Neurology
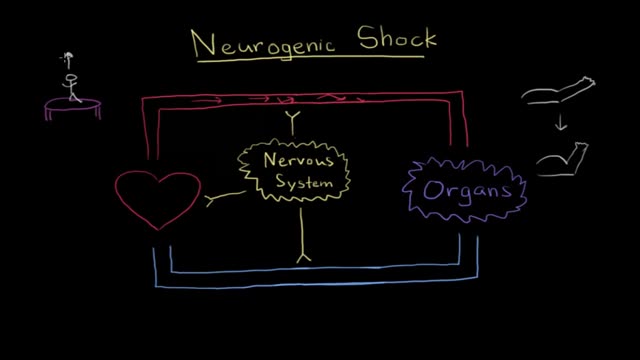
Neurogenic shock is a distributive type of shock resulting in low blood pressure, occasionally with a slowed heart rate, that is attributed to the disruption of the autonomic pathways within the spinal cord. It can occur after damage to the central nervous system such as spinal cord injury.
A man set to become the world’s first head transplant patient has scheduled the procedure for December 2017. Valery Spiridonov, 30, was diagnosed with a genetic muscle-wasting condition called Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, and volunteered for the procedure despite the risks involved, Central European News (CEN) reported. “When I realized that I could participate in something really big and important, I had no doubt left in my mind and started to work in this direction,” Spiridonov, a Russian computer scientist, told CEN. “The only thing I feel is the sense of pleasant impatience, like I have been preparing for something important all my life and it is starting to happen.”

What is peripheral neuropathy? Your peripheral nervous system connects the nerves from your brain and spinal cord, or central nervous system, to the rest of your body. This includes your: arms hands feet legs internal organs mouth face The job of these nerves is to deliver signals about physical sensations back to your brain.

Amnesia refers to the loss of memories, such as facts, information and experiences. Though having no sense of who you are is a common plot device in movies and television, real-life amnesia generally doesn't cause a loss of self-identity. Instead, people with amnesia — also called amnestic syndrome — are usually lucid and know who they are, but may have trouble learning new information and forming new memories. Amnesia can be caused by damage to areas of the brain that are vital for memory processing. Unlike a temporary episode of memory loss (transient global amnesia), amnesia can be permanent. There's no specific treatment for amnesia, but techniques for enhancing memory and psychological support can help people with amnesia and their families cope.

Tests. This test tracks electrical signals from the brain. There are a number of blood tests that may be recommended as part of your epilepsy diagnosis and treatment. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan may be used to locate the part of the brain that is causing seizures.

The majority of epileptic seizures are controlled by medication, particularly anticonvulsant drugs. The type of treatment prescribed will depend on several factors, including the frequency and severity of the seizures and the person's age, overall health, and medical history. An accurate diagnosis of the type of epilepsy is also critical to choosing the best treatment. Drug Therapy Many drugs are available to treat epilepsy. Although generic drugs are safely used for most medications, anticonvulsants are one category where doctors proceed with caution. Most doctors prefer to use brand-name anticonvulsants, but realize that many insurance companies will not cover the cost. As a result, it is acceptable to start taking a generic anticonvulsant medication, but if the desired control is not achieved, the patient should be switched to the brand-name drug.

A stroke occurs when the blood supply to your brain is interrupted or reduced. This deprives your brain of oxygen and nutrients, which can cause your brain cells to die. A stroke may be caused by a blocked artery (ischemic stroke) or the leaking or bursting of a blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke)

