Latest videos

Surgery is an elective procedure done in people who have had extensive testing to decide if they are potential candidates. The following criteria are considered when determining if a person may be a good candidate for surgery. Person has failed adequate trials of two first-line seizure medicines (ones that are commonly effective in controlling the type of seizures the person is experiencing) and one combination of at least two drugs. A trial of a medication is considered adequate when it has been increased gradually to the maximum dosage that does not cause serious side effects. If the person has frequent seizures, any improvement will be obvious after a short time. If the seizures generally occur far apart, however, it may take months to determine whether a medication is helping. At some epilepsy centers, patients are offered additional conventional or experimental medications before surgery is considered. But research suggests that each time a trial of medication fails to control a person's seizures, it becomes less likely that a different medicine or combination will be successful. Since uncontrolled seizures present serious physical risks and social and psychological consequences, the trend these days is to proceed with surgery much sooner than in the past if it seems appropriate for that person.

Epilepsy surgery is reserved for people whose seizures are not well controlled by seizure medicines. This situation is sometimes called being "medically refractory" or "drug resistant." In children, the definition of medically refractory is even more individualized to the specific child's situation. Surgery may be considered for some children after weeks to months of treatment with seizure medicines.
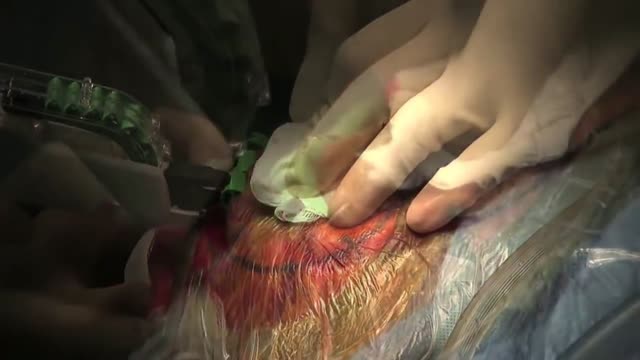
Surgery is an alternative for some people whose seizures cannot be controlled by medications. It has been used for more than a century, but its use dramatically increased in the 1980s and 90s, reflecting its effectiveness as an alternative to seizure medicines. The benefits of surgery should be weighed carefully against its risks, however, because there is no guarantee that it will be successful in controlling seizures. People with partial epilepsy who are considered for surgery have difficult-to-control seizures that have not responded to aggressive treatment with medication. In the past, patients usually tried several medications with poor results for many years, even decades, before being considered for surgery. More recently, surgery is being considered sooner. Studies have shown that the earlier surgery is performed, the better the outcome. Surgery is now being performed on some people whose seizures have been uncontrolled for only 1 or 2 years. At least two single drugs and a combination of two or more drugs should be tried before surgery is considered. Epilepsy surgery can be especially helpful to people who have seizures from structural brain problems (such as benign brain tumors, strokes or malformations of blood vessels).

