Other
Busadagur í fss 2008
Busa 08 í fs
The real end for all kinds of migraine was done. You can read all about this video in my web site: www.alisultaneh.8m.com or www.migrainesurgery.4t.com
Endoscope-assisted pocket grafting of autologous collagen for correction of facial wrinkles
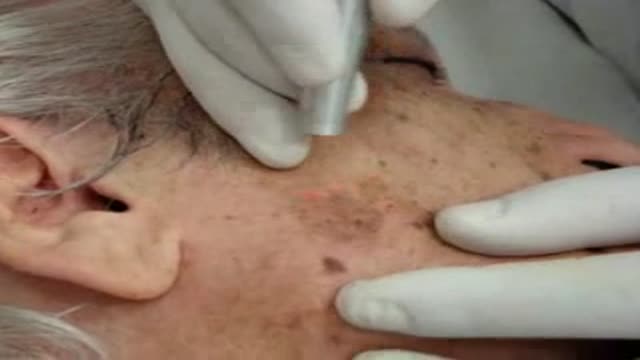
different aging and other skin spots can be treated succesfully with Co2 laser.
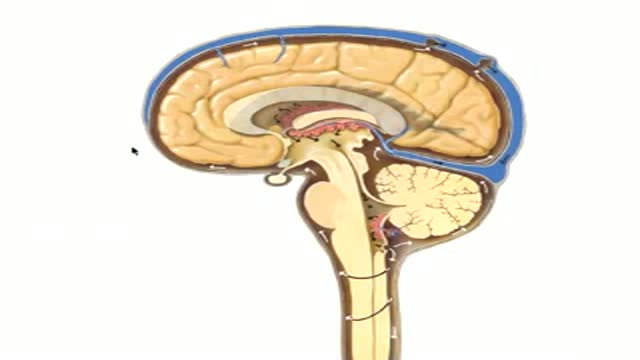
Neuroanatomy of CSF Flow
The complex circuitry interconnecting different areas in the brain, known collectively as white matter, is composed of millions of axons organized into fascicles and bundles. Upon macroscopic examination of sections of the brain, it is difficult to discern the orientation of the fibers. The same is true for conventional imaging modalities. However, recent advancements in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) make such task possible in a live subject. By sensitizing an otherwise typical MRI sequence to the diffusion of water molecules it is possible to measure their diffusion coefficient in a given direction1. Normally, the axonal membrane and myelin sheaths pose barriers to the movement of water molecules and, thus, they diffuse preferentially along the axon2. Therefore, the direction of white matter bundles can be elucidated by determining the principal diffusivity of water. The three-dimensional representation of the diffusion coefficient can be given by a tensor and its mathematical decomposition provides the direction of the tracts3; this MRI technique is known as diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). By connecting the information acquired with DTI, three-dimensional depictions of white matter fascicles are obtained4. The virtual dissection of white matter bundles is rapidly becoming a valuable tool in clinical research.
Our journey begins with a transverse section of tightly packed axons as seen through light microscopy. Although represented as a two-dimensional "slice", we see that these axons in fact resemble tubes. A simulation of water molecules diffusing randomly inside the axons demonstrates how the membranes and myelin hinder their movement across them and shows the preferred diffusion direction --along the axons. The tracts depicted through DTI slowly blend in and we ride along with them. As we zoom out even more, we realize that it is a portion of the corpus callosum connecting the two sides of the brain we were traveling on and the great difference in relative scale of the individual axons becomes evident. The surface of the brain is then shown, as well as the rest of the white matter bundles--a big, apparently chaotic tangle of wires. Finally, the skin covers the brain.
With the exception of the simulated water molecules, all the data presented in the animation is obtained through microscopy and MRI. Computer algorithms for the extraction of the cerebral structures and a custom-built graphics engine make our journey through the brain's anatomy possible in a living person.
Micrograph courtesy of Dr. Christian Beaulieu, University of Alberta.
Music by Mario Mattioli.
