Latest videos

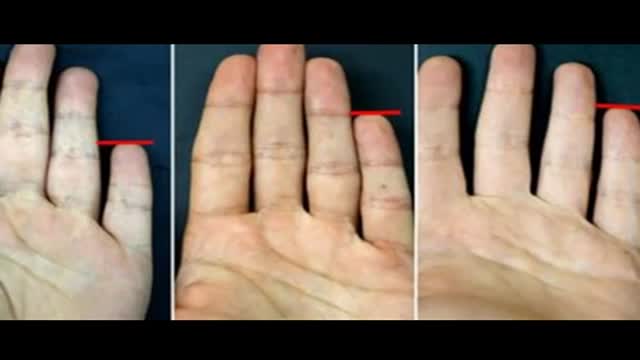
A Hundred Orgasms A Day follow the story of 3 women who were tormented every hour of everyday with the need to have orgasm. This documentary explain how Persistent Sexual Arousal Syndrome or PSAS causes this unusual condition. PSAS is a little know neurological disorder where women have symptoms of continuous uncontrollable genital arousal. This condition is unrelated to any kind of sensations of sexual desire. PSAS was initially documented by Doctor Sandra Leiblum in mid 2001, just recently recognized as a unique syndrome in medical science which has a comparable equivalent progressively more claimed by men. A few physicians makes use of the name Persistent Sexual Arousal Syndrome to reference the disorder in women; some others look at the syndrome of priapism in adult males to be a similar disorder. Most importantly, it is really not connected with hyper-sexuality, also known as nymphomania. Both hyper-sexuality, and nymphomania are not known diagnosable health conditions. Not only is it very rare, the disorder is also seldom reported by affected individual who may think it is embarrassing.

