Latest videos
Psychological testing refers to the administration of psychological tests. A psychological test is "an objective and standardized measure of a sample of behavior" (p. 4). The term sample of behavior refers to an individual's performance on tasks that have usually been prescribed beforehand.
Hoover's sign of leg paresis is one of two signs named for Charles Franklin Hoover. It is a maneuver aimed to separate organic from non-organic paresis of the leg. The sign relies on the principle of synergistic contraction. ... Feeling this would indicate an organic cause of the paresis.
Conversion disorder, also called functional neurological symptom disorder, is a condition in which you show psychological stress in physical ways. The condition was so named to describe a health problem that starts as a mental or emotional crisis — a scary or stressful incident of some kind — and converts to a physical problem.
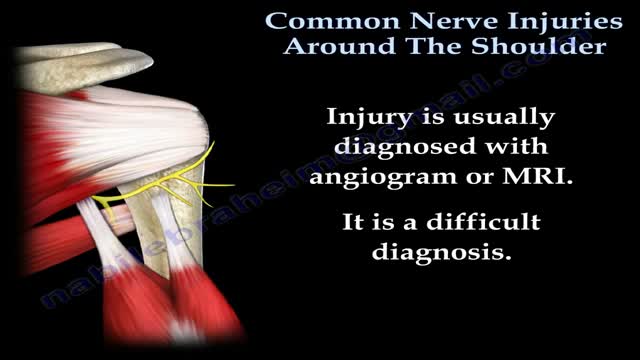
The shoulder and arm receives its nerve supply through the brachial plexus. The brachial plexus is a complex network of nerves which come out of the neck, passes down to the front of the shoulder and then splits into many separate nerves to travel to different muscles and parts of the skin. Normally an arm movement is produced by initially thinking of the movement, then a message passes from the brain, down through the spinal cord to the appropriate nerve. Then the instruction to move is conveyed along the nerve to the specific arm muscle which then contracts and moves the arm.
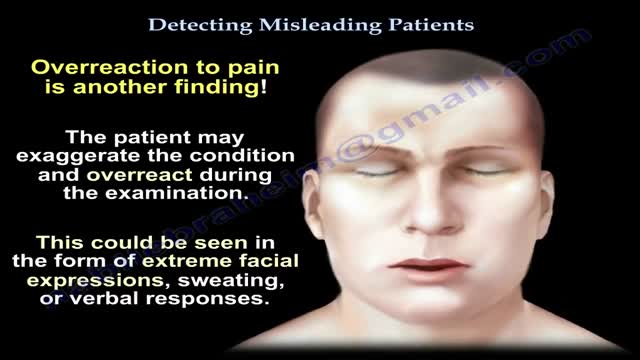
Factitious disorder is the term used to describe a pattern of behavior centered on the exaggeration or outright falsifications of one’s own health problems or health problems of others. Some people with this disorder fake or exaggerate physical problems; others fake or exaggerate psychological problems or a combination of physical and psychological problems. Factitious disorder differs from a pattern of falsified or exaggerated behavior called malingering. While malingerers make their claims out of a motivation for personal gain, people with factitious disorder have no such motivation.
Factitious disorder is the term used to describe a pattern of behavior centered on the exaggeration or outright falsifications of one’s own health problems or the health problems of others. Some people with this disorder fake or exaggerate physical problems; others fake or exaggerate psychological problems or a combination of physical and psychological problems. Factitious disorder differs from a pattern of falsified or exaggerated behavior called malingering. While malingerers make their claims out of a motivation for personal gain, people with factitious disorder have no such motivation.
Depression (major depressive disorder or clinical depression) is a common but serious mood disorder. It causes severe symptoms that affect how you feel, think, and handle daily activities, such as sleeping, eating, or working. To be diagnosed with depression, the symptoms must be present for at least two weeks.
People with panic disorder have sudden and repeated attacks of fear that last for several minutes or longer. These are called panic attacks. Panic attacks are characterized by a fear of disaster or of losing control even when there is no real danger. A person may also have a strong physical reaction during a panic attack. It may feel like having a heart attack. Panic attacks can occur at any time, and many people with panic disorder worry about and dread the possibility of having another attack.
