Latest videos

New Minimally Invasive Procedure with No Pain or Downtime… From Dr. Michael Goodman, Caring For Women Wellness Center Laser Vaginal Tightening for Improved Sexual Pleasure and Relief from Minimal Urinary Incontinence Laser Vaginal Therapy for reversing Vaginal Atrophy (Good also for Breast Cancer Survivors with Vaginal Atrophy)

To get started, you need to find your pelvic floor muscles by stopping urination in midstream. If you succeed, you have located the right muscles. Once you have located your pelvic floor muscles, tighten the contraction for about 5 seconds, before relaxing for another 5 seconds.

The vagina is the most delicate and sensitive part of every woman’s body. Naturally female vagina appears to be darker compared to the complexion of other parts of the body. Hence, it is every woman’s dream to have a white complexioned vagina just like their body skin. Most of the women feel that using shop every day may keep their vagina clean and help to make it lighter. But reality is just the opposite. Soaps contain harsh chemicals which not only irritate the delicate skin of vagina and make it darker but they also dis-balance the ph level which plays an important role in maintaining the normal texture of the skin. Well, women need not get disappointed as now there are alternatives of harsh soaps in the market. These alternatives are none other than natural creams which are the best solution to have a naturally fair and glowing vagina without any side effects. Mentioned below are some of the best natural products available in the market to whiten vagina naturally.

Uterine rupture is usually when the scar from your previous caesarean section tears open. Though it's uncommon, you should be aware of this risk, particularly if you're thinking about giving birth vaginally next time. It's possible for your scar to gape slightly while you're pregnant (scar dehiscence).

In breech position, the baby's bottom is down. There are a few types of breech: Complete breech means the baby is bottom-first, with knees bent. Frank breech means the baby's legs are stretched up, with feet near the head. Footling breech means one leg is lowered over the mother's cervix. You are more likely to have a breech baby if you: Go into early labor Have an abnormally shaped uterus, fibroids, or too much amniotic fluid Have more than one baby in your womb Have placenta previa (when the placenta is on the lower part of the uterine wall, blocking the cervix)

The AutoPulse® Resuscitation System provides high-quality automated CPR to victims of sudden cardiac arrest. Easy to use and battery operated, the AutoPulse squeezes the patient’s entire chest to improve blood flow to the heart and brain.1,2,3 The only device of its kind, the AutoPulse automatically sizes to the patient, and has shown improved outcomes in numerous clinical trials.4,5 Designed for Patient Movement and Transport When the AutoPulse’s stabilizing board is placed on a soft stretcher, rescuers can continue providing high-quality CPR down steep stairwells, around sharp corners, or even in a cramped elevator. Compared with manual CPR, the AutoPulse has been shown to reduce interruptions in compressions during transport by more than 85%.6 The AutoPulse is made for resuscitation on the move.

Cardiac arrest is the abrupt loss of heart function in a person who may or may not have diagnosed heart disease. The time and mode of death are unexpected. It occurs instantly or shortly after symptoms appear. Each year, more than 350,000 emergency medical services-assessed out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occur in the United States