Inflammation of the uvula is known as uvulitis. Your uvula will appear red, puffy, and larger than normal. Other symptoms of uvulitis may include: itching burning a sore throat spots on your throat snoring difficulty swallowing trouble breathing If you have a swollen uvula along with a fever or abdominal pain, consult with your doctor right away. In rare cases, the uvula can swell enough to block your airway. Swelling of the throat is a life-threatening event. If this happens, seek immediate medical attention. What causes a swollen uvula? Causes Inflammation is your body’s response when it’s under attack. Triggers for inflammation include: environmental and lifestyle factors an infection trauma genetics Environmental and Lifestyle Factors The most common food allergies are peanuts tree nuts milk eggs wheat soy fish, including shellfish You could be having an allergic reaction to something you touched, swallowed, or breathed in. Some common allergens include: food irritants , such as dust, animal dander, or pollen medication exposure to chemicals or other toxic substances, including tobacco Infection You can get viral infections or bacterial infections. Examples of viral infections include: the common cold the flu mononucleosis chickenpox measles croup The most common bacterial infection is strep throat, which occurs due to Streptococcus pyogenes, which is a type of group A Streptococcus. If you have infected tonsils, or tonsillitis, severe inflammation can cause them to push against and irritate your uvula. Trauma Trauma to the uvula can happen if you need an intubation, such as during surgery. Your uvula can also be injured during a tonsillectomy. This is a procedure to remove your tonsils, which are located on both sides of your uvula. Your throat and uvula can also become irritated if you have acid reflux disease or if you vomit frequently. Genetics A condition called hereditary angioedema (HAE) can cause swelling of the uvula and throat, as well as swelling of the face, hands, and feet. Other symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. It’s an uncommon genetic mutation that occurs in 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 50,000 people. It’s rare, but there are case reports of individuals who have an elongated uvula, which can also interfere with breathing. What are the risk factors for a swollen uvula? Risk Factors Anyone can get uvulitis, but adults get it less often than children do. You’re at increased risk if you: have allergies use tobacco products are exposed to chemicals and other irritants in the environment have a weakened immune system, making you more susceptible to infections How is a swollen uvula diagnosed? Diagnosis If you have fever or swelling of your throat, see your doctor. Be prepared to give a complete medical history. Tell your doctor: about all the over-the-counter and prescription medications you take if you’re a smoker or you chew tobacco if you’ve recently tried new foods if you’ve been exposed to chemicals or unusual substances about your other symptoms, such as abdominal pain, fever, or dehydration Your doctor may be able to make a diagnosis through a physical exam. It’s likely you’ll also need a throat swab to evaluate for strep or to obtain secretions for culture to determine if you have another bacterial or fungal infection. This test is known as the rapid strep test. You may also need a nasal swab to test for influenza. Blood testing can help identify or rule out some other infectious agents. If those tests are inconclusive, you may need to see an allergist. Blood and skin tests can help identify foods or other substances that cause a reaction. Learn more: Allergy testing » If necessary, imaging tests can provide a more detailed view of your throat and the surrounding area. What’s the treatment for a swollen uvula? Treatment When you have something like the common cold, swelling usually clears up on its own without treatment. Otherwise, treatment will depend on how severe your symptoms are, as well as what’s causing the inflammation. Infection Viral infections tend to clear up without treatment. The only upper respiratory infection for which an antiviral medication is available is influenza. Antibiotics can treat bacterial infections. Even after symptoms clear up, take all the medication as prescribed. If your condition may be contagious, stay home until your doctor tells you that you’re no longer at risk of spreading it to others. Allergy If you test positive for an allergy, try to avoid the allergen in the future. Doctors usually treat allergies with antihistamines or steroids. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction. Doctors use epinephrine to treat this reaction. Hereditary angioedema Your doctor may treat HAE with any of the following: anabolic steroids, or androgens antifibrinolytics C1 inhibitors, such as C1 esterase inhibitor (Berinert) or C1 esterase inhibitor (recombinant) (Ruconest) a plasma kallikrein inhibitor, such as ecallantide (Kalbitor) bradykinin receptor antagonist, such as icatibant injection (Firazyr) Tell your doctor if you have new or worsening symptoms, and follow up as necessary. Tips for relief home treatment If you have a swollen uvula or sore throat, it’s your body’s way of telling you that something is wrong. A few home remedies can help keep you strong and soothe your irritated throat. Make sure you’re getting enough fluids. If your throat hurts when you drink, try drinking small amounts throughout the day. Your urine should be light in color. If it’s dark yellow or brown, you’re not drinking enough and may be dehydrated. Additional tips include the following: Cool your throat by sucking on ice chips. Frozen juice bars or ice cream may also do the trick. Gargle with warm salt water to ease your dry, scratchy throat. Aim for a full night’s sleep, and nap during the day if you can. What’s the outlook? Outlook A swollen uvula isn’t a common occurrence. Most of the time it clears up without treatment. If you have an infection, prompt treatment should take care of the problem within a week or two. If you have allergies that lead to swelling of the uvula or throat, do your best to avoid that allergen. You should also be prepared to deal with an attack if you come into contact with the substance again. If you’ve ever had anaphylaxis, ask your doctor if you should carry injectable epinephrine (EpiPen) in case of emergency. People with HAE must learn to recognize triggers and early warning signs of an attack. Talk to your doctor about how to manage HAE. Article Resources Was this article helpful?Yes No Share Tweet Email Print Read This Next 9-Month-Old Baby: Developmental Milestones and Guidelines 9-Month-Old Baby: Developmental Milestones and Guidelines Read More » All of the ‘Firsts’ That Come with Breast-Feeding All of the ‘Firsts’ That Come with Breast-Feeding Read More » 5 Types of Health Professionals You Should Know About 5 Types of Health Professionals You Should Know About Read More » What’s the Difference Between a Fracture and a Break? What’s the Difference Between a Fracture and a Break? Read More » Is Corn a Vegetable? Is Corn a Vegetable? Read More » Advertisement Advertisement Advertisement

Strep throat is a bacterial infection that can make your throat feel sore and scratchy. Strep throat accounts for only a small portion of sore throats. If untreated, strep throat can cause complications, such as kidney inflammation or rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever can lead to painful and inflamed joints, a specific type of rash or heart valve damage. Strep throat is most common in children, but it affects people of all ages. If you or your child has signs or symptoms of strep throat, see your doctor for prompt testing and treatment.

Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the body lacks sufficient thyroid hormone. Since the main purpose of thyroid hormone is to "run the body's metabolism," it is understandable that people with this condition will have symptoms associated with a slow metabolism. The estimates vary, but approximately 10 million Americans have this common medical condition. In fact, as many as 10% of women may have some degree of thyroid hormone deficiency. Hypothyroidism is more common than you would believe, and millions of people are currently hypothyroid and don't know it.
Although most women have had enough experience to know how to pleasure a man in the bedroom, but you can be sure that are several girls who would be virgins when you first take them to bed. Though most Indian men actually prefer to make love with a virgin. There are also numerous men who dislike the idea due to the pressure of making love to someone with no experience. So if you happen to be dating a virgin then there are a few important things that you should always keep in mind when you take her to bed. Though you have made love to different women before, you need to understand that this one being a virgin will know little or nothing about what is expected of her in bed. Because she will be anxious and nervous, you have to be all the more careful to ensure that she gets to enjoy her first time with you. Kiss her Whether you are doing it with a virgin or someone with a record that would put Pam Anderson to shame, you should take your time to make love to her just with your lips. Use your lips with passion, and kiss her parts that other guys tend to ignore. Kiss her lips, her hips, her shoulders, her hands, nuzzle her ears - parts which aren’t necessary sexual. Give your girl a hand Okay this one may look straight out of a B-grade south Indian movie, but starting off with a sensual full body massage is an excellent way of warming her up. So use some nice aromatic oils like lavender or Yang-Yang to massage her body. If you are more experienced, you would be aware the various erogenous zones of a woman’s body. Start with the nape of her neck and slowly work your way down to her back, gently knead her breasts and play with her nipples, gently flick at them and manipulate them to erection. Get her to lie on her stomach and massage her inner thighs. Lovingly caress her buttocks and move your hands close to her valley of pleasure. She might be too shy to tell you, but her ultimate pleasure point would be dying for your attention. Gently, stroke her outer lips or the labia. Whatever, apprehensions or fears she may have had about sex will all disappear once your finger start creating magic in her nether regions. Never criticise her Remember, she has never felt a man’s body before, which essentially means that when she tries to explore your body you may not necessarily enjoy it. So let her hold your penis and fondle it, let her lick and nibble you and tickle you body. You may not find her amateurish attentions very arousing but don’t make her feel like an amateur in bed. If she does something right let her know how much you are enjoying it. Guide her fingers to your pleasure points and tell her what you would like a girl to do in bed. Being the more experienced partner you should be like her loving mentor, and teach her the intricacies of pleasuring a man. Make her touch herself While she may or may not have masturbated before, by getting her to touch herself you would be able to make her feel the unknown. Tell her how badly you want to see her masturbate. The idea is open her to own sexuality. Its time to penetrate When you think that she is finally ready to be penetrated, enter her as gently as possible. Also make sure that she is producing enough lubrication to facilitate the act. Keep your strokes slow and shallow and avoid pushing too deep during your first few strokes. If you are able to make her feel comfortable and safe, any pain that she may experience in the beginning will soon disappear, and be replaced by moans of ecstasy. The first time can be nerve racking for most men. Just remember how nervous you were when you had sex for the first time. So when your take your virginal girlfriend to bed for first time makes the experience as pleasurable for her as possible.

Thalassemia (thal-uh-SEE-me-uh) is an inherited blood disorder characterized by less hemoglobin and fewer red blood cells in your body than normal. Several types of thalassemia exist, including alpha-thalassemia, beta-thalassemia intermedia, Cooley's anemia and Mediterranean anemia. Hemoglobin is the substance in your red blood cells that allows them to carry oxygen. The low hemoglobin and fewer red blood cells of thalassemia may cause anemia, leaving you fatigued. If you have mild thalassemia, you may not need treatment. But, if you have a more severe form of thalassemia, you may need regular blood transfusions. You can also take steps on your own to cope with fatigue, such as choosing a healthy diet and exercising regularly.
Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder characterized by less hemoglobin and fewer red blood cells in your body than normal. Several types of thalassemia exist, including alpha-thalassemia, beta-thalassemia intermedia, Cooley's anemia and Mediterranean anemia. Hemoglobin is the substance in your red blood cells that allows them to carry oxygen. The low hemoglobin and fewer red blood cells of thalassemia may cause anemia, leaving you fatigued. If you have mild thalassemia, you may not need treatment. But, if you have a more severe form of thalassemia, you may need regular blood transfusions. You can also take steps on your own to cope with fatigue, such as choosing a healthy diet and exercising regularly.

