Latest videos
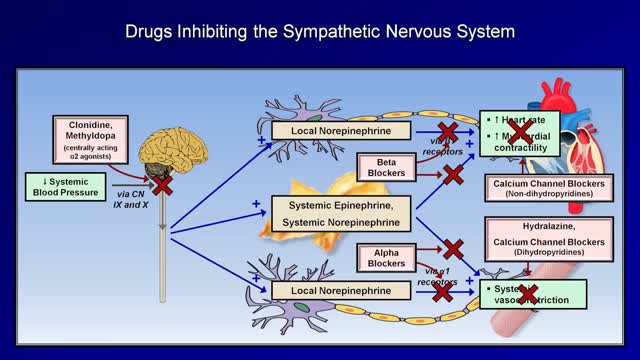
Although drug treatment of hypertension is associated with improved survival and decreased vascular complications, drug compliance is a major problem in the control of hypertension. All antihypertensive medications are associated with side effects; thus, it is a physician's responsibility to explain to each patient the side effects of the drugs he prescribes to treat hypertension, and to instill in the patient a sense of necessity for the treatment of hypertension. The choice of antihypertensive drug should be made based on each patient's lifestyle, overall health and ability to tolerate the drug. Ideally, the antihypertensive regimen should be simple, effective, convenient to take and have very few side effects.
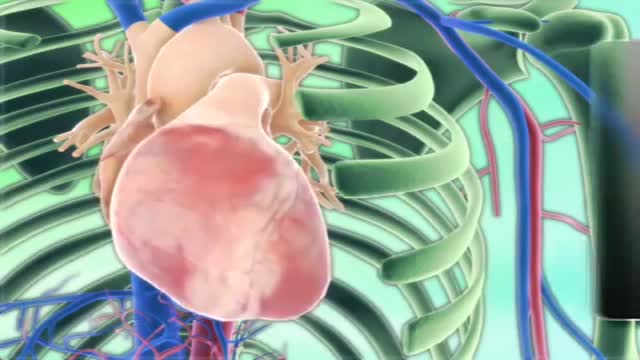
Myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, is defined pathologically as the irreversible death of myocardial cells caused by ischemia. Clinically, MI is a syndrome that can be recognized by a set of symptoms, chest pain being the hallmark of these symptoms in most cases, supported by biochemical laboratory changes, electrocardiographic (ECG) changes, or findings on imaging modalities able to detect myocardial injury and necrosis. According to the third universal definition of MI, implemented by a joint task force from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), American College of Cardiology (ACC) Foundation, American Heart Association (AHA), and the World Heart Federation (WHF), MI is diagnosed when either of the following two criteria are met
Fifth disease is a mild rash illness caused by parvovirus B19. This disease, also called erythema infectiosum, got its name because it was fifth in a list of historical classifications of common skin rash illnesses in children. It is more common in children than adults. A person usually gets sick with fifth disease within 4 to 14 days after getting infected with parvovirus B19.
What causes rheumatic fever? Rheumatic fever is not an infection itself, but rather the result of an untreated strep infection. When your body senses the strep infection, it sends antibodies to fight it. Sometimes, these antibodies attack the tissues of your joints or heart instead. If the antibodies attack your heart, they can cause your heart valves to swell, which can lead to scarring of the valve "doors" (called leaflets or cusps). Who is at risk for rheumatic fever? Fewer than 0.3% of people who have strep throat also get rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever is most common among children aged 5 to 15, but adults may have the condition as well. Doctors think that a weakened immune system may make some people more likely to get rheumatic fever. And, although antibiotic medicines have reduced the number of cases of rheumatic fever in developed countries, there are still thousands of reported cases. What are the symptoms of rheumatic fever and how is it diagnosed? Symptoms of rheumatic fever usually begin 1 to 6 weeks after you have had a strep infection. They are Fever Joint pain or swelling in your wrists, elbows, knees, or ankles Small bumps under the skin over your elbows or knees (called nodules) A raised, red rash on your chest, back, or stomach Stomach pain or feeling less hungry Weakness, shortness of breath, or feeling very tired Your doctor will begin by doing a throat culture to find out if you have a strep infection. Then, your doctor will use a stethoscope to listen to your heart. He or she will also look for nodules on your joints. Sometimes, blood tests, chest x-rays, or an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) may be needed for a more definite diagnosis. How is rheumatic fever treated? Rheumatic fever must be treated right away. If you have a sore throat that lasts longer than 3 days, or if you have a fever and headache along with your sore throat, you should see your doctor for a throat culture. Even if you do not have a sore throat but have a fever and a skin rash, this could also mean a strep infection, and you should get tested. Remember rheumatic fever can result from an untreated strep infection, so it is very important to treat the infection before it leads to a worse condition.
