Physical Examination
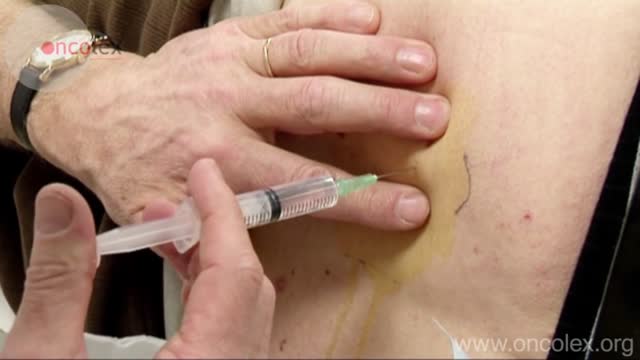
Lumbar puncture is a common emergency department procedure used to obtain information about the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic and, less commonly, therapeutic reasons. Please refer to the full article on Lumbar Puncture for more details on the lumbar puncture procedure. Lumbar puncture is typically performed via “blind” surface landmark guidance. The surface landmark technique is reported to be successful in a high percentage of attempted lumbar punctures; however, surface landmark identification of underlying structures has been shown to be accurate only 30% of the time. [1] Unsuccessful identification of proper landmarks often leads to increased difficulty in obtaining CSF, if the procedure is performed, and a higher rate of complications. Few alternatives are available in these cases. If available, fluoroscopic-guided lumbar puncture may be performed. If not, treatment is sometimes initiated empirically without obtaining CSF. Disadvantages of using fluoroscopy include limited availability or necessary transport of the patient outside of the emergency department, inability to directly visualize the spinal canal, and inherent radiation exposure
The examination room should be quiet, warm and well lit. After you have finished interviewing the patient, provide them with a gown (a.k.a. "Johnny") and leave the room (or draw a separating curtain) while they change. Instruct them to remove all of their clothing (except for briefs) and put on the gown so that the opening is in the rear. Occasionally, patient's will end up using them as ponchos, capes or in other creative ways. While this may make for a more attractive ensemble it will also, unfortunately, interfere with your ability to perform an examination! Prior to measuring vital signs, the patient should have had the opportunity to sit for approximately five minutes so that the values are not affected by the exertion required to walk to the exam room. All measurements are made while the patient is seated. Observation: Before diving in, take a minute or so to look at the patient in their entirety, making your observations, if possible, from an out-of-the way perch. Does the patient seem anxious, in pain, upset? What about their dress and hygiene? Remember, the exam begins as soon as you lay eyes on the patient. Temperature: This is generally obtained using an oral thermometer that provides a digital reading when the sensor is placed under the patient's tongue. As most exam rooms do not have thermometers, it is not necessary to repeat this measurement unless, of course, the recorded value seems discordant with the patient's clinical condition (e.g. they feel hot but reportedly have no fever or vice versa). Depending on the bias of a particular institution, temperature is measured in either Celcius or Farenheit, with a fever defined as greater than 38-38.5 C or 101-101.5 F. Rectal temperatures, which most closely reflect internal or core values, are approximately 1 degree F higher than those obtained orally. Respiratory Rate: Respirations are recorded as breaths per minute. They should be counted for at least 30 seconds as the total number of breaths in a 15 second period is rather small and any miscounting can result in rather large errors when multiplied by 4. Try to do this as surreptitiously as possible so that the patient does not consciously alter their rate of breathing. This can be done by observing the rise and fall of the patient's hospital gown while you appear to be taking their pulse. Normal is between 12 and 20. In general, this measurement offers no relevant information for the routine examination. However, particularly in the setting of cardio-pulmonary illness, it can be a very reliable marker of disease activity. Pulse: This can be measured at any place where there is a large artery (e.g. carotid, femoral, or simply by listening over the heart), though for the sake of convenience it is generally done by palpating the radial impulse. You may find it helpful to feel both radial arteries simultaneously, doubling the sensory input and helping to insure the accuracy of your measurements. Place the tips of your index and middle fingers just proximal to the patients wrist on the thumb side, orienting them so that they are both over the length of the vessel.
Rectal Examination
Gynecological Examination
Hoover's sign of leg paresis is one of two signs named for Charles Franklin Hoover. It is a maneuver aimed to separate organic from non-organic paresis of the leg. The sign relies on the principle of synergistic contraction. ... Feeling this would indicate an organic cause of the paresis.
