Latest videos
Alendronate Sodium is used for the following diseases and conditions: osteoporosis, and osteogenesis imperfecta. Alendronate Sodium improves the patient's condition by performing the following functions: slowing down the bone loss and helps to keep the bones strong and less likely to break. Side effects are possible with Alendronate Sodium, but do not always occur. Some of the side effects may be rare but serious. Consult your doctor if you observe any side effects, especially if they do not go away. Alendronate Sodium may cause the following side-effects: stomach pain, constipation, diarrhea, gas, nausea, and jaw pain
How to Check Cervical Mucus
Cervical Mucus
Most women have vaginal discharge at many different times throughout their cycle. During ovulation, white and watery discharge is common and accepted as normal. But, discharge after ovulation is widely believed to be a sign of pregnancy.
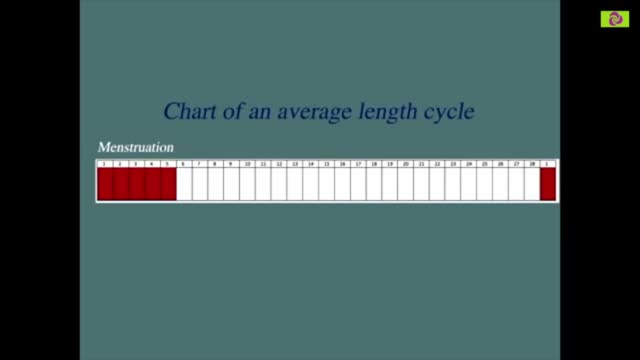
Our calculator can help you discover the most fertile days of your menstrual cycle or your “Estimated Fertility Window” based on information you provide.
You may have heard that some positions, such as your partner on top (missionary position), are better than others for getting pregnant. In fact, there's no evidence to back these theories up. Experts just haven't done the research yet. What experts have done, though, is use scanning to show what's going on inside when you're doing the deed. The research looked at two positions: the missionary position and doggy style. (Doggy style being when you're on all fours, and your partner enters you from behind). Common sense tells us that these positions allow for deep penetration. This means that they're more likely to place sperm right next to your cervix (the opening of your uterus). The scans confirm that the tip of the penis reaches the areas between the cervix and vaginal walls in both of these positions. The missionary position allows the penis to reach the area at the front of the cervix. The rear entry position reaches the area at back of the cervix. It's amazing what some experts spend their time doing, isn't it! Other positions, such as standing up, or woman on top, may be just as good for getting sperm right next to the cervix. We just don't know yet. http://www.babycentre.co.uk/sex-for-getting-pregnant#ixzz4XKnPLbxL
Hypothyroidism during pregnancy is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone, thyroxine (T4). Postpartum thyroiditis—inflammation of the thyroid gland—causes a brief period of hyperthyroidism, often followed by hypothyroidism that usually goes away within a year. Sometimes the hypothyroidism is permanent.
If your levels are too low, you have hypothyroidism and may not be ovulating as you should. Taking the right dose of thyroxine, the hormone you lack, can restore your fertility. You may have discovered your underactive thyroid as a result of trying to get pregnant.
The vast majority of glucocorticoid activity in most mammals is from cortisol, also known as hydrocortisone. Corticosterone, the major glucocorticoid in rodents, is another glucocorticoid. Cortisol binds to the glucocorticoid receptor in the cytoplasm and the hormone-receptor complex is then translocated into the nucleus, where it binds to its DNA response element and modulates transcription from a battery of genes, leading to changes in the cell's phenotype. Only about 10% of circulating cortisol is free. The remaining majority circulates bound to plasma proteins, particularly corticosteroid-binding globulin (transcortin). This protein binding likely decreases the metabolic clearance rate of glucocorticoids and, because the bound steroid is not biologically active, tends to act as a buffer and blunt wild fluctuations in cortisol concentration.
When taking oral corticosteroids longer term, you may experience: Clouding of the lens in one or both eyes (cataracts) High blood sugar, which can trigger or worsen diabetes. Increased risk of infections. Thinning bones (osteoporosis) and fractures. Suppressed adrenal gland hormone production
Diabetic retinopathy is classified into two types: Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) is the early stage of the disease in which symptoms will be mild or nonexistent. In NPDR, the blood vessels in the retina are weakened. ... Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) is the more advanced form of the disease.
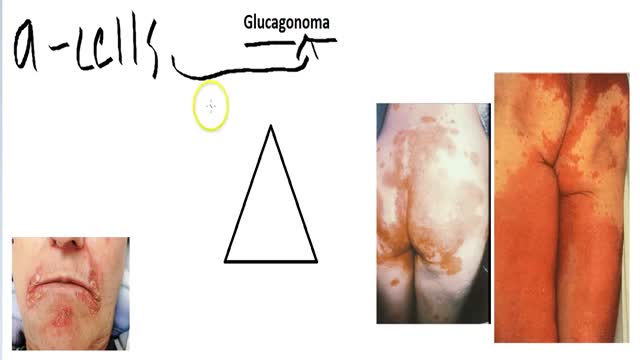
A glucagonoma is a rare tumor of the alpha cells of the pancreas that results in the overproduction of the hormone glucagon. Alpha cell tumors are commonly associated with glucagonoma syndrome, though similar symptoms are present in cases of pseudoglucagonoma syndrome in the absence of a glucagon-secreting tumor.
Diabetic retinopathy involves changes to retinal blood vessels that can cause them to bleed or leak fluid, distorting vision. Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of vision loss among people with diabetes and a leading cause of blindness among working-age adults.