The preferred route of access for temporary transvenous pacing is the internal jugular vein followed by subclavian and femoral veins. However, all the major venous access sites (internal and external jugular, subclavian, brachial, femoral) have been used and each is associated with particular problems.
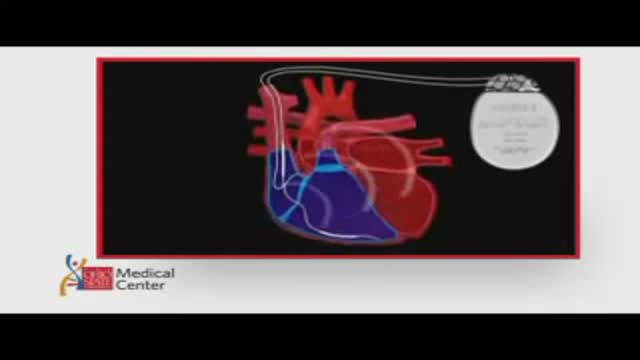
ICDs are useful in preventing sudden death in patients with known, sustained ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation. Studies have shown ICDs to have a role in preventing cardiac arrest in high-risk patients who haven't had, but are at risk for, life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias. View an animation of an ICD. Newer-generation ICDs may have a dual function which includes the ability to serve as a pacemaker. The pacemaker feature would stimulate the heart to beat if the heart rate is detected to be too slow. What is an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)? An ICD is a battery-powered device placed under the skin that keeps track of your heart rate. Thin wires connect the ICD to your heart. If an abnormal heart rhythm is detected the device will deliver an electric shock to restore a normal heartbeat if your heart is beating chaotically and much too fast. ICDs have been very useful in preventing sudden death in patients with known, sustained ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation. Studies have shown that they may have a role in preventing cardiac arrest in high-risk patients who haven't had, but are at risk for, life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
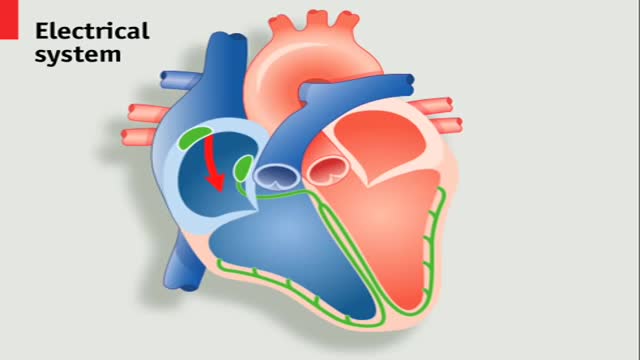
A pacemaker is a small device that's placed in the chest or abdomen to help control abnormal heart rhythms. This device uses electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat at a normal rate. Pacemakers are used to treat arrhythmias (ah-RITH-me-ahs). Arrhythmias are problems with the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat.Feb 28, 2012
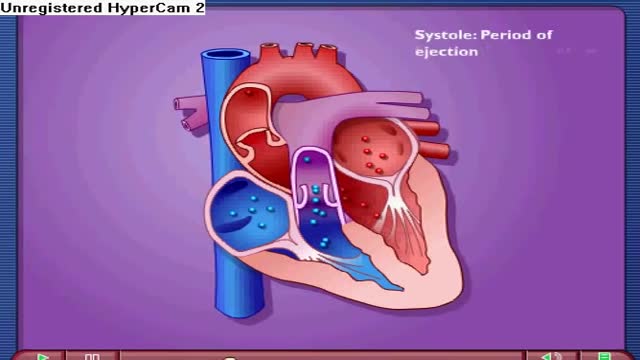
Near the end of diastole, the ventricles nearly fill with blood, and then the atria contract, adding even more volume to the ventricles. The volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole is referred to as the end-diastolic volume. The other phase of the cardiac cycle is called systole.
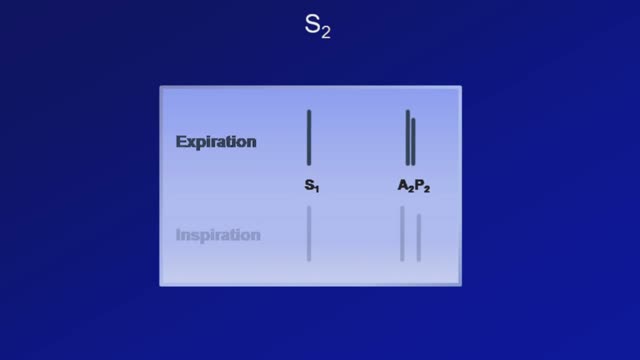
Heart sounds are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it. Specifically, the sounds reflect the turbulence created when the heart valves snap shut. In cardiac auscultation, an examiner may use a stethoscope to listen for these unique and distinct sounds that provide important auditory data regarding the condition of the heart. In healthy adults, there are two normal heart sounds often described as a lub and a dub (or dup), that occur in sequence with each heartbeat. These are the first heart sound (S1) and second heart sound (S2), produced by the closing of the atrioventricular valves and semilunar valves, respectively. In addition to these normal sounds, a variety of other sounds may be present including heart murmurs, adventitious sounds, and gallop rhythms S3 and S4.