Latest videos
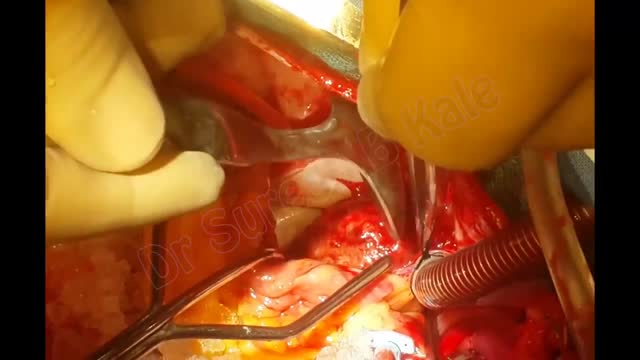
watch to see the Large Clot in the heart
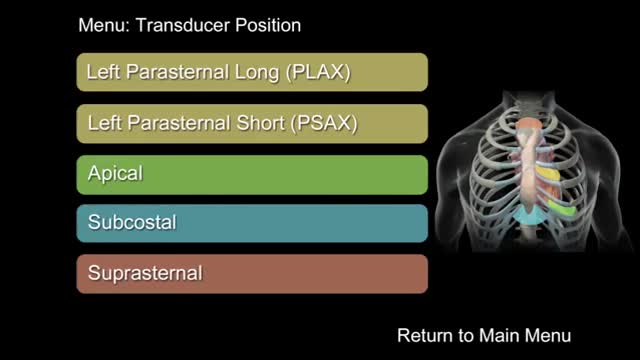
Probes, landmarks, and general windows to obtain transthoracic echo views
"How to Perform a Transthoracic Echocardiographic Study Volume 1: Transducer Position and Anatomy" is an instructional video, offered by ASE, and can be used for professional lectures and offers an interactive section for flexible presentations. The video includes an overview of relevant cardiac anatomy, a step by step presentation of all Transducer Positions, and the sequential transducer movements to acquire standard echo images needed to complete a Transthoracic Echocardiographic Study.
This video: Blisters caused by friction or minor burns do not require a doctor's care. New skin will form underneath the affected area and the fluid is simply absorbed. Do not puncture a blister unless it is large, painful, or likely to be further irritated. The fluid-filled blister keeps the underlying skin clean, which prevents infection and promotes healing.
A cesarean delivery is a surgical procedure in which a fetus is delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen and uterus. ... According to the CDC, in 2010, almost 33% of births were by cesarean delivery.
Simple technique to harvest Connective tissue graft from the Palate.
giant systolic pulsations, known as C-V waves, were noticeable during jugular venous examination of a 33-year-old woman who had tricuspid-valve endocarditis. In video 2, transthoracic echocardiography revealed severe tricuspid regurgitation.
Hirschsprung's (HIRSH-sproongz) disease is a condition that affects the large intestine (colon) and causes problems with passing stool. The condition is present at birth (congenital) as a result of missing nerve cells in the muscles of the baby's colon. A newborn who has Hirschsprung's disease usually can't have a bowel movement in the days after birth. In mild cases, the condition might not be detected until later in childhood. Uncommonly, Hirschsprung's disease is first diagnosed in adults.
Ebstein anomaly is a congenital malformation of the heart that is characterized by apical displacement of the septal and posterior tricuspid valve leaflets, leading to atrialization of the right ventricle with a variable degree of malformation and displacement of the anterior leaflet.
