Neurology
The core features of migraine are headache, which is usually throbbing and often unilateral, and associated features of nausea, sensitivity to light, sound, and exacerbation with head movement. Migraine has long been regarded as a vascular disorder because of the throbbing nature of the pain.
A patient who has a problem with proprioception can still maintain balance by using vestibular function and vision. In the Romberg test, the standing patient is asked to close his or her eyes. A loss of balance is interpreted as a positive Romberg's test.
Definition. The principal signs of cerebellar dysfunction are the following: Ataxia: unsteadiness or incoordination of limbs, posture, and gait. A disorder of the control of force and timing of movements leading to abnormalities of speed, range, rhythm, starting, and stopping.
-Hypopigmented spots, in combination with a family history of bilateral deafness, strongly suggest neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF-2), an autosomal-dominant disorder. The spots described actually represent cafe-au-lait spots that are usually hypopigmented (unlike the hyperpigmented cafe-au-lait spots found in NF-1 ). Deafness is caused by bilateral acoustic neuromas, a characteristic neurologic manifestation of the syndrome.
Encephalopathy means disorder or disease of the brain. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of global brain dysfunction; this syndrome can have many different organic and inorganic causes.
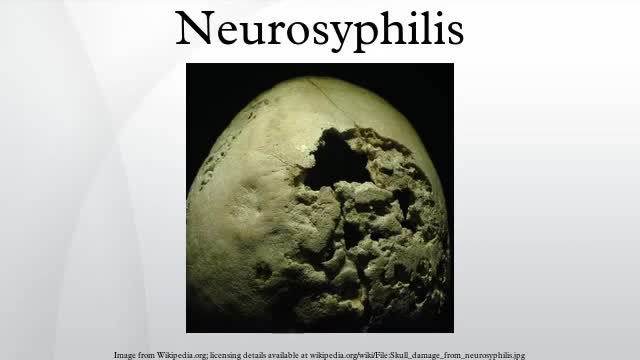
Neurosyphilis is an infection of the brain or spinal cord caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum. It usually occurs in people who have had chronic, untreated syphilis, usually about 10 to 20 years after first infection and develops in about 25%–40% of persons who are not treated. The United States' Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advises that neurosyphilis can occur at any stage of a syphilis infection.
ADC was first identified early in the AIDS epidemic as a common and novel CNS syndrome.(4,5) The three components of the term, AIDS dementia complex embody central features of the condition. AIDS emphasizes its morbidity and poor prognosis, particularly when its severity is at stage 2 or greater (see Table 1), a severity comparable to other clinical AIDS-defining complications of HIV-1 infection. Dementia designates the acquired and persistent cognitive decline with preserved alertness that usually dominates the clinical presentation and determines its principal disability. Complex emphasizes that this disease not only impairs the intellect, but also concomitantly alters motor performance and, at times, behavior. This involvement of the nervous system beyond cognition is evidence of a wider involvement of the CNS than occurs in some other types of dementia such as Alzheimer's disease. Additionally, myelopathy may be an important, indeed predominating, aspect of ADC, and organic psychosis may also be a feature in a subset of patients (see Rheumatologic and Musculoskeletal Manifestations of HIV). These manifestations are therefore also encompassed within this term. By contrast, neither neuropathy nor functional psychiatric disturbance are included in ADC.
Meningococcal meningitis - causes, features, symptoms and treatment
-Rapidly progressive weakness of the lower extremities following an upper respiratory infection, accompanied by sensory loss and urinary retention, is characteristic for transverse myelitis.