http://123-paleo.info-pro.co Gesunde Ernährung, Ernährung Umstellen, Marcumar Ernährung, Paleo Lebensmittel, Paleo Rezept. Wahrscheinlich wirst du dich als Paleo-Anhänger schon einmal gefragt haben, warum die Steinzeiternährung Getreide meidet wie die Pest. Gut, die Begründung, dass Menschen vor Tausenden von Jahren ebenfalls kein Getreide hatten, ist ja schön. Aber das kann ja nicht alles sein. Ist es auch nicht. Wie immer liegt der Teufel im Detail. Hauptverantwortlich für die große „Angst“ vor Getreideprodukten sind vor allem Gluten, sogenannte Anti-Nährstoffe. Bereits dieser Name ist angsteinflößend. Und das durchaus zu Recht. Denn Gluten besitzen nur wenige positive, dafür jedoch umso mehr negative Eigenschaften, die sich längerfristig schlecht auf deine Gesundheit auswirken können. Was ist Gluten und welche Lebensmittel enthalten Gluten? Gluten ist ein Eiweiß mit besonders starken Klebeeigenschaften. Dies ist auch der Grund, weswegen beispielsweise Brotteig so gut zusammenklebt. Gluten findet sich hauptsächlich in Getreide, beispielsweise ein Roggen oder Gerste, Dinkel oder Weizen und Hafer. Hieraus ergibt sich zwangsläufig, dass auch viele Lebensmittel des täglichen Lebens jede Menge Gluten enthalten. Hierzu gehören nicht nur Schokolade oder Bier, Reis oder Nudeln, sondern auch Pommes oder Milcherzeugnisse. Auch in den meisten Fertiggerichten ist Gluten vorzufinden.

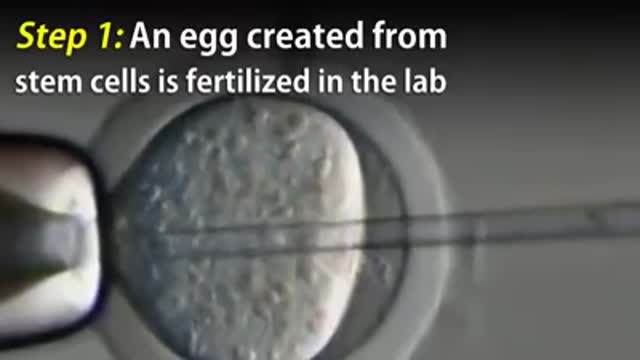
How do you make a working human heart? Scientists can turn stem cells into beating heart cells, but getting them to organize into a 3D heart requires a scaffold. At the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, Harald Ott and his team are reusing the scaffold that nature provides. They’re stripping away all the living cells from dead hearts, before filling in the leftover matrix with healthy new cells. In this video, Brendan Maher finds out how the technique could be used to develop parts of the heart, like the aortic root and valve, for transplant.

In a small but promising Phase II clinical trial of breast cancer treatment, cryoablation killed 25 early-stage tumors in 13 women. The tumors ranged in size from .5 cm (very small) to 5.8 cm (very large), with an average size of 1.7cm. Patients were first given a local anesthesia with mild sedation before physicians used ultrasound with or without computed tomography (CT) imaging to guide needle-like probes to deliver very low temperature gas to the tumor site. The ultra-cold gas forms a ball of ice around the probe tip, then expands and destroys surrounding tumor cells. A harmless saline solution was first injected into the chest wall and skin of the breast to protect the tissue surrounding the tumor from the freezing effects. Patients experienced very little pain and most healed completely within six months with no complications and with little or no scarring. The cryotherapy margins of each participant were biopsied immediately after the procedures, and all were negative, with no evidence of cancerous tissue. All 13 patients were without recurrence at an average of 18 months and up to five years following the procedure. These results are promising, but larger studies with lengthier follow-up are needed to determine whether cryotherapy as effective as lumpectomy. A study involving cryoablation of mouse tumors at the University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center found that the freezing procedure also works like a vaccine, boosting the immune system to reduce the likelihood of recurrence. Just how quickly the tumor was frozen made a difference: a 30-second freeze killed tumors and also boosted the immune system, inhibiting metastases to the lungs. A slower freezing lasting several minutes destroyed tumors just as effectively, but actually suppressed the immune system, resulting in greater metastases to the lungs.