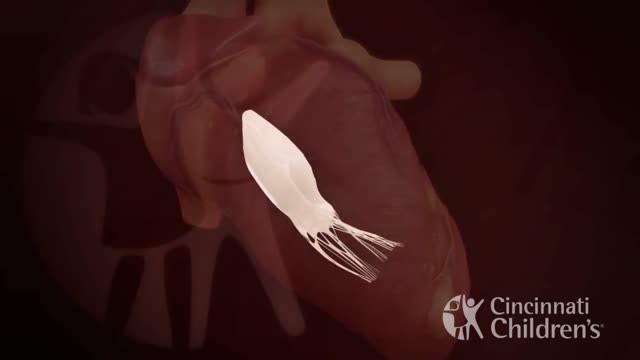
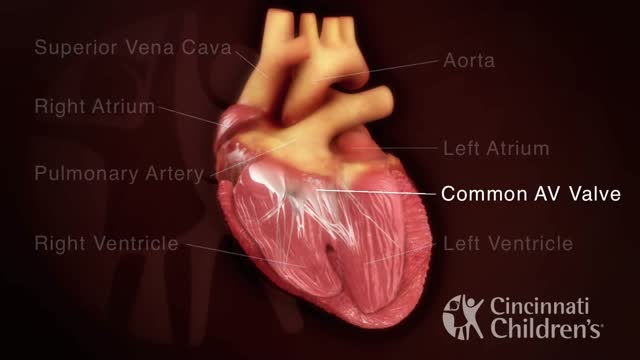
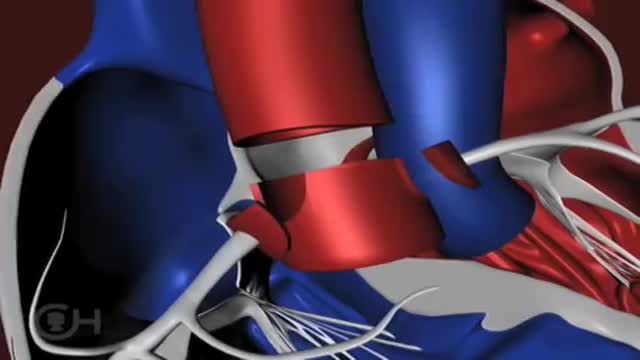
An atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) is a heart defect in which there are holes between the chambers of the right and left sides of the heart, and the valves that control the flow of blood between these chambers may not be formed correctly. This condition is also called atrioventricular canal (AV canal) defect or endocardial cushion defect. In AVSD, blood flows where it normally should not go. The blood may also have a lower than normal amount of oxygen, and extra blood can flow to the lungs. This extra blood being pumped into the lungs forces the heart and lungs to work hard and may lead to
The "great arteries" in this anomaly refer to the aorta and the pulmonary artery, the two major arteries carrying blood away from the heart. In cases of transposition of the great arteries, these vessels arise from the wrong ventricle. They are "transposed" from their normal position so that the aorta arises from the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery from the left ventricle. Other heart defects may occur along with transposition of the great arteries. About 25 percent of children with transposition will also have a ventricular septal defect (VSD) . In nearly a third, the branching pattern of the coronary arteries as they leave the transposed aorta is unusual. Infants may also have narrowing below the pulmonary valve that blocks blood flow from the left ventricle to the lungs.
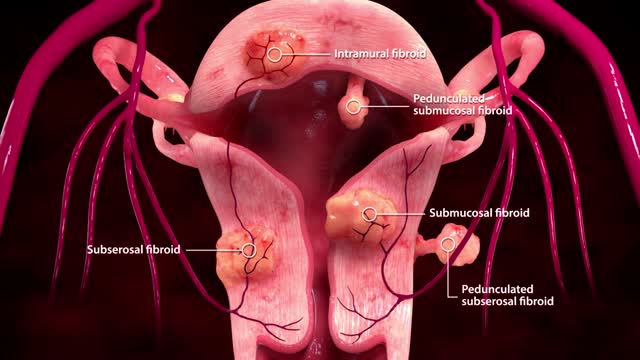
Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE), also known as uterine artery embolization, is a minimally invasive procedure that is performed by an Interventional Radiologist (IR), a doctor who uses advanced imaging technology to see inside the body without surgery. UFE is often performed as an outpatient service and offers a much shorter recovery time than surgery. For more information on uterine fibroids and all your treatment options, including UFE,
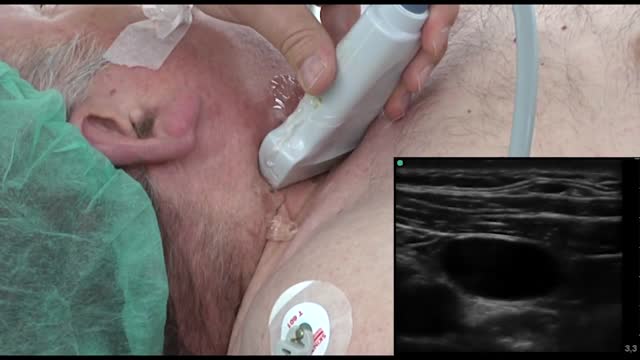
Central catheters provide dependable intravenous access and enable hemodynamic monitoring and blood sampling [1-3]. The jugular veins are one of the most popular sites for central venous access due to accessibility and overall low complication rates, and are the preferred site for temporary hemodialysis.