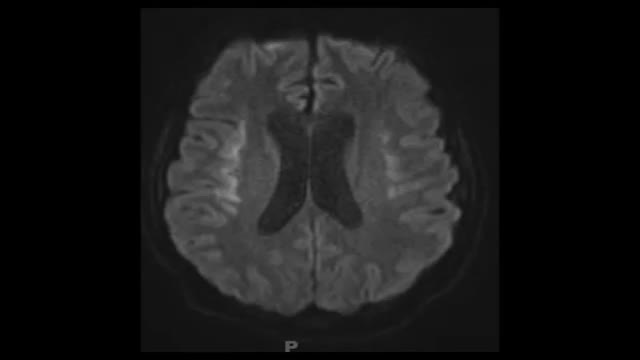
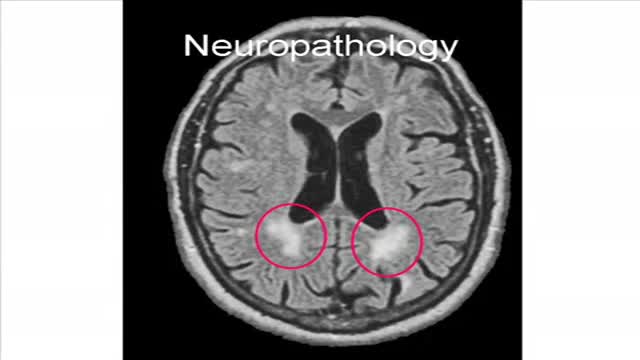
Progressive multifocalleukoencephalopathy is a demyelinating illness of the central nervous system that typically occurs in immunosuppressed patients, especially those with AIDS. It is caused by reactivation of the polyomavirus JC (JC virus) and presents with neurologic deficits including hemiparesis, gait ataxia, visual symptoms, and altered mental status. It is not seen in non-immunosuppressed patients, and fever is not typical
Herpes simplex encephalitis is characterized by acute-onset (<1 week) fever, headaches, seizures, altered mental status, and focal neurologic findings such as hemiparesis or cranial nerve deficits. This patient's weakness/fatigue for >1 week, heart murmur, history of drug abuse, and absence of focal neurologic deficits make endocarditis with mycotic aneurysm more likely than herpes encephalitis
If you suspect that you have sleep apnea, the usual first step is to discuss your suspicions with your primary care physician. If you don’t have a primary care physician, you can go directly to a clinician who is a sleep specialist. But check your health care insurance coverage first. Some policies require you to see a primary care physician first, and some policies limit the sleep centers and testing facilities whose services they will pay for. Unfortunately, you may discover that your policy offers limited or no coverage for the diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea, in which case you may wish to switch insurers if and when you can.
Narcolepsy is a chronic sleep disorder characterized by overwhelming daytime drowsiness and sudden attacks of sleep. People with narcolepsy often find it difficult to stay awake for long periods of time, regardless of the circumstances. Narcolepsy can cause serious disruptions in your daily routine. Sometimes, narcolepsy can be accompanied by a sudden loss of muscle tone (cataplexy) that leads to weakness and loss of muscle control. Cataplexy is often triggered by a strong emotion, most commonly laughter. Narcolepsy is a chronic condition for which there's no cure. However, medications and lifestyle changes can help you manage the symptoms. Support from others — family, friends, employer, teachers — can help you cope with narcolepsy.
Migraine headaches are recurrent throbbing or pulsatile headaches often associated with a prodrome, nausea, vomiting, photophobia, and phonophobia. When they occur, the prodromes are characterized by visual scintillations, scotomas, dizziness, or tinnitus
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency is typically secondary to emboli, thrombi, or arterial dissection. The labyrinth and brainstem are commonly affected, and symptoms may include vertigo, dizziness, dysarthria, diplopia, and numbness.
Cataplexy is a sudden, temporary loss of muscle tone that can result in collapse. It is often caused by intense emotions, including laughter
Binswanger's disease is a type of vascular dementia that involves white matter infarcts. Patients with this disease usually present with apathy, agitation, and bilateral corticospinal or bulbar signs
The patient has spasticity in the lower extremities greater than the upper extremities. The hips and knees are flexed and adducted with the ankles extended and internally rotated. When the patient walks both lower extremities are circumducted and the upper extremities are held in a mid or low guard position. This type of gait is usually seen with bilateral periventricular lesions. The legs are more affected than the arms because the corticospinal tract axons that are going to the legs are closest to the ventricles.
Cerebral palsy refers to brain damage that occurs before a child is five years old. Therefore, adults cannot develop cerebral palsy. However, cerebral palsy does not get better or worse with age, so when a child has the condition, he or she will continue to have the condition into adulthood.
Scissor gait is a form of gait abnormality primarily associated with spastic cerebral palsy.