Sporotrichosis (also known as "rose gardener's disease") is a disease caused by the infection of the fungus Sporothrix schenckii. This fungal disease usually affects the skin, although other rare forms can affect the lungs, joints, bones, and even the brain.
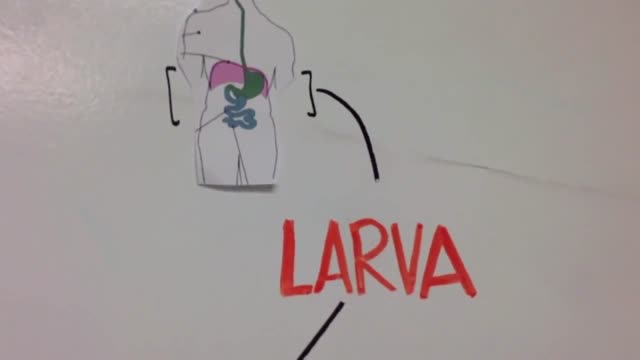
Trichinosis (trik-ih-NO-sis), sometimes called trichinellosis (trik-ih-nuh-LOW-sis), is a type of roundworm infection. Roundworm parasites use a host body to live and reproduce. Occurring primarily among meat-eating animals (carnivores) — especially bears, foxes and walruses — the infection is acquired by eating roundworm larvae in raw or undercooked meat. When humans eat undercooked meat containing trichinella larvae, the larvae mature into adult worms in the intestine over several weeks. The adult worms then produce larvae that travel through various tissues, including muscle. Trichinosis is most widespread in rural areas throughout the world. Trichinosis can be treated with medication, though it's not always necessary. It's also easy to prevent.
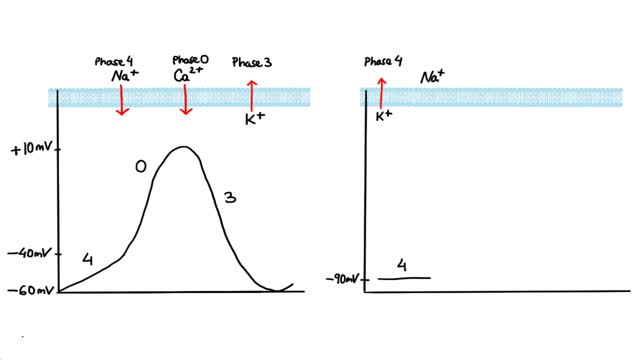
Antiarrhythmics are drugs that are used to treat abnormal heart rhythms resulting from irregular electrical activity of the heart. There are many different types of antiarrhythmic drugs. Examples include: Amiodarone (Cordarone) Flecainide (Tambocor) Procainamide (Procanbid) Sotalol (Betapace) In addition, there are other types of heart drugs that can be used to treat arrhythmias, including: Beta-blockers such as metoprolol or Toprol XL, which reduce the heart's workload and heart rate. Calcium channel blockers such as verapamil or Calan, which also reduces the heart rate.

Angina results from a reduction in the oxygen supply/demand ratio. Therefore, in order to alleviate the pain, it is necessary to improve this ratio. This can be done either by increasing blood flow (which increases oxygen delivery or supply), or by decreasing oxygen demand (i.e., by decreasing myocardial oxygen consumption).

Are you a first time would be mom? If yes, then you must be very excited to feel the first movement and kick from your baby. It is undoubtedly the most exciting experience for many expecting moms. It is an indication that there is a little angel growing inside you. There are interesting facts about baby kicks during pregnancy that you need to know.
The baby will move head down if there is room or if there is tone in the support to the uterus to direct baby head down. Before 24-26 weeks most babies lie diagonal or sideways in the Transverse Lie position. Between 24-29 weeks most babies turn vertical and some will be breech.
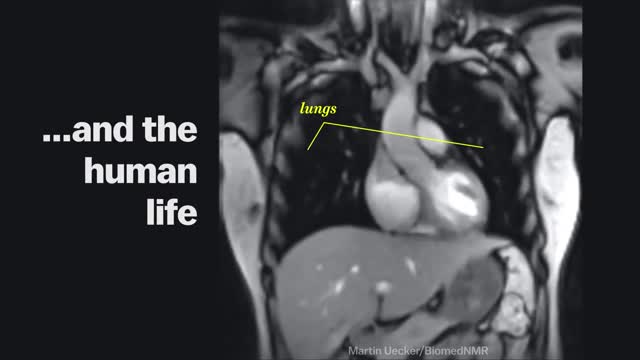
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) "sees" inside the body by mapping the position of water molecules, which exist at different densities in different types of tissue. Watch the video above for a sample of some impressive MRI images of the human body in action.

Nosebleeds are common due to the location of the nose on the face, and the large amount of blood vessels in the nose. The most common causes of nosebleeds are drying of the nasal membranes and nose picking (digital trauma), which can be prevented with proper lubrication of the nasal passages and not picking the nose.