Kawasaki disease is a condition that causes inflammation in the walls of medium-sized arteries throughout the body, including the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle. Kawasaki disease is also called mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome because it also affects lymph nodes, skin, and the mucous membranes inside the mouth, nose and throat. Signs of Kawasaki disease, such as a high fever and peeling skin, can be frightening. The good news is that Kawasaki disease is usually treatable, and most children recover from Kawasaki disease without serious problems.
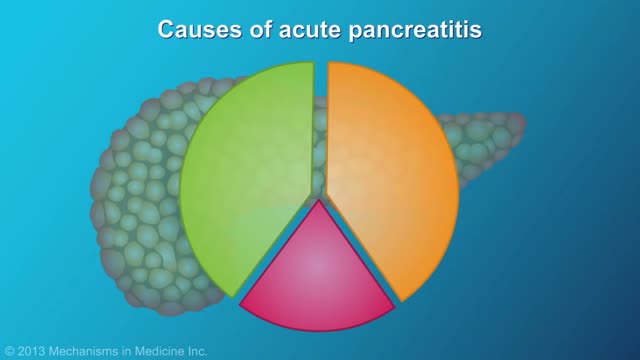
Pancreatitis is inflammation in the pancreas. The pancreas is a long, flat gland that sits tucked behind the stomach in the upper abdomen. The pancreas produces enzymes that assist digestion and hormones that help regulate the way your body processes sugar (glucose). Pancreatitis can occur as acute pancreatitis — meaning it appears suddenly and lasts for days. Or pancreatitis can occur as chronic pancreatitis, which describes pancreatitis that occurs over many years. Mild cases of pancreatitis may go away without treatment, but severe cases can cause life-threatening complications.
Esophageal cancer is cancer that occurs in the esophagus — a long, hollow tube that runs from your throat to your stomach. Your esophagus carries food you swallow to your stomach to be digested. Esophageal cancer usually begins in the cells that line the inside of the esophagus. Esophageal cancer can occur anywhere along the esophagus, but in people in the United States, it occurs most often in the lower portion of the esophagus. More men than women get esophageal cancer. Esophageal cancer isn't common in the United States. In other areas of the world, such as Asia and parts of Africa, esophageal cancer is much more common.