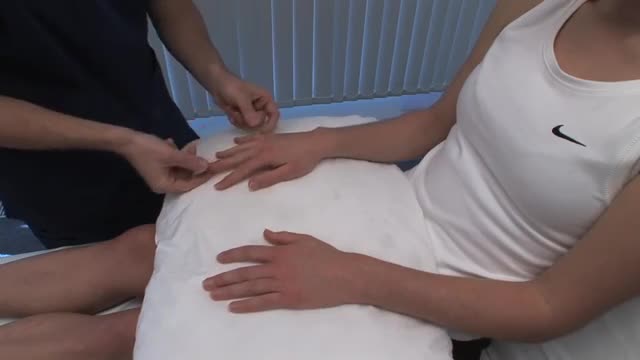
Bone marrow biopsy and bone marrow aspiration are procedures to collect and examine bone marrow — the spongy tissue inside some of your larger bones. Bone marrow biopsy and aspiration can show whether your bone marrow is healthy and making normal amounts of blood cells. Doctors use these procedures to diagnose and monitor blood and marrow diseases, including some cancers, as well as fevers of unknown origin. Bone marrow has a fluid portion and a more solid portion. In bone marrow biopsy, your doctor uses a needle to withdraw a sample of the solid portion. In bone marrow aspiration, a needle is used to withdraw a sample of the fluid portion.
Examination of the Hands
MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION
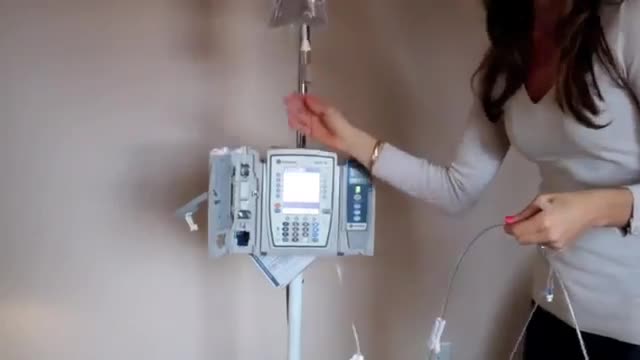
IV Dose Calculations
How to use an IV pump..
How to Start an IV
Urinary incontinence isn't a disease, it's a symptom. It can be caused by everyday habits, underlying medical conditions or physical problems. A thorough evaluation by your doctor can help determine what's behind your incontinence. Temporary urinary incontinence Certain drinks, foods and medications can act as diuretics — stimulating your bladder and increasing your volume of urine. They include: Alcohol Caffeine Decaffeinated tea and coffee Carbonated drinks Artificial sweeteners Corn syrup Foods that are high in spice, sugar or acid, especially citrus fruits Heart and blood pressure medications, sedatives, and muscle relaxants Large doses of vitamins B or C Urinary incontinence also may be caused by an easily treatable medical condition, such as: Urinary tract infection. Infections can irritate your bladder, causing you to have strong urges to urinate, and sometimes incontinence. Other signs and symptoms of urinary tract infection include a burning sensation when you urinate and foul-smelling urine. Constipation. The rectum is located near the bladder and shares many of the same nerves. Hard, compacted stool in your rectum causes these nerves to be overactive and increase urinary frequency. Persistent urinary incontinence Urinary incontinence can also be a persistent condition caused by underlying physical problems or changes, including: Pregnancy. Hormonal changes and the increased weight of the uterus can lead to stress incontinence. Childbirth. Vaginal delivery can weaken muscles needed for bladder control and also damage bladder nerves and supportive tissue, leading to a dropped (prolapsed) pelvic floor. With prolapse, the bladder, uterus, rectum or small intestine can get pushed down from the usual position and protrude into the vagina. Such protrusions can be associated with incontinence. Changes with age. Aging of the bladder muscle can decrease the bladder's capacity to store urine. Menopause. After menopause women produce less estrogen, a hormone that helps keep the lining of the bladder and urethra healthy. Deterioration of these tissues can aggravate incontinence. Hysterectomy. In women, the bladder and uterus are supported by many of the same muscles and ligaments. Any surgery that involves a woman's reproductive system, including removal of the uterus, may damage the supporting pelvic floor muscles, which can lead to incontinence. Enlarged prostate. Especially in older men, incontinence often stems from enlargement of the prostate gland, a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate cancer. In men, stress incontinence or urge incontinence can be associated with untreated prostate cancer. But more often, incontinence is a side effect of treatments for prostate cancer. Obstruction. A tumor anywhere along your urinary tract can block the normal flow of urine, leading to overflow incontinence. Urinary stones — hard, stone-like masses that form in the bladder — sometimes cause urine leakage. Neurological disorders. Multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, stroke, a brain tumor or a spinal injury can interfere with nerve signals involved in bladder control, causing urinary incontinence.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Uc6ZotU5mxA
stage of pregnancy 2016
The procedure is very simple, safe & relatively pain free. The technique takes 5 to 8 hours depending on grafts quantity. Most of the transplanted hair goes through a healing phase of couple of months after that these transplanted hair starts growing same like non-transplanted hair. The best benefit of the procedure is that they have different genetic make-up than the lost hair and are genetically permanent. Patient can cut, dye and colour these hair and grow continuously like non-transplanted hair.
