Latest videos
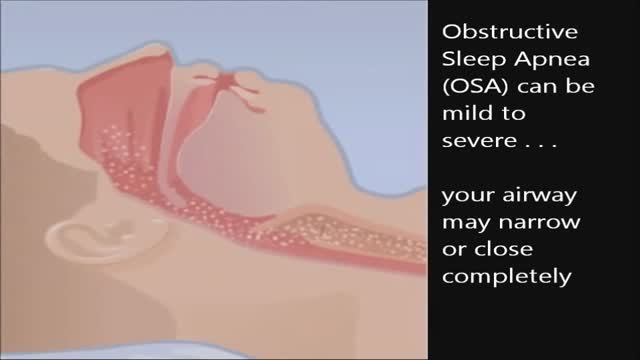
CPAP, or continuous positive airway pressure, is a treatment that uses mild air pressure to keep the airways open. CPAP typically is used by people who have breathing problems, such as sleep apnea. CPAP also may be used to treat preterm infants whose lungs have not fully developed.

CPAP is a treatment that uses mild air pressure to keep your breathing airways open. It involves using a CPAP machine that includes a mask or other device that fits over your nose or your nose and mouth, straps to position the mask, a tube that connects the mask to the machine’s motor, and a motor that blows air into the tube. CPAP is used to treat sleep-related breathing disorders including sleep apnea. It also may be used to treat preterm infants who have underdeveloped lungs.

Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a general term that describes a disease of the heart or blood vessels. Blood flow to the heart, brain or body can be reduced as the result of a blood clot (thrombosis), or by a build-up of fatty deposits inside an artery that cause the artery to harden and narrow (atherosclerosis).
Recommended range without diabetes is 70 to 130mg/dL. (The standard for measuring blood glucose is "mg/dL" which means milligrams per deciliter.) If your blood glucose level is above 130mg/dL, that's fasting hyperglycemia. Fasting hyperglycemia is a common diabetes complication.
The usual reason given for people getting fat is that they eat too much and/or exercise too little. That reflects one of the basic laws of thermodynamics—I forget which one. The amount of energy you put into a system minus the energy you take out has to be stored somewhere i.e. FAT! This formulation—true though it is—does not entirely explain obesity since some people seem to eat more than fat people and exercise no more than these same fat people, and yet they are not fat! Chalking this fact up to the general perversity of the universe is not sufficient explanation. Other factors must come into play. I mention below some of the ideas thoughtful people have proposed to explain why fat people become fat:
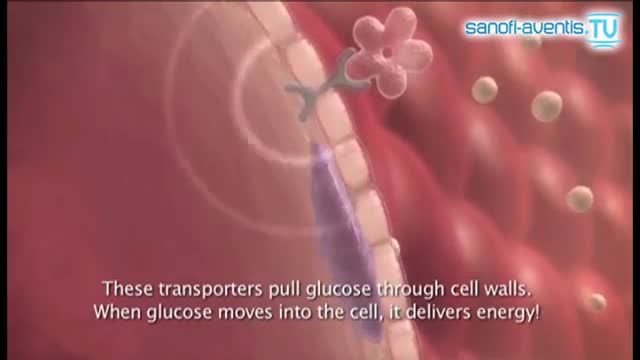
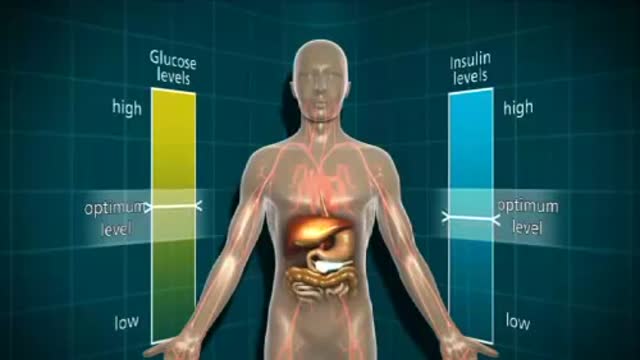
Insulin is a hormone made naturally in the pancreas that helps move sugar into the cells of your body. Your cells use the sugar as fuel to make energy. Without enough insulin, sugar stays in your bloodstream, raising your blood sugar. High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, can lead to the signs and symptoms of diabetes:
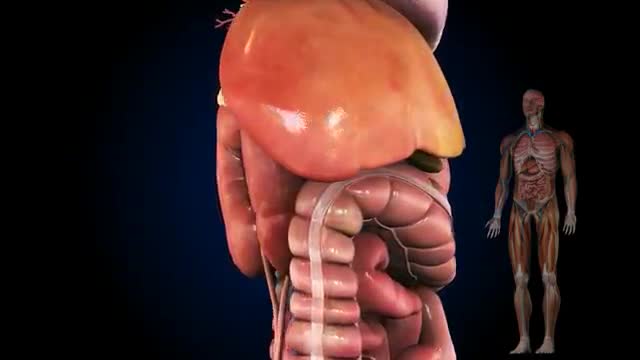
Possible complications include: Cardiovascular disease. ... Nerve damage (neuropathy). ... Kidney damage (nephropathy). ... Eye damage (retinopathy). ... Foot damage. ... Skin conditions. ... Hearing impairment. ... Alzheimer's disease.