http://barretts-esophagus-cure.info-pro.co Barrett's Esophagus, Barrett's Esophagus Metaplasia, Barrett's Esophagus Bulimia. Are you lost, scared, frustrated, or confused? Have you been recently diagnosed with Barrett’s? Maybe your loved one or a close family member is now a victim of this painful disease. If so, I’d like to share with you some possibly life changing information on how I personally cured my own Barrett’s Esophagus. But before I do I’d like you to take a deep breath, relax for a moment, and let your worry subside because. Even though the Society of Thoracic Surgeons has determined that people with Barrett’s Esophagus are 40x’s more likely to get esophageal cancer, this diagnosis isn’t always a death sentence. Having been a victim of Barrett’s myself, I can relate to the excruciating pain this disease can cause. Maybe you’re like I was, trying to hide the symptoms when the burning, the heartburn, and the PAIN would become so unbearable I’d try doing anything to block it out. I can clearly recall the feeling of those scorching corroding acids inside my throat that would burn like fire, tearing up my esophagus from the inside out. It’s a pain I will NEVER forget. For me, maybe like you, many of my days were spent in anguish and painful agony. Barrett’s Reversed Without Surgery, Pills, PPI Pumps, Antacids, or Drugs. Clicking Here http://barretts-esophagus-cure.info-pro.co
Middle cerebral artery syndrome is a condition whereby the blood supply from the middle cerebral artery (MCA) is restricted, leading to a reduction of the function of the portions of the brain supplied by that vessel: the lateral aspects of frontal, temporal and parietal lobes, the corona radiata, globus pallidus, caudate and putamen. The MCA is the most common site for the occurrence of ischemic stroke.[1] Depending upon the location and severity of the occlusion, signs and symptoms may vary within the population affected with MCA syndrome. More distal blockages tend to produce milder deficits due to more extensive branching of the artery and less ischemic response. In contrast, the most proximal occlusions result in widespread effects that can lead to significant cerebral edema, increased intracranial pressure, loss of consciousness and could even be fatal.[1] In such occasions, mannitol (osmotic diuretic) or hypertonic saline are given to draw fluid out of the oedematus cerebrum to minimise secondary injury. Hypertonic saline is better than mannitol, as mannitol being a diuretic will decrease the mean arterial pressure and since cerebral perfusion is mean arterial pressure minus intracranial pressure, mannitol will also cause a decrease in cerebral perfusion. Contralateral hemiparesis and hemisensory loss of the face, upper and lower extremities is the most common presentation of MCA syndrome.[1] Lower extremity function is more spared than that of the faciobrachial region.[2] The majority of the primary motor and somatosensory cortices are supplied by the MCA and the cortical homunculus can, therefore, be used to localize the defects more precisely.it is important to note that middle cerebral artery lesions mostly affect the dominant hemisphere i.e. the left cerebral hemisphere.
LBD is not a rare disease. It affects an estimated 1.4 million individuals and their families in the United States. Because LBD symptoms can closely resemble other more commonly known diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, it is currently widely underdiagnosed. Many doctors or other medical professionals still are not familiar with LBD. LBD is an umbrella term for two related diagnoses. LBD refers to both Parkinson’s disease dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies. The earliest symptoms of these two diseases differ, but reflect the same underlying biological changes in the brain. Over time, people with both diagnoses will develop very similar cognitive, physical, sleep, and behavioral symptoms. While it may take more than a year or two for enough symptoms to develop for a doctor to diagnose LBD, it is critical to pursue a formal diagnosis. Early diagnosis allows for important early treatment that may extend quality of life and independence. LBD is a multisystem disease and typically requires a comprehensive treatment approach. This approach involves a team of physicians from different specialties who collaborate to provide optimum treatment of each symptom without worsening other LBD symptoms. Many people with LBD enjoy significant improvement of their symptoms with a comprehensive approach to treatment, and some can have remarkably little change from year to year. Some people with LBD are extremely sensitive or may react negatively to certain medications used to treat Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s in addition to certain over-the-counter medications.
