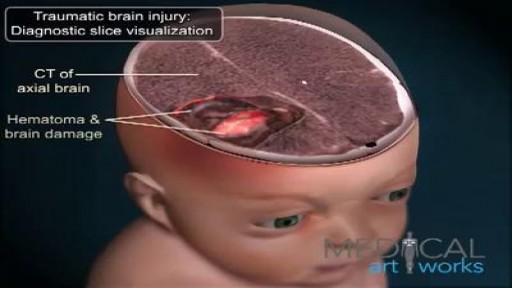
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) TBI is defined as an alteration in brain function, or other evidence of brain pathology, caused by an external force. Adopted by the Brain Injury Association Board of Directors in 2011. This definition is not intended as an exclusive statement of the population served by the Brain Injury Association of America. Acquired Brain Injury An acquired brain injury is an injury to the brain, which is not hereditary, congenital, degenerative, or induced by birth trauma. An acquired brain injury is an injury to the brain that has occurred after birth. There is sometimes confusion about what is considered an acquired brain injury. By definition, any traumatic brain injury (e.g. from a motor vehicle accident or assault) could be considered an acquired brain injury. In the field of brain injury, acquired brain injuries are typically considered any injury that is non traumatic. Examples of acquired brain injury include stroke, near drowning, hypoxic or anoxic brain injury, tumor, neurotoxins, electric shock or lightning strike.
Epilepsy is the fourth most common neurological disorder and affects people of all ages Epilepsy means the same thing as "seizure disorders" Epilepsy is characterized by unpredictable seizures and can cause other health problems Epilepsy is a spectrum condition with a wide range of seizure types and control varying from person-to-person Public perception and misunderstanding of epilepsy causes challenges often worse than the seizures
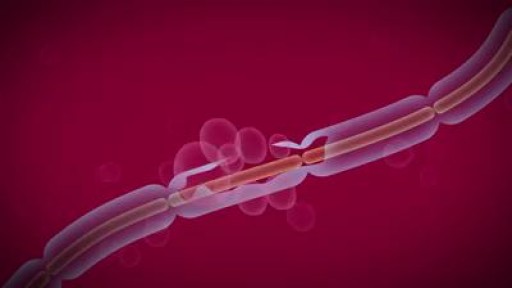
Treatment of a stroke interventionaly
Researchers have received approval to bring 20 brain-dead humans back to life
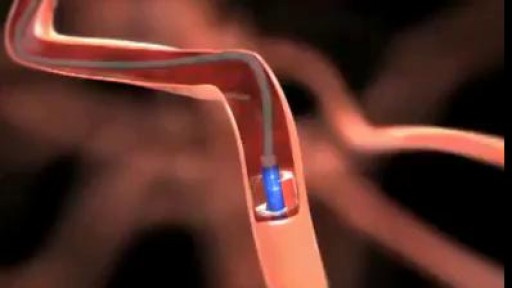
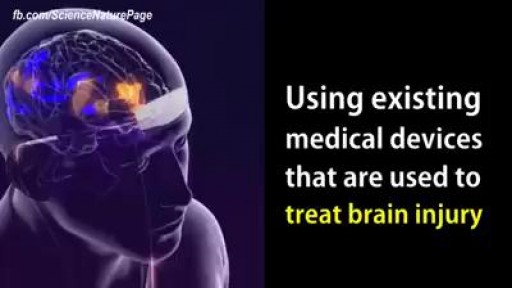
This device could prevent migraine headaches.
Nerve damage can start as numbness or tingling and progress to an intense feeling of burning or stabbing. What to know about treatment options:
Watch as this wireless brain implant allows a paralyzed monkey to walk again
Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects the brain and spinal cord. Early MS symptoms include weakness, tingling, numbness, and blurred vision. Other signs are muscle stiffness, thinking problems, and urinary problems. Treatment can relieve MS symptoms and delay disease progression.
Hydrocephalus can be fatal if left untreated. The damage to the brain can cause headaches, vomiting, blurred vision, cognitive problems, and walking difficulties. The term water on the brain is incorrect, because the brain is surrounded by CSF (cerebrospinal fluid), and not water.Oct 8, 2015
Some common signs of spinal tumors may include the following: Pain (back and/or neck pain, arm and/or leg pain) Muscle weakness or numbness in the arms or legs. Difficulty walking. General loss of sensation. Difficulty with urination (incontinence) Change in bowel habits (retention) Paralysis to varying degrees.