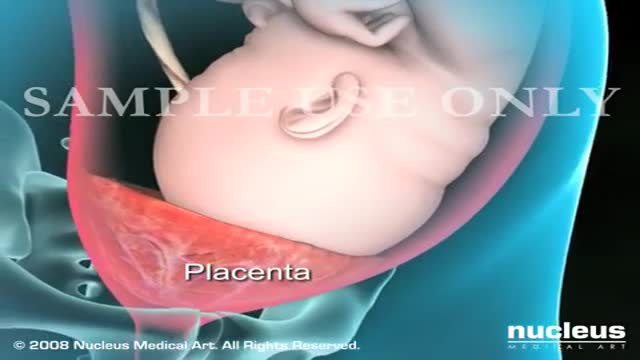
A Cesarean section (C-section) is surgery to deliver a baby. The baby is taken out through the mother's abdomen. In the United States, almost one in three women has their babies this way. Some C-sections are planned, but many are done when unexpected problems happen during delivery. Reasons for a C-section may include
Zip Surgical Skin Closure
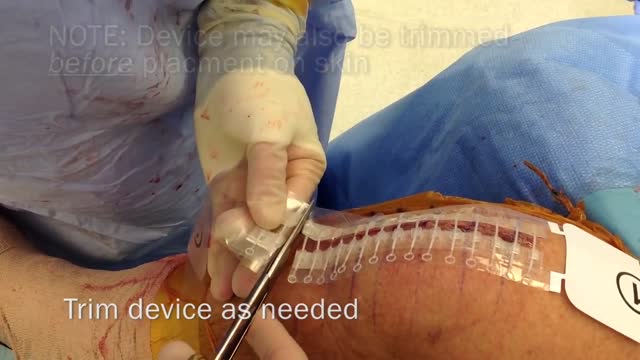
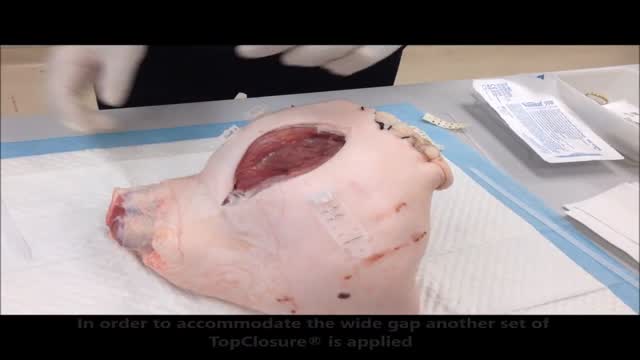
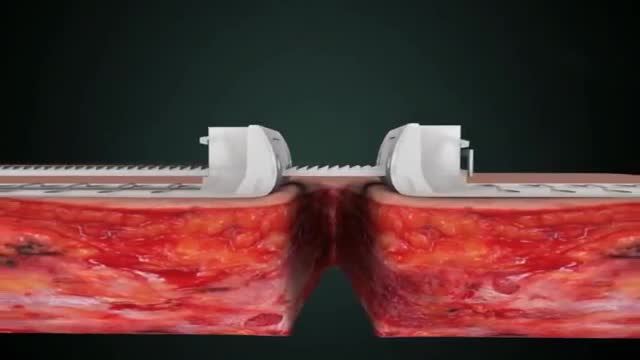
Stress-relaxation is a well-established mechanism for laboratory skin stretching, with limited clinical application in conventional suturing techniques due to the inherent, concomitant induction of ischemia, necrosis and subsequent suture failure. Skin defects that cannot be primarily closed are a common difficulty during reconstructive surgery. The TopClosure tension-relief system (TRS) is a novel device for wound closure closure, providing secured attachment to the skin through a wide area of attachment, in an adjustable manner, enabling primary closure of medium to large skin defects. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficiency of the TopClosure TRS as a substitute for skin grafting and flaps for primary closure of large soft tissue defects by stress-relaxation. We present three demonstrative cases requiring resection of large to huge tumors customarily requiring closure by skin graft or flaps. TRS was applied during surgery serving as a tension-relief platform for tension sutures, to enable primary skin-defect closure by cycling of stress-relaxation, and following surgery as skin-secure system until complete wound closure. All skin defects ranging from 7 to 26 cm in width were manipulated by the TRS through stress-relaxation, without undermining of skin, enabling primary skin closure and eliminating the need for skin grafts and flaps. Immediate wound closure ranged 26 to 135 min. TRS was applied for 3 to 4 weeks. Complications were minimal and donor site morbidity was eliminated. Surgical time, hospital stay and costs were reduced and wound aesthetics were improved. In this case series we present a novel technology that enables the utilization of the viscoelastic properties of the skin to an extreme level, extending the limits of primary wound closure by the stress-relaxation principle. This is achieved via a simple device application that may aid immediate primary wound closure and downgrade the complexity of surgical procedures for a wide range of applications on a global scale.