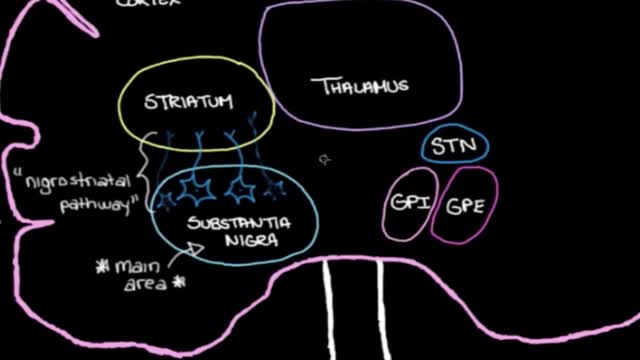
Parkinson disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative condition. Typically beginning in the sixth or seventh decade of life, it is characterized by the unilateral onset of resting tremor in combination with varying degrees of rigidity and bradykinesia. PD was originally described by James Parkinson (1755-1824), a man of many talents and interests. Parkinson published works on chemistry, paleontology, and other diverse topics. Early in his career he was a social activist championing the rights of the disenfranchised and poor. His efforts in this area were enough to result in his arrest and appearance before the Privy Council in London on at least one occasion. In collaboration with his son, who was a surgeon, he also offered the first description in the English language of a ruptured appendix. His small but famous publication, "Essay on the Shaking Palsy," was published in 1817, seven years before his death. The clinical descriptions of 6 cases was remarkable in part because he never actually examined the people he described. Instead, he had simply observed these people on the streets of London.
Alzheimer’s disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills, and eventually the ability to carry out the simplest tasks. In most people with Alzheimer’s, symptoms first appear in their mid-60s. Estimates vary, but experts suggest that more than 5 million Americans may have Alzheimer’s. Alzheimer's disease is currently ranked as the sixth leading cause of death in the United States, but recent estimates indicate that the disorder may rank third, just behind heart disease and cancer, as a cause of death for older people. Alzheimer’s is the most common cause of dementia among older adults. Dementia is the loss of cognitive functioning—thinking, remembering, and reasoning—and behavioral abilities to such an extent that it interferes with a person’s daily life and activities. Dementia ranges in severity from the mildest stage, when it is just beginning to affect a person’s functioning, to the most severe stage, when the person must depend completely on others for basic activities of daily living. The causes of dementia can vary, depending on the types of brain changes that may be taking place. Other dementias include Lewy body dementia, frontotemporal disorders, and vascular dementia. It is common for people to have mixed dementia—a combination of two or more disorders, at least one of which is dementia. For example, some people have both Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. Alzheimer’s disease is named after Dr. Alois Alzheimer. In 1906, Dr. Alzheimer noticed changes in the brain tissue of a woman who had died of an unusual mental illness. Her symptoms included memory loss, language problems, and unpredictable behavior. After she died, he examined her brain and found many abnormal clumps (now called amyloid plaques) and tangled bundles of fibers (now called neurofibrillary, or tau, tangles). These plaques and tangles in the brain are still considered some of the main features of Alzheimer’s disease. Another feature is the loss of connections between nerve cells (neurons) in the brain. Neurons transmit messages between different parts of the brain, and from the brain to muscles and organs in the body.
Como Engravidar De Menino, Engravidar De Uma Menina, Como Faço Para Engravidar De Menina. Revelado: Maneira Incomum para Engravidar de uma MENINA! Fiquei impressionada pela grande quantidade de mulheres que possuem uma preferência para o sexo do seu bebê, e portanto vou falar hoje de como aumentar as suas chances de conceber uma menininha! Para aumentar as chances de engravidar de uma menina, devem-se considerar as características dos espermatozoides que carregam o gene X (que irá gerar uma menina) e dos que carregam o gene Y (que gerará um menino). Os espermatozoides femininos são mais lentos, porém mais resistentes que os espermatozoides masculinos. E como mencionei lá em cima a duração é diferente: os espermatozoides que carregam o gene X duram, em média, 72 horas, já os que carregam o gene Y duram menos, cerca de 24 horas. Com essas informações, a dica é ter relações sexuais dois ou três dias antes do período fértil, visto que os espermatozoides femininos são mais resistentes e conseguem “sobreviver” no corpo da mulher até que ela esteja ovulando. Para calcular o período fértil, deve-se considerar o dia da ovulação (em média, 14 dias após o primeiro dia da menstruação) e deixar uma margem de três dias antes e três dias depois da ovulação. Para saber o dia da ovulação, existem testes vendidos em farmácias, que funcionam como os testes de gravidez. Outra dica é observar o