A torn meniscus is one of the most common knee injuries. Any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, especially when putting the pressure of your full weight on it, can lead to a torn meniscus. Each of your knees has two menisci — C-shaped pieces of cartilage that act like a cushion between your shinbone and your thighbone. A torn meniscus causes pain, swelling and stiffness. You also might have trouble extending your knee fully. Conservative treatment — such as rest, ice and medication — is sometimes enough to relieve the pain of a torn meniscus and give the injury time to heal on its own. In other cases, however, a torn meniscus requires surgical repair.
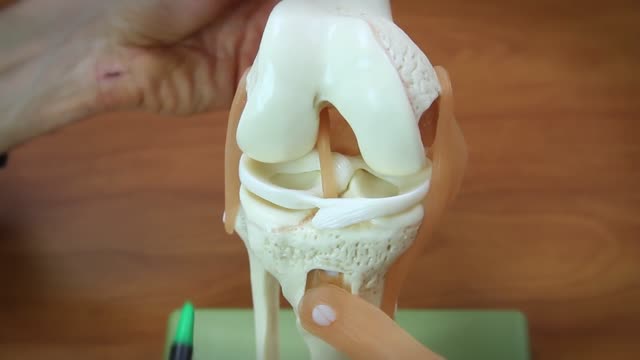
There are many factors that will determine how quickly, or completely you recover from your meniscal tear surgery. Key elements include your age, weight, and activity demands. The older you are, the heavier you are, the longer your recovery will be. The type of surgery you had will also impact upon your recovery. In some cases we only remove the torn piece — in general you will progress faster than someone who had sutures placed to repair the meniscus tear. Whether or not arthritis was found at the time of your meniscus surgery will also significantly influence your recovery from meniscus surgery. If you have arthritis then you are missing some or all of the cartilage on the ends of the bones. Knees with arthritis are prone to being more “cranky” during the recovery process. In those cases, a knee ice compression device can provide relief of pain/swelling. Many patients note they feel better wearing a compression sleeve during recovery. People with arthritis sometimes report improvement in their symptoms with supplements like Glucosamine, Curcumin, or Hyaluronic Acid which they believe (not proven) will smooth out the surface of the joint. Many try Tart Cherry juice because of its natural anti-inflammatory properties.. In the first few months following surgery, a knee compression sleeve does actually help many feel better. Some of the variables affecting your recovery from meniscus surgery are under your surgeon’s control. We can improve your immediate response after surgery with the use of various medications we inject within the knee before the surgery. We can also block a nerve on the side of your leg which will improve your pain for 18-24 hours after surgery. Many of you will purchase a ice compression sleeve to help minimize the pain after the surgery. In general, young, healthy active people with no evidence of osteoarthritis will experience a much more rapid recovery. Typically measured in days or a few weeks. Most people are off crutches in a day, and stop taking pain medicine within a day or two. In contrast, if you are a older, heavier and have arthritis as well as a meniscus tear, then you may take longer to recover — and may not experience a “full” recovery. This group can take weeks to months to improve. To ensure a good response to surgery, we also need to look at your health before surgery. Smoking leads to an increased infection rate and poorer healing. Diabetics with poor sugar control are at higher risk for infection and delays in healing as well. Obesity is a potential problem with anesthesia, the recovery from surgery and it may lead to more rapid progression of arthritis after surgery. The better shape you are in prior to surgery can influence your recovery.
Constipation is a common problem. It means either going to the toilet less often than usual to empty the bowels, or passing hard or painful stools (faeces). Constipation may be caused by not eating enough fibre, or not drinking enough fluids. It can also be a side-effect of certain medicines, or related to an underlying medical condition. In many cases, the cause is not clear. Laxatives are a group of medicines that can treat constipation. Ideally, laxatives should only be used for short periods of time until symptoms ease. Note: there is a separate leaflet on constipation in children. What is constipation? Constipation is common. If you are constipated it causes one or more of the following: Stools (faeces) become hard and difficult or painful to pass. The time between toilet trips increases compared with your usual pattern. (Note: there is a large range of normal bowel habit. Some people normally go to the toilet to pass stools 2-3 times per day. For others, 2-3 times per week is normal. It is a change from your usual pattern that may mean that you are constipated.) Sometimes, crampy pains occur in the lower part of your tummy (abdomen) You may also feel bloated and feel sick if you have severe constipation. What are the causes of constipation? Known causes include the following: Not eating enough fibre (roughage) is a common cause. The average person in the UK eats about 12 g of fibre each day. But, 18 g per day is recommended by the British Nutrition Foundation. Fibre is the part of plant food that is not digested. It remains in your gut. It adds bulk to the stools (faeces) and helps your bowels to work well. Foods high in fibre include fruit, vegetables, cereals and wholemeal bread. Not drinking much may make constipation worse. Stools are usually soft and easily passed if you eat enough fibre and drink enough fluid. However, some people need more fibre and/or fluid than others in order to avoid constipation. Some special slimming diets are low in fibre and may cause constipation. Some medicines can cause constipation as a side-effect. Examples are painkillers (particularly those with codeine, such as co-codamol, or very strong painkillers, such as morphine), some antacids, some antidepressants (including amitriptyline) and iron tablets; however, there are many others. See the list of possible side-effects on the leaflet that comes with any medicine that you may be taking. Tell a doctor if you suspect a medicine is making you constipated. A change of medication may be possible. Various medical conditions can cause constipation. For example, an underactive thyroid gland, irritable bowel syndrome, some gut disorders and conditions that cause poor mobility, particularly in the elderly. Pregnancy. About 1 in 5 pregnant women will become constipated. It is due to the hormonal changes of pregnancy that slow down the gut movements. In later pregnancy, it can simply be due to the baby taking up a lot of room in the tummy and the bowels being pushed to one side.