References:
1. Stejskal, E.O., et al., J. Chem. Phys., 1965. 42:
2. Beaulieu, C., NMR Biomed., 2002. 15:435-55.
3. Basser, P.J., et al., J. Magn. Reson. B, 1994. 103:247-54.
4. Mori, S., et al., NMR Biomed., 2002. 15:468-80.
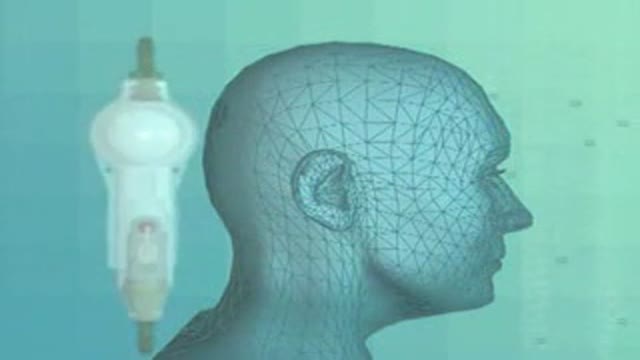
Insertion of a CSF shunt
I call this technique deep rendering. I basically stacked graphical cross-sections (in this case, MRI rendering data), using proper increments and clip through them with the camera. This way I am able to explore all internal components in full 3D real-time.
I actually was able to figure out how to colorize different organs to help distinguish them apart from each other but couldn't get the shader to render real-time in Maya.
Credit: MRI scans courtesy of University of Washington Digital Anatomist Program
Endoscopic fenestration of suprasellar cyst in a 4 years old girl
Endoscopic fenestration of arachnoid cyst in middle fossa
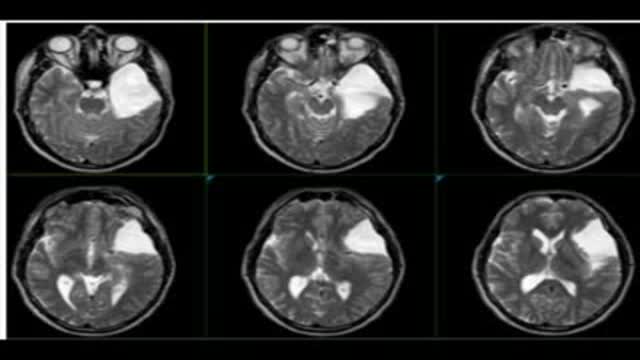
brain scans with arachnoid cyst, pre and post operative
Endoscopic Management of Brain Cyst, ForaminoPlasty
Endoscopic Brain Surgery, third Ventriculostomy
Hydatid Cyst Removal from the brain
Watch as Dr. Benjamin Carson performs risky brain surgery on young Payton to remove a brain tumor. Dr. Carson, director of pediatric neurosurgery, is just one of the many reasons why Johns Hopkins Children's Center was recently ranked #1 in neurology and neurosurgery in America's Best Children's Hospitals 2008
Vanderbilt Medical Center neurosurgeons and neurologists will be online demonstrating their 4-stage innovative technique used for Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS). Deep brain stimulation therapy utilizes an implantable neuro-stimulator to treat movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, essential tremor, and dystonia.
On Tuesday May 29th at 3:00pm EDT, University Hospitals Case Medical Center Cleveland, Ohio, will host a live webcast to demonstrate the removal of brain tumor and epileptic focus from an awake patient using intra-operative MRI and brain mapping. See this on OR-Live.com
The patient was a middle-aged gentleman with new onset seizures. An MRI showed what appeared to be a low grade glioma near the motor strip on the right. Studies have shown that complete removal can cure the seizures, improve quality of life and survival, but this is difficult to do with conventional technology without harming the surrounding normal brain because its difficult to determine where tumor ends and normal brain begins.
olusegun adekanye's spinal disc replacement operation performed by Dr. Nick Thomas at the Blackheath Hospital.Part 2
olusegun adekanye's spinal disc replacement operation performed by Dr. Nick Thomas at the Blackheath Hospital.