Invasive intracranial pressure monitoring. The most common surgically placed monitors for ICP measurement are intraventricular catheters (external ventricular drain [EVD] or a ventriculostomy drain) and fiberoptic ICP monitors implanted into the parenchyma of the brain.
Good abdominal wall closure is one of the basic surgical skills and is a common feature of almost all modern-day CSF shunt operations. The fact that some patients require multiple abdominal operations highlights the need for a simple and effective technique for peritoneal catheter insertion through the abdominal wall and abdominal wall closure. Although technically simple, abdominal wall closure becomes more complex when combined with the requirement to maintain CSF shunt function in cases in which the shunt catheter passes through the abdominal wall into the peritoneal cavity. In this report, the authors describe a simple technique for passing the peritoneal catheter of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt through the abdominal wall on a pathway separate from the fascial opening. This technique minimizes the risk of abdominal wall-related complications and is especially important in high-risk patients such as those with obesity and/or diabetes and in children.
The management of acute ischemic stroke has advanced greatly over the past 2 decades. New interventions, including intravenous and endovascular treatment strategies, have evolved to recanalize arteries and salvage the ischemic brain. The evolution of interventional approaches to the treatment of acute stroke has been prompted by the limitations of intravenous therapy and intended to extend the treatment window, improve recanalization rates, and subsequently long-term clinical outcomes. The major techniques that have defined the current field of interventional acute stroke management and the relevant past and current data, and ongoing clinical trials on interventional stroke therapy will be reviewed. New issues, such as futile recanalization, and time to microcatheter, will also be discussed.
Here are seven ways to start reining in your risks today, before a stroke has the chance to strike. Lower blood pressure. ... Lose weight. ... Exercise more. ... Drink — in moderation. ... Treat atrial fibrillation. ... Treat diabetes. ... Quit smoking.

Cluster headaches, occur in cyclical patterns or clusters, are one of the most painful types of headache. A cluster headache commonly awakens you in the middle of the night with intense pain in or around one eye on one side of your head. Bouts of frequent attacks, known as cluster periods, can last from weeks to months, usually followed by remission periods when the headaches stop. During remission, no headaches occur for months and sometimes even years. Fortunately, cluster headache is rare and not life-threatening. Treatments can make cluster headache attacks shorter and less severe. In addition, medications can reduce the number of cluster headaches.

Cerebral palsy is a disorder of movement, muscle tone or posture that is caused by damage that occurs to the immature, developing brain, most often before birth. Signs and symptoms appear during infancy or preschool years. In general, cerebral palsy causes impaired movement associated with abnormal reflexes, floppiness or rigidity of the limbs and trunk, abnormal posture, involuntary movements, unsteady walking, or some combination of these. People with cerebral palsy may have problems swallowing and commonly have eye muscle imbalance, in which the eyes don't focus on the same object. People with cerebral palsy also may suffer reduced range of motion at various joints of their bodies due to muscle stiffness. Cerebral palsy's effect on functional abilities varies greatly. Some affected people can walk while others can't. Some people show normal or near-normal intellectual capacity, but others may have intellectual disabilities. Epilepsy, blindness or deafness also may be present.

Encephalitis (en-sef-uh-LIE-tis) is inflammation of the brain. Viral infections are the most common cause of the condition. Encephalitis can cause flu-like symptoms, such as a fever or severe headache. It can also cause confused thinking, seizures, or problems with senses or movement. However, many cases of encephalitis result in only mild flu-like symptoms or even no symptoms. Severe cases of encephalitis, while relatively rare, can be life-threatening. Because the course of any single case of encephalitis can be unpredictable, it's important to get a timely diagnosis and treatment.

What are the symptoms of spinal meningitis in adults? Causes. The most common cause of viral meningitis is. ... Symptoms. Viral meningitis usually begins with symptoms of a viral infection, such as fever, a general feeling of illness (malaise), cough, muscle aches, vomiting, loss of appetite, and headache. ... Diagnosis. ... Treatment. ... Prognosis.

Bacterial meningitis is very serious and can be deadly. Death can occur in as little as a few hours. While most people with meningitis recover, permanent disabilities such as brain damage, hearing loss, and learning disabilities can result from the infection. There are several types of bacteria that can cause meningitis. Some of the leading causes of bacterial meningitis in the United States include Streptococcus pneumoniae, group B Streptococcus, Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus influenzae, and Listeria monocytogenes.

Infections can cause inflammation of the brain ( encephalitis). Viruses are the most common causes of encephalitis. Infections can also cause inflammation of the layers of tissue (meninges) that cover the brain and spinal cord—called meningitis. Often, bacterial meningitis spreads to the brain, causing encephalitis.