Ultrasound-guided internal jugular cannulation
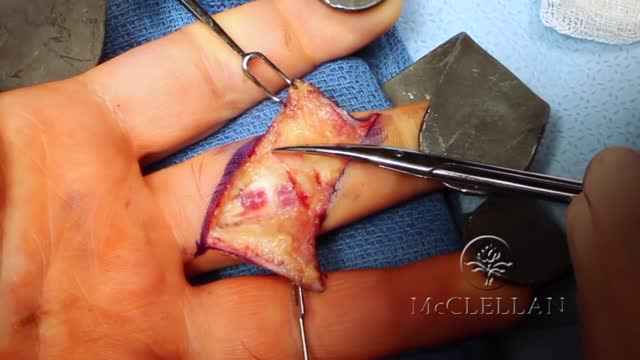
A deep cut on the palm side of your fingers, hand, wrist, or forearm can damage your flexor tendons, which are the tissues that help control movement in your hand. A flexor tendon injury can make it impossible to bend your fingers or thumb.
Is there scientific proof we can heal ourselves?
Meet Toby, the baby who was born premature at 24 weeks. He may be small, but he's definitely a fighter! Share his story
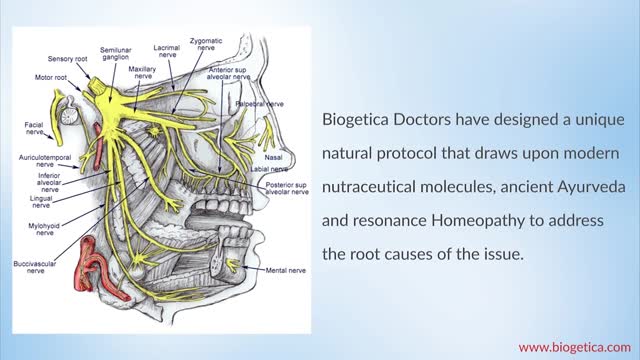
You may initially experience short, mild attacks. But trigeminal neuralgia can progress and cause longer, more-frequent bouts of searing pain. Trigeminal neuralgia affects women more often than men, and it's more likely to occur in people who are older than 50.
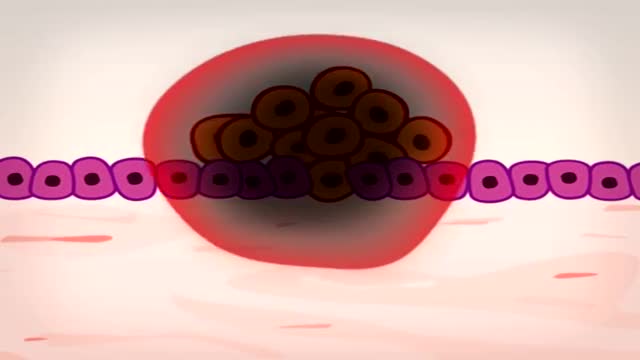
In 5 minutes find out how and why a normal cell becomes a cancer cell: risk factors and treatment.
This medical animation illustrates how acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the most common type of cancer in adults, develops in the blood and bone marrow. The narrator also discusses the symptoms of AML and AML treatment options.