Latest videos
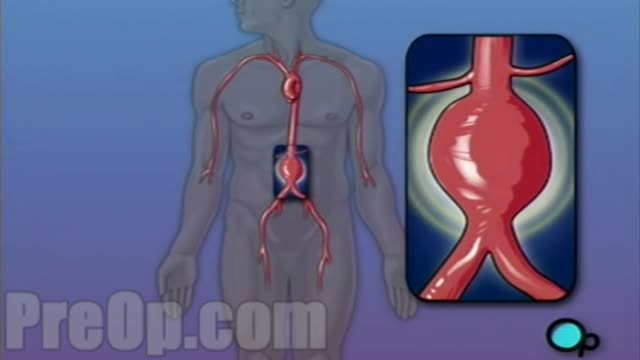
Indications for intervention in patients with a renal artery aneurysm (RAA) include the following [20, 8, 13, 14] : Rupture Symptomatic RAA - Hypertension (from associated renal artery stenosis, refractory to medical management), pain, renal ischemia or infarction secondary to embolization from the aneurysm sac RAAs in females who are pregnant or are contemplating pregnancy Diameter greater than 2 cm Enlarging RAA RAA associated with acute dissection Currently, there is no consensus regarding the size at which an RAA should be repaired in an asymptomatic patient. Experts have recommended RAA repair at diameters ranging from 1.5 to 3 cm, [8] though most suggest 2 cm. Some reports have even suggest that larger asymptomatic saccular aneurysms may be managed expectantly. Note that aneurysm rupture at a diameter of 1.5 cm has been reported. Complete calcification of the wall of the aneurysm sac manifests in about 40% of patients. This was once believed to confer protection against rupture [21] ; however, this belief has since been questioned. [30] Asymptomatic, small (<2 cm in diameter) RAAs do not usually require treatment. One notable exception is an RAA in a woman who is pregnant or contemplating pregnancy. In view of the increased risk of rupture in such cases, even small asymptomatic aneurysms should be repaired in this population. For diagnosis and preinterventional planning, gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and computed tomography (CT) angiography (CTA) with three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction have essentially replaced conventional arteriography. Regular follow-up examination with ultrasonography (US) or CT) is recommended in patients who are treated expectantly. Spontaneous cure by thrombosis of small aneurysms has been described. Further refinements in endovascular techniques may allow more RAAs to be treated in this manner. So far, excellent short- and intermediate-term results have been described in the literature [40] ; however, there remains a need for further long-term outcome data.
Renal artery stenosis is the narrowing of one or more arteries that carry blood to your kidneys (renal arteries). Narrowing of the arteries prevents normal amounts of oxygen-rich blood from reaching your kidneys. Your kidneys need adequate blood flow to help filter waste products and remove excess fluids. Reduced blood flow may increase blood pressure in your whole body (systemic blood pressure) and injure kidney tissue.
Gastric Bypass Surgery - Maagverkleining - Weight Loss Surgery - WLS
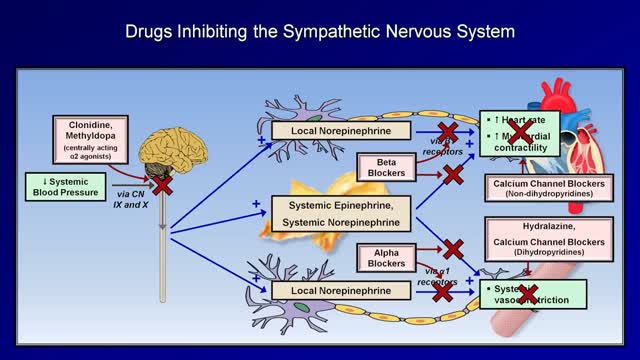
Medications to treat high blood pressure Thiazide diuretics. ... Beta blockers. ... Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. ... Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). ... Calcium channel blockers. ... Renin inhibitors
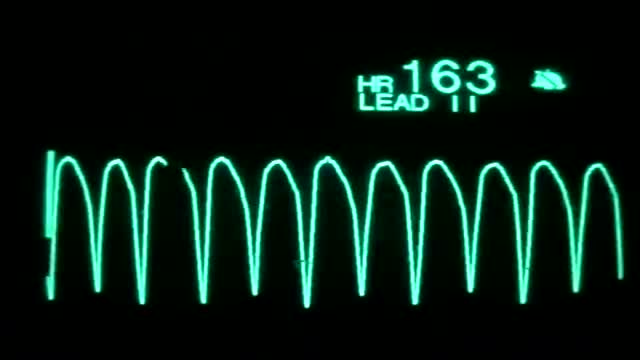
On the rhythm strip, the QRS might be somewhat taller or wider. One commonly seen type of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is torsades de pointes. Torsades and other polymorphic VT are advanced rhythms which require additional expertise and expert consultation is advised.