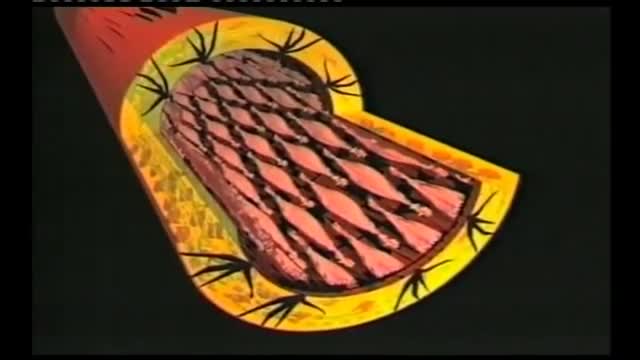
Wound closure techniques have evolved from the earliest development of suturing materials to comprise resources that include synthetic sutures, absorbables, staples, tapes, and adhesive compounds. The engineering of sutures in synthetic material along with standardization of traditional materials (eg, catgut, silk) has made for superior aesthetic results. Similarly, the creation of topical skin adhesives (the monomer 2-octyl cyanoacrylate), surgical staples, and tapes to substitute for sutures has supplemented the armamentarium of wound closure techniques. Aesthetic closure of a wound, whether traumatic or surgically induced, is based on knowledge of healing mechanisms and skin anatomy (see the image below), as well as an appreciation of suture material and closure technique. Choosing the proper materials and wound closure technique ensures optimal healing.[1]
Instructional Video - Cardiovascular disease
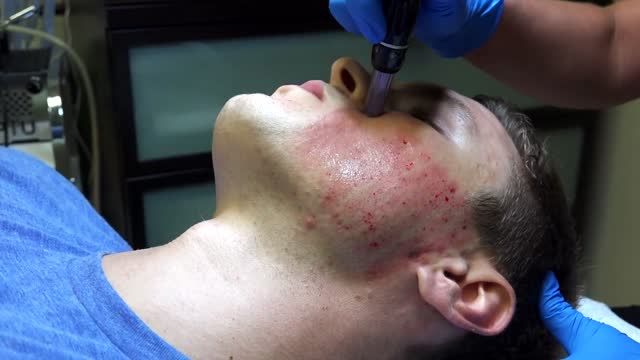
Well, That Was Bloody | My Acne Scar Surgery (DermaPen)
Fremale to male gender reassignment surgery
Before Dr. Benjamin Carson became the first person to successfully separate twins conjoined at the head, before he had a TV movie made about his life, before he became known for his "gifted hands" and before he became head of pediatric neurosurgery at Johns Hopkins, Ben Carson was headed down the wrong path in life.
A pilonidal sinus (PNS) is a small cyst or abscess that occurs in the cleft at the top of the buttocks. A PNS usually contains hair, dirt, and debris. It can cause severe pain and can often become infected. If it becomes infected, it may ooze pus and blood and have a foul odor. A PNS is a condition that mostly affects men and is also common in young adults. It’s also more common in people who sit a lot, like cab drivers.
A surgeon begins the PPH stapled hemorrhoidectomy by inserting a circular anal dilator and obturator into the anal canal and then securing the dilator in place with four sutures. The surgeon then inserts a PPH anoscope into the obturator. Next, he places a circumferential purse-string suture of 2-0 Monocryl on a UR-6 needle 4 cm proximal to the dentate line. The surgeon opens a PPH stapler and places its anvil across the purse string. The stapler is then closed and fired; it is held closed for two minutes to improve hemostasis. Prior to firing the stapler in a female patient, the surgeon places a gloved finger in the vagina to ensure the vaginal mucosa and rectal-vaginal septum are not trapped within the jaws of the closed stapler. The surgeon then opens and removes the stapler.
HYSTERECTOMY RECOVERY: ALL PROCEDURES ARE NOT CREATED EQUAL Too often, women are only given the option of an open hysterectomy for conditions like large fibroids or an enlarged uterus. Surgical techniques have evolved in the last decade, but across the United States, the number of women still having open hysterectomy procedures is unnecessarily staggering. Robotic procedures are becoming more common as hospitals invest nearly $2 million in the machine. While the robot does allow surgeons who are not necessarily trained in laparoscopic procedures to perform a more minimally invasive surgery, tools cannot replace skill. There is no added benefit to the patient and the surgery can cost on average up to $2,000 more than other laparoscopic options, and in some cases much higher.
Ganglion cysts are noncancerous lumps that most commonly develop along the tendons or joints of your wrists or hands. They also may occur in the ankles and feet. Ganglion cysts are typically round or oval and are filled with a jellylike fluid. Small ganglion cysts can be pea-sized, while larger ones can be around an inch (2.5 centimeters) in diameter. Ganglion cysts can be painful if they press on a nearby nerve. Their location can sometimes interfere with joint movement. If your ganglion cyst is causing you problems, your doctor may suggest trying to drain the cyst with a needle. Removing the cyst surgically also is an option. But if you have no symptoms, no treatment is necessary. In many cases, the cysts go away on their own.