Dementia is not a specific disease. It's an overall term that describes a wide range of symptoms associated with a decline in memory or other thinking skills severe enough to reduce a person's ability to perform everyday activities. Alzheimer's disease accounts for 60 to 80 percent of cases. Vascular dementia, which occurs after a stroke, is the second most common dementia type. But there are many other conditions that can cause symptoms of dementia, including some that are reversible, such as thyroid problems and vitamin deficiencies.
Frontotemporal dementia is the name for a range of conditions in which cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are damaged. These lobes control behaviour, emotional responses and language. This means that people will experience changes in personality and behaviour, or may struggle with language – for example, in finding the right word. Frontotemporal dementia is a less common form of dementia which is more likely to affect younger people – those under 65.
Vascular dementia is a general term describing problems with reasoning, planning, judgment, memory and other thought processes caused by brain damage from impaired blood flow to your brain. You can develop vascular dementia after a stroke blocks an artery in your brain, but strokes don't always cause vascular dementia. Whether a stroke affects your thinking and reasoning depends on your stroke's severity and location. Vascular dementia also can result from other conditions that damage blood vessels and reduce circulation, depriving your brain of vital oxygen and nutrients
Dementia is the name for a group of symptoms that commonly include problems with memory, thinking, problem solving, language and perception. In a person with dementia, these symptoms are bad enough to affect daily life.