The key difference between monophasic and biphasic defibrillator is that the monophasic defibrillator is a type of defibrillation waveform where a shock is delivered to the heart from one vector as shown below. Whereas, in biphasic defibrillation, shock is delivered to the heart via two vectors.

Coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG) is a procedure used to treat coronary artery disease. Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the narrowing of the coronary arteries – the blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle. CAD is caused by a build-up of fatty material within the walls of the arteries. This build-up narrows the inside of the arteries, limiting the supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. One way to treat the blocked or narrowed arteries is to bypass the blocked portion of the coronary artery with a piece of a healthy blood vessel from elsewhere in the body. Blood vessels, or grafts, used for the bypass procedure may be pieces of a vein from the legs or an artery in the chest. An artery from the wrist may also be used. One end of the graft is attached above the blockage and the other end is attached below the blockage. Blood is routed around, or bypasses, the blockage by going through the new graft to reach the heart muscle. This is called coronary artery bypass surgery. Traditionally, to bypass the blocked coronary artery, a large incision is made in the chest and the heart is temporarily stopped so that the surgeon can perform the delicate procedure. To open the chest, the breastbone (sternum) is cut in half and spread apart. Once the heart is exposed, tubes are inserted into the heart so that the blood can be pumped through the body by a cardiopulmonary bypass machine (heart-lung machine). The bypass machine is necessary to pump blood while the heart is stopped and kept still in order for the surgeon to perform the bypass operation. While the traditional "open heart" procedure is still commonly done and often preferred in many situations, less invasive techniques have been developed to bypass blocked coronary arteries. "Off-pump" procedures, in which the heart does not have to be stopped, were developed in the 1990's. Other minimally invasive procedures, such as keyhole surgery (performed through very small incisions) and robotic procedures (performed with the aid of a moving mechanical device), may be used.
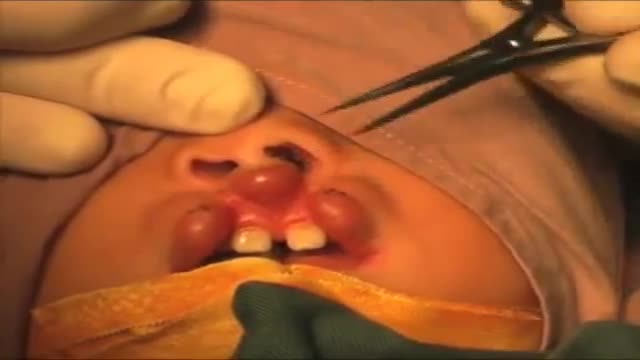
A bilateral complete cleft lip, which has been previously treated with nasoalvoelar molding, is repaired with the Millard-Mulliken technique, which employs reconstruction of the orbicularis oris muscle by advancing bilateral muscular segments. This tutorial for medical professionals was developed to supplement learning of a common surgical technique and is not intended to replace formal surgical training. This slideshow is primarily intended for use on tablets or larger screens. Some detail might be lost on mobile screens.