There are 3 genetic types of FHH based on chromosome location. FHH type 1 accounts for 65% of cases and is due to inactivating mutations in the CASR gene, localized to 3q21.1. This gene encodes the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Loss of CaSR function results in a reduction in the sensitivity of parathyroid and renal cells to calcium levels so hypercalcemia is perceived as normal. The other 35% have either a mutation GNA11 (19p13.3) seen in FHH type 2 or AP2S1 (19q13.2-q13.3) seen in FHH type 3 (see these terms) or in genes not yet discovered. FHH is rarely caused by auto-antibodies against CaSR in those without a mutation.
NTIS refers to a syndrome found in seriously ill or starving patients with low fT3, usually elevated RT3, normal or low TSH, and if prolonged, low fT4. It is found in a high proportion of patients in the ICU setting, and correlates with a poor prognosis if TT4 is <4ug/dl. The patho-physiology includes suppression of TRH release, reducedT3 and T4 turnover, reduction in liver generation of T3, increased formation of RT3, and tissue specific down-regulation of deiodinases, transporters, and TH receptors. Although long debated, tissue TH levels are definitely reduced, and tissue hypothyroidism is presumably present. This is often not clinically evident because of the brief duration, and reduced but not absent tissue levels of TH. Although recognized for nearly 4 decades, interpretation of the syndrome is contested, because of lack of data. Some observes, totally without data, argue that it is a protective response and should not be treated. Other observers (as in this review) present available data suggesting, but not proving, that thyroid hormone replacement is appropriate, not harmful, and may be beneficial. The best form of treatment (TRH,TSH,or T3+T4) and possible accompanying treatments (GHRH, Cortisol, nutrition, insulin) lack consensus. In this review current data are laid out for reader’s review and judgment.
Euthyroid sick syndrome (ESS), sick euthyroid syndrome (SES), thyroid allostasis in critical illness, tumours, uremia and starvation (TACITUS), non-thyroidal illness syndrome (NTIS) or low T3 low T4 syndrome is a state of adaptation or dysregulation of thyrotropic feedback control where the levels of T3 and/or T4 are ...
Parathyroid cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of a parathyroid gland. The parathyroid glands are four pea-sized organs found in the neck near the thyroid gland. The parathyroid glands make parathyroid hormone (PTH or parathormone). PTH helps the body use and store calcium to keep the calcium in the blood at normal levels.
Thyroid cancer is a disease that you get when abnormal cells begin to grow in your thyroid gland . The thyroid gland is shaped like a butterfly and is located in the front of your neck. It makes hormones that regulate the way your body uses energy and that help your body work normally.
Multiple endocrine neoplasia is a group of disorders that affect the body's network of hormone-producing glands (the endocrine system). Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream and regulate the function of cells and tissues throughout the body. Multiple endocrine neoplasia typically involves tumors (neoplasia) in at least two endocrine glands; tumors can also develop in other organs and tissues. These growths can be noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). If the tumors become cancerous, the condition can be life-threatening.
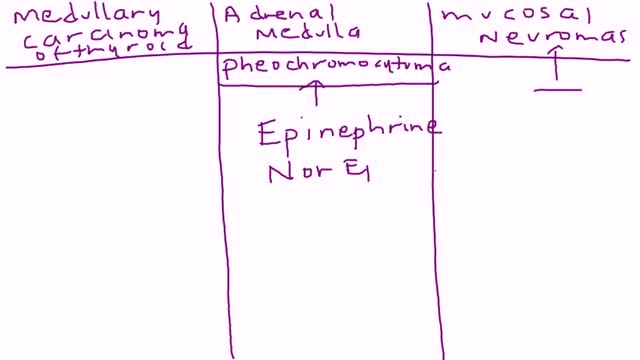
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN2) is a hereditary condition associated with three primary types of tumors: medullary thyroid cancer, parathyroid tumors, and pheochromocytoma. MEN2 is classified into three subtypes based on clinical features. MEN2A, which affects 60% to 90% of MEN2 families Medullary thyroid cancer: 98% to 100% with MEN2A are affected Pheochromocytoma, a typically benign (noncancerous) tumor of the adrenal glands: 50% with MEN2A affected Parathyroid adenoma (benign tumor) or hyperplasia, meaning increased size, of the parathyroid gland: 5% to 10% with MEN2A affected MEN2B, which affects 5% of MEN2 families Medullary thyroid cancer: 98% to 100% with MEN2B affected Pheochromocytoma: 50% with MEN2B affected Mucosal neuromas, which is a benign tumor of nerve tissue on the tongue, lips and throughout the gastrointestinal tract: 95% to 98% affected Digestive problems caused by disordered nerves in the gastrointestinal tract: 75% to 90% affected Muscle, joint, and spinal problems: 95% affected Typical facial features, including swollen lips and thick eyelids: 75% to 90% affected Familial medullary thyroid cancer (FMTC), which affects 5% to 35% of MEN2 families Medullary thyroid carcinoma only Sources: Gagel RF, Marx SJ. “Multiple endocrine neoplasia.” Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, Chapter 40, 11th ed., Philadelphia, 2008, and Eng C, Clayton D, et al. Grubbs EG, Gagel RF. My, How Things Have Changed in Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2A! J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(7):2532-5, 7/2015. PMID: 26151398. What causes MEN2? MEN2 is a genetic condition. This means that the cancer risk and other features of MEN2 can be passed from generation to generation in a family. The gene associated with MEN2 is called RET. A mutation (alteration) in the RET gene gives a person an increased risk of developing medullary thyroid cancer and other tumors associated with MEN2.