Video terbaru
What is a laparoscopic cholecystectomy? Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a procedure in which the gallbladder is removed by laparoscopic techniques. Laparoscopic surgery also referred to as minimally invasive surgery describes the performance of surgical procedures with the assistance of a video camera and several thin instruments. During a laparoscopic surgical procedure, small incisions of up to half an inch are made and plastic tubes called ports are placed through these incisions. The camera and the instruments are then introduced through the ports which allow access to the inside of the patient. The camera transmits an image of the organs inside the abdomen onto a television monitor.The surgeon is not able to see directly into the patient without the traditional large incision. The video camera becomes a surgeon’s eyes in laparoscopy surgery, since the surgeon uses the image from the video camera positioned inside the patient’s body to perform the procedure.
A video showing Two port laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Reusable Lap Instruments Multi-functional laparoscopic instruments. Choose from many handle styles, three instrument styles, 33cm or 45cm lengths, and dozens of dissectors, graspers, forceps, and scissors. Lap Needle Electrodes Monopolar needle electrodes for laparoscopic surgery.
It is held in place with a balloon at the end, which is filled with sterile water to prevent the catheter from being removed from the bladder. The urine drains through the catheter tube into a bag, which is emptied when full. The procedure to insert a catheter is called catheterization.
Another video showing different technique of child birth
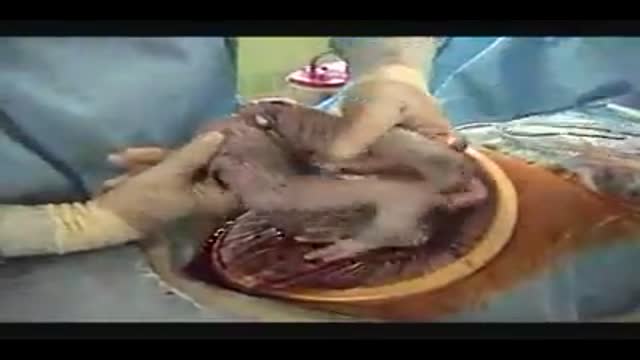
A Cesarean section (C-section) is surgery to deliver a baby. The baby is taken out through the mother's abdomen. In the United States, almost one in three women has their babies this way. Some C-sections are planned, but many are done when unexpected problems happen during delivery. Reasons for a C-section may include Health problems in the mother The mother carrying more than one baby The size or position of the baby The baby's health is in danger Labor is not moving along as it should
A c-section, or cesarean section, is the delivery of a baby through a surgical incision in the mother's abdomen and uterus. In some circumstances, a c-section is scheduled in advance. In others, the surgery is needed due to an unforeseen complication. If you or your baby is in imminent danger, you'll have an emergency c-section. Otherwise, it's called an unplanned section. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control, about 32 percent of American women who gave birth in 2015 had a cesarean delivery.
An interesting documentary video from Discovery channel from the show "Human Files Night" explaining the anatomy and everything related to female genital tract in a very interesting professional way.
The cervix is fully dilated to about 10 cm,with the baby's head moving beyond the cervical opening , into the birth canal. The mother is encouraged to push during contractions,and rest in between them. In a normal delivery, the head rotates to face the mother's back
Vaginal delivery is the most common and safest type of childbirth. When necessary in certain circumstances, forceps (instruments resembling large spoons) may be used to cup your baby's head and help guide the baby through the birth canal. Vacuum delivery is another way to assist delivery and is similar to forceps delivery. In vacuum delivery, a plastic cup is applied to the baby's head by suction and the health care provider gently pulls the baby from the birth canal.
The Motor Assessment Scale (MAS) is a performance-based scale that was developed as a means of assessing everyday motor function in patients with stroke (Carr, Shepherd, Nordholm, & Lynne, 1985). The MAS is based on a task-oriented approach to evaluation that assesses performance of functional tasks rather than isolated patterns of movement
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm. The condition occurs when one of the major nerves to the hand — the median nerve — is squeezed or compressed as it travels through the wrist. In most patients, carpal tunnel syndrome gets worse over time, so early diagnosis and treatment are important. Early on, symptoms can often be relieved with simple measures like wearing a wrist splint or avoiding certain activities. If pressure on the median nerve continues, however, it can lead to nerve damage and worsening symptoms. To prevent permanent damage, surgery to take pressure off the median nerve may be recommended for some patients.
A videos showing the procedure of amniocentesis video
Ptosis is when the upper eyelid droops over the eye. The eyelid may droop just a little, or so much that it covers the pupil (the black dot at the center of your eye that lets light in). Ptosis can limit or even completely block normal vision. Children and adults can have ptosis. Fortunately, this condition can be treated to improve vision as well as appearance.
This request usually follows orbit examination of a patient with thyroid eye disease. The aim is to look for signs of hyperthyroidism and less commonly hypothyroidism.
Eye tests are important for the detection of many common eye infections and diseases. Eyes are also an important indicator to detect chronic systemic diseases like Hypertension and Diabetes. Must after maxillofacial trauma to rule out any near and late complications emerging for the eyes. 2. There are two perspectives for examining the eyes : 1. Ophthalmic Perspective – because eyes are prone to many infections, diseases and conditions. 2. Maxillofacial Perspective – because the eyes and the orbit forms an integral component of facial and mid-facial fractures and trauma.
To avoid pupil constriction while accommodating, ask to the patient to fix on a distant object throughout your examination. Look for equal pupil sizes, and check again with the lights off. Anisocoria is not a feature of an afferent defect. They dilate again after the light is removed.
Examination of a patient with post-enucleation socket syndrome.