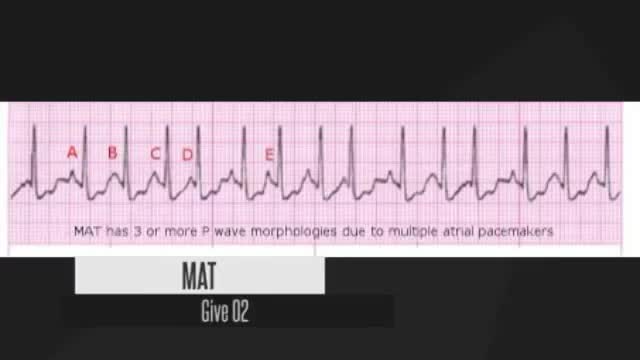
short review for ECG
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HP_geMHUHVU
https://www.facebook.com/medical.hint
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0N7Yy1UYEWk
visit https://www.facebook.com/medical.hint
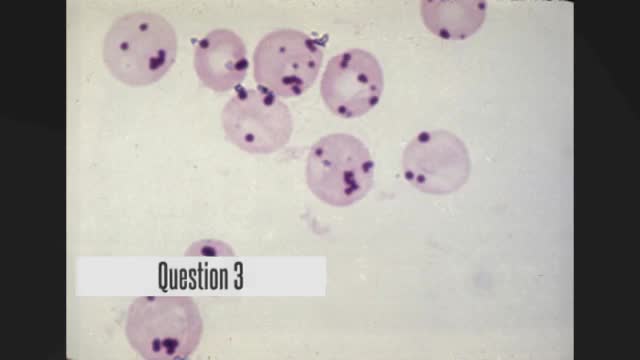
to check the answers
Que Es Fibromas, Curar Fibromas, Tratamientos De Miomas Uterinos, Utero Con Miomas, Tumor Mioma
http://no-mas-fibromas-uterinos.plus101.com
¿Usted está luchando para deshacerse de sus Fibromas Uterinos?
¿Sufre, o siente ansiedad por no ser capaz de curar sus Fibromas Uterinos correctamente a pesar de todos sus esfuerzos?
¿Está experimentando períodos irregulares, dolor en la parte baja del abdomen o hinchazón?
Usted está a punto de descubrir lo que podría ser el potente sistema de cura de los Fibromas Uterinos jamás desarrollado. Es el mismo sistema que miles de mujeres, como usted, han usado para revertir de manera permanente sus Fibromas Uterinos y mejorar su fertilidad y la calidad de sus vidas.
Sentirse más ligera, más saludable, más joven y con más energía.
¡Más Rápido de lo Que Usted Pensó Sería Posible!. Haga Click Aqui:
http://no-mas-fibromas-uterinos.plus101.com
Subscribete A Nuestro Canal
https://www.youtube.com/user/VivirConSalud1
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4IfA7NZ1CeA
Que Es Fibromas, Curar Fibromas, Tratamientos De Miomas Uterinos, Utero Con Miomas, Tumor Mioma, homeopatia para miomas uterinos, mioma síntomas, fibromas utero, que es un tumor benigno, tumores en el útero, que es un miomas uterinos, que es un fibromas, Curar Fibromas, Fibromas Uterinos Submucosos, Fibromas Uterinos Intramurales, Fibromas Uterinos Subserosos, Sintomas De Fibromas Uterinos, Operacion De Fibromas Uterinos, Fibroma Uterino, Tipos De Fibromas Uterinos