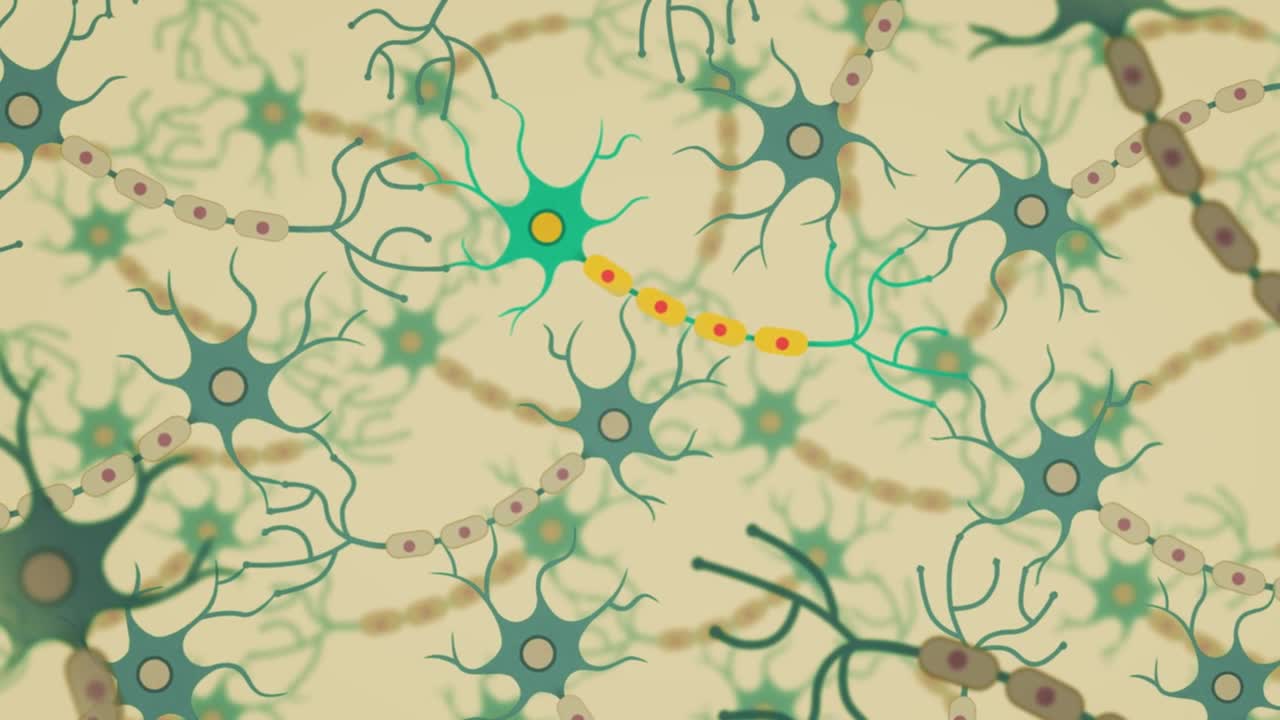
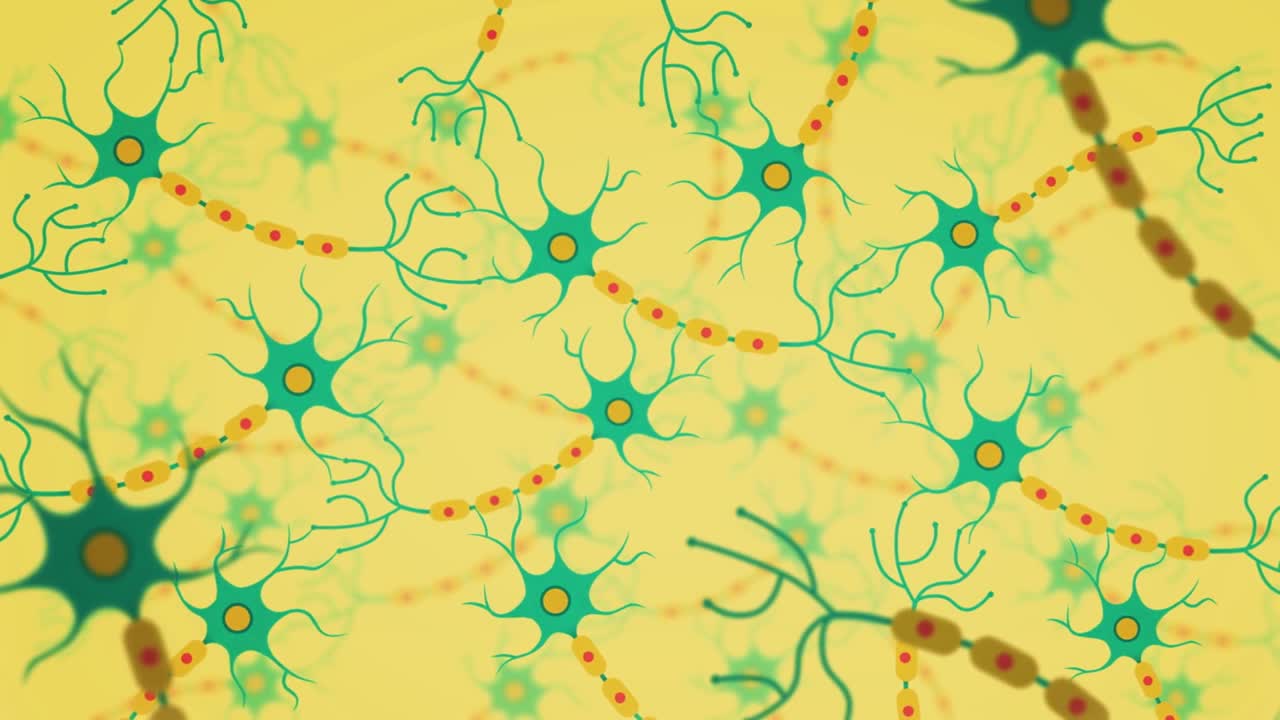
The brain is made up of billions of nerve cells that are specially designed to communicate with each other. They form many connections with one another, creating an intricate network between cells.
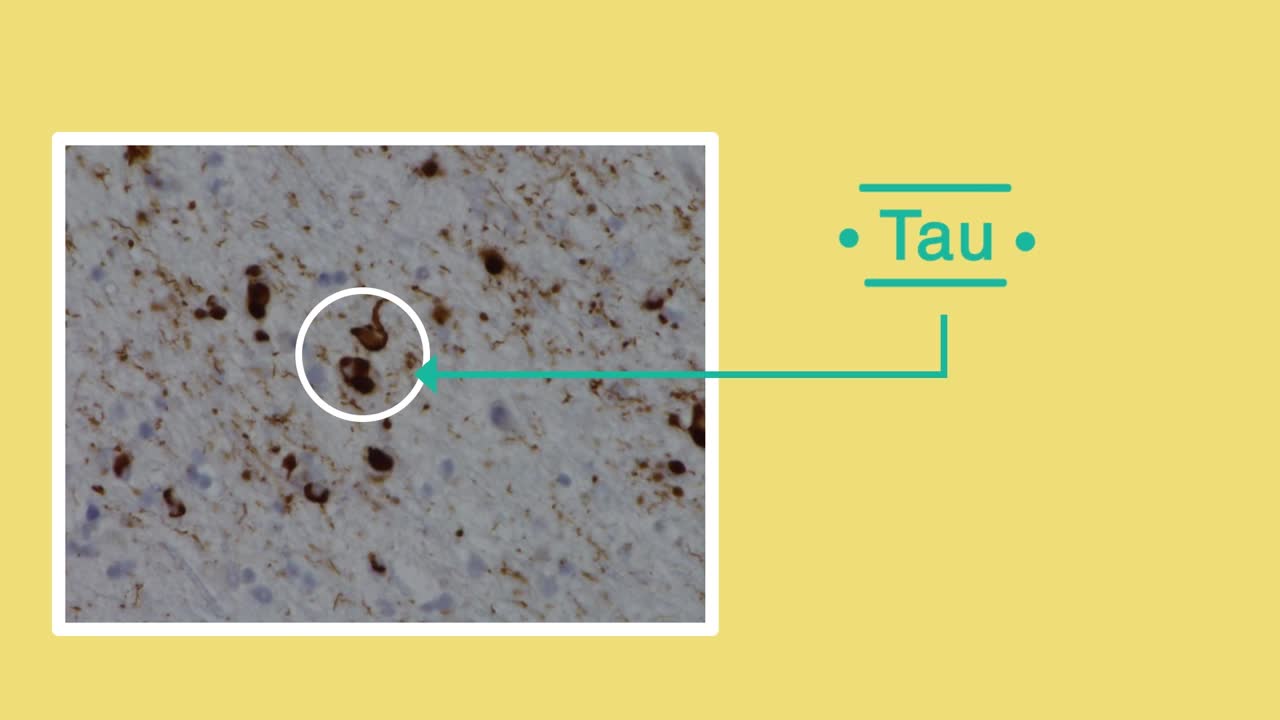
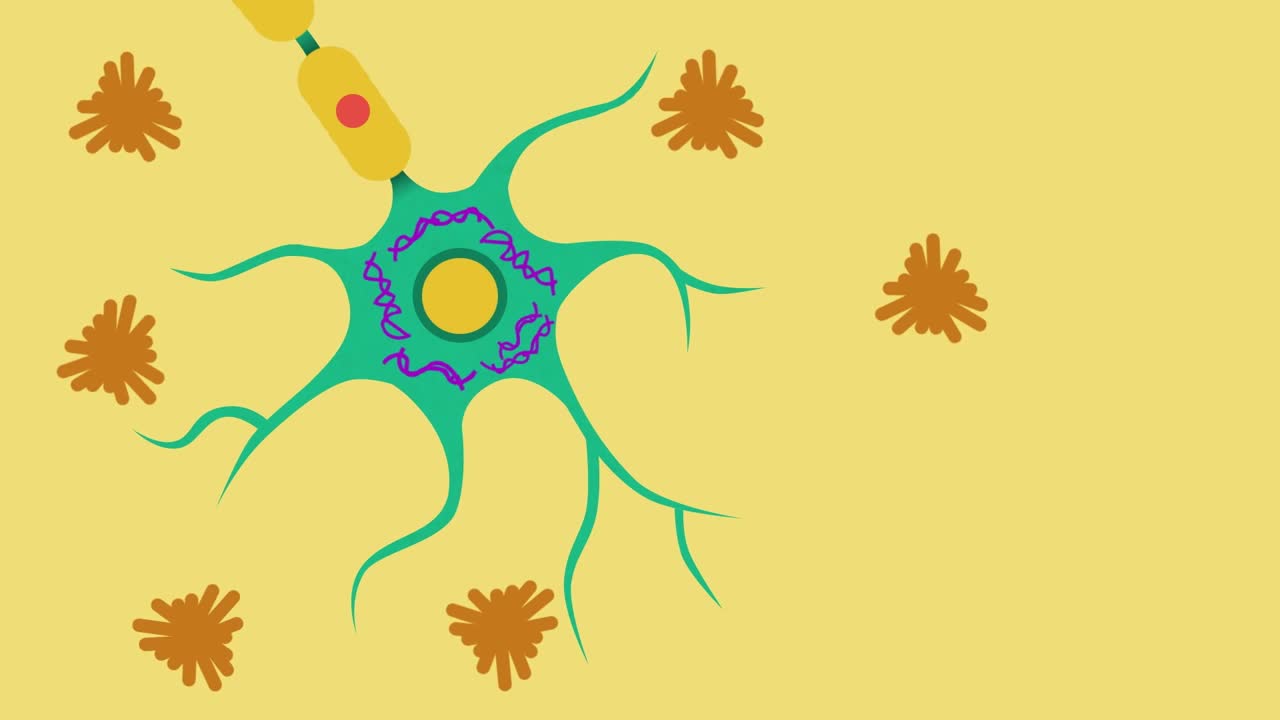
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia and also the best understood. It is thought to be caused by the formation of abnormal deposits of protein in the brain.
The brain is the most complex organ in our body. It controls everything we do, from simple things such as breathing, to complex things such as co-ordinating our movements. The brain stores our memories, allows us to think and speak, and controls how we behave