A silent heart attack is a heart attack that has few, if any, symptoms. You may have never had any symptoms to warn you that you've developed a heart problem, such as chest pain or shortness of breath. Having diabetes or prediabetes puts you at increased risk for heart disease and stroke. You can lower your risk by keeping your blood glucose (also called blood sugar), blood pressure, and blood cholesterol close to the recommended target numbersthe levels suggested by diabetes experts for good health. (
As a result, the amount of glucose in the blood increases while the cells are starved of energy. Over time, high blood glucose levels damage nerves and blood vessels, leading to complications such as heart disease and stroke, the leading causes of death among people with diabetes.

Alendronate Sodium is used for the following diseases and conditions: osteoporosis, and osteogenesis imperfecta. Alendronate Sodium improves the patient's condition by performing the following functions: slowing down the bone loss and helps to keep the bones strong and less likely to break. Side effects are possible with Alendronate Sodium, but do not always occur. Some of the side effects may be rare but serious. Consult your doctor if you observe any side effects, especially if they do not go away. Alendronate Sodium may cause the following side-effects: stomach pain, constipation, diarrhea, gas, nausea, and jaw pain
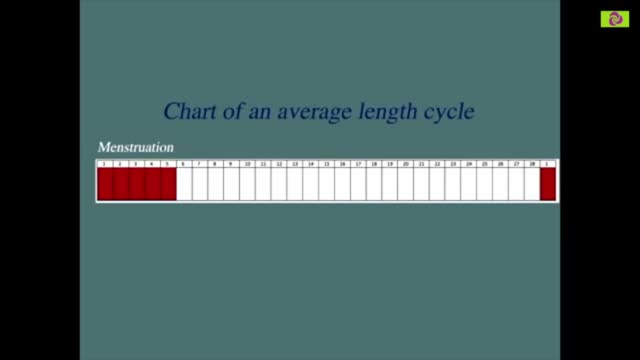
Most women have vaginal discharge at many different times throughout their cycle. During ovulation, white and watery discharge is common and accepted as normal. But, discharge after ovulation is widely believed to be a sign of pregnancy.

You may have heard that some positions, such as your partner on top (missionary position), are better than others for getting pregnant. In fact, there's no evidence to back these theories up. Experts just haven't done the research yet. What experts have done, though, is use scanning to show what's going on inside when you're doing the deed. The research looked at two positions: the missionary position and doggy style. (Doggy style being when you're on all fours, and your partner enters you from behind). Common sense tells us that these positions allow for deep penetration. This means that they're more likely to place sperm right next to your cervix (the opening of your uterus). The scans confirm that the tip of the penis reaches the areas between the cervix and vaginal walls in both of these positions. The missionary position allows the penis to reach the area at the front of the cervix. The rear entry position reaches the area at back of the cervix. It's amazing what some experts spend their time doing, isn't it! Other positions, such as standing up, or woman on top, may be just as good for getting sperm right next to the cervix. We just don't know yet. http://www.babycentre.co.uk/sex-for-getting-pregnant#ixzz4XKnPLbxL

Hypothyroidism during pregnancy is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone, thyroxine (T4). Postpartum thyroiditis—inflammation of the thyroid gland—causes a brief period of hyperthyroidism, often followed by hypothyroidism that usually goes away within a year. Sometimes the hypothyroidism is permanent.

If your levels are too low, you have hypothyroidism and may not be ovulating as you should. Taking the right dose of thyroxine, the hormone you lack, can restore your fertility. You may have discovered your underactive thyroid as a result of trying to get pregnant.