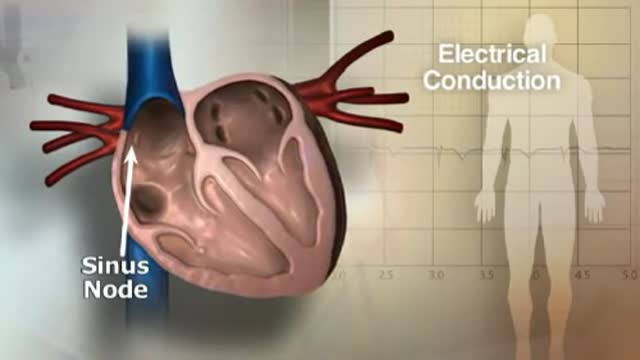
If you or someone you love has atrial fibrillation, learn more about what AFib is, why treatment can save lives, and what you can do to reach your goals, lower your risks and live a healthy life.
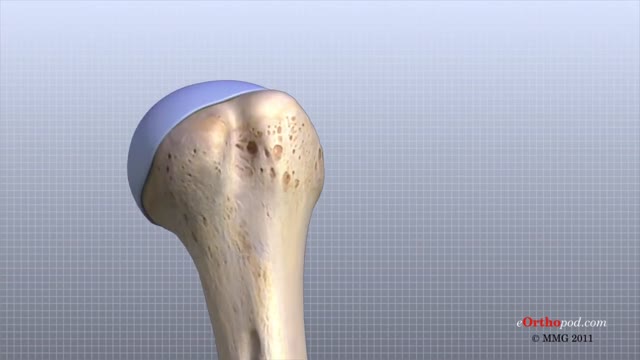
The shoulder joint is formed where the humerus (upper arm bone) fits into the scapula (shoulder blade), like a ball and socket. Other important bones in the shoulder include: The acromion is a bony projection off the scapula. The clavicle (collarbone) meets the acromion in the acromioclavicular joint.
Shoulder impingement syndrome, also called subacromial impingement, painful arc syndrome, supraspinatus syndrome, swimmer's shoulder, and thrower's shoulder, is a clinical syndrome which occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles become irritated and inflamed as they pass through the subacromial space ...
Treatment may include: Rest. Ice or heat. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications. Strengthening exercises. Ultrasound therapy. Corticosteroid injection. Surgery (for severe injuries)
Inner Workings tells the story of the ceaseless pull of the human heart — even as it works against the very stoic realism of the brain.
For this surgery, your doctor makes a large incision in the abdomen to expose the aorta. Once he or she has opened the abdomen, a graft can be used to repair the aneurysm. Open repair remains the standard procedure for an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR).
The management of acute ischemic stroke has advanced greatly over the past 2 decades. New interventions, including intravenous and endovascular treatment strategies, have evolved to recanalize arteries and salvage the ischemic brain. The evolution of interventional approaches to the treatment of acute stroke has been prompted by the limitations of intravenous therapy and intended to extend the treatment window, improve recanalization rates, and subsequently long-term clinical outcomes. The major techniques that have defined the current field of interventional acute stroke management and the relevant past and current data, and ongoing clinical trials on interventional stroke therapy will be reviewed. New issues, such as futile recanalization, and time to microcatheter, will also be discussed.
Interventional Nephrology is a new and emerging subspecialty of Nephrology that mainly deals with ultrasonography of kidneys and ultrasound-guided renal biopsy, insertion of peritoneal dialysis catheters, tunneled dialysis catheters as a vascular access for patients undergoing hemodialysis as well as percutaneous ...
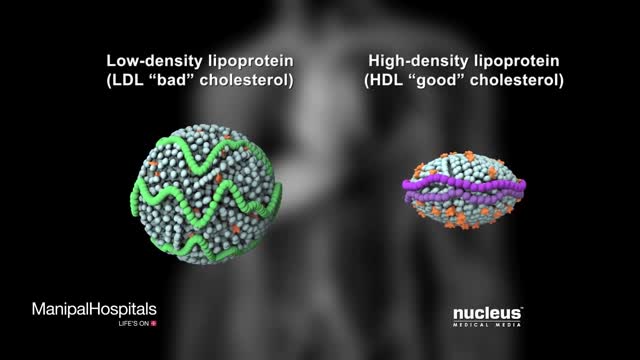
High cholesterol, or dyslipidemia, means that there is an imbalance of fats (lipids), circulating in your blood stream. Cholesterol is a fatty substance your body uses to make hormones and metabolize food.
Tension pneumothorax describes the progressive accumulation of air in the pleural cavity (normally a potential space) through a defect in the visceral pleura. This leads to positive pressure being maintained and increasing throughout the respiratory cycle causing vessels within the mediastinum to be compressed with catastrophic consequences if left untreated. Clinical signs include hypoxia, hypotension, tachycardia, reduced breath sounds and hyper resonance ipsilaterally, with tracheal deviation (away from the affected side) and distended neck veins being late clinical signs.
Thoracentesis (THOR-ah-sen-TE-sis) is a procedure to remove excess fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest wall. This space is called the pleural space. Normally, the pleural space is filled with a small amount of fluid—about 4 teaspoons full.
Paracentesis is a procedure to take out fluid that has collected in the belly (peritoneal fluid). This fluid buildup is called ascites . Ascites may be caused by infection, inflammation, an injury, or other conditions, such as cirrhosis or cancer. The fluid is taken out using a long, thin needle put through the belly.
A spider nevus is a collection of small, dilated arterioles (blood vessels) clustered very close to the surface of the skin. The cluster of vessels is web-like, with a central spot and radiating vessels.
Varicose veins are caused by weakened valves and veins in your legs. Normally, one-way valves in your veins keep blood flowing from your legs up toward your heart. When these valves do not work as they should, blood collects in your legs, and pressure builds up. The veins become weak, large, and twisted.
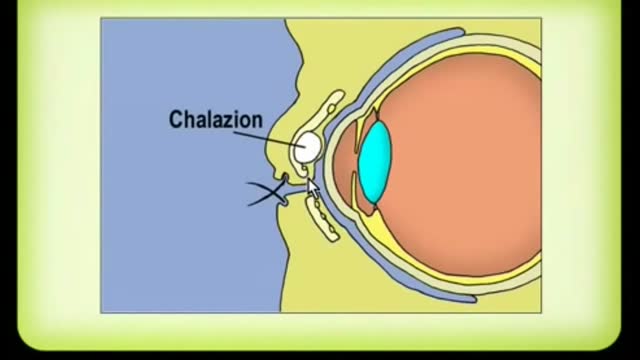
A chalazion is a lump of the lid that is caused by obstruction of the drainage duct of an oil gland within the upper or lower eyelid. This lump may increase in size over days to weeks and may occasionally become red, warm, or painful.