muco cervical, que fica com aspecto de clara de ovo no período fértil. Outra recomendação é adotar posições em que a penetração não seja tão profunda. É importante ainda que a mulher tenha orgasmo depois do homem, porque a secreção que ela libera quando atinge o clímax deixa a vagina menos ácida, facilitando a movimentação dos espermatozoides que carregam o gene Y (que irá gerar um menino). No caso da alimentação deve alterar o cardápio algumas semanas antes da ovulação, dando preferência para alimentos com muito cálcio e em magnésio como leite e derivados, frutas, verduras verde-escuras, como espinafre, couve e rúcula. Além disso, é necessário evitar comidas com muito sódio e potássio e reduzir o consumo de carne. Para mais dicas de como engravidar e uma menina acesse o link abaixo Dicas de como engravidar de uma MENINA Vídeo + Informações http://escolher-sexo-bebe.info-pro.co
What is Venipuncture? While venipuncture can refer to a variety of procedures, including the insertion of IV tubes into a vein for the direct application of medicine to the blood stream, in phlebotomy venipuncture refers primarily to using a needle to create a blood evacuation point. As a phlebotomist, you must be prepared to perform venipuncture procedures on adults, children, and even infants while maintaining a supportive demeanor and procedural accuracy. Using a variety of blood extraction tools, you must be prepared to respond to numerous complications in order to minimize the risk to the patient while still drawing a clean sample. In its entirety, venipuncture includes every step in a blood draw procedure—from patient identification to puncturing the vein to labeling the sample. Patient information, needle placement, and emotional environment all play a part in the collection of a blood sample, and it's the fine details that can mean the difference between a definite result and a false positive. After placing the tourniquet and finding the vein, it's time for the phlebotomist to make the complex choice on what procedure will best suit the specific situation. Keeping this in mind, it should be noted that the following information is not an instructional guide on how to perform these phlebotomy procedures. Rather, the information below is intended to serve as an educational resource to inform you of the equipment and procedures you will use. Venipuncture Technqiues Venipuncture with an Evacuated or Vacuum Tube: This is the standard procedure for venipuncture testing. Using a needle and sheath system, this procedure allows multiple sample tubes to be filled through a single puncture. This procedure is ideal for reducing trauma to patients. After drawing the blood, the phlebotomist must make sure the test stopper is correctly coded and doesn't contact exposed blood between samples. Venipuncture with a Butterfly Needle : This is a specialized procedure that utilizes a flexible, butterfly needle adaptor. A butterfly needle has two plastic wings (one on either side of the needle) and is connected to a flexible tube, which is then attached to a reservoir for the blood. Due to the small gauge of the needle and the flexibility of the tube, this procedure is used most often in pediatric care, where the patients tend to have smaller veins and are more likely to move around during the procedure. After being inserted into a vein at a shallow angle, the butterfly needle is held in place by the wings, which allow the phlebotomist to grasp the needle very close to the skin. Phlebotomists should be careful to watch for blood clots in the flexible tubing. Venipuncture with a Syringe: This technique is typically only used when there is a supply shortage, or when a technician thinks it is the appropriate method. It uses the classic needle, tube, and plunger system, operating in a similar manner to the vacuum tube but requiring multiple punctures for multiple samples. Additionally, after the blood is drawn it must be transferred to the appropriate vacuum tube for testing purposes. If you choose to use this method, remember to check for a sterile seal, and use a safety device when transferring the sample. Fingerstick (or Fingerprick): This procedure uses a medical lance to make a small incision in the upper capillaries of a patient's finger in order to collect a tiny blood sample. It is typically used to test glucose and insulin levels. When performing a Fingerstick, the phlebotomist should remember to lance the third or fourth finger on the non-dominant arm. Never lance the tip or the center of the finger pad; instead, lance perpendicular to the fingerprint lines. Heelstick (or Heelprick): Similar to the Fingerstick procedure, this process is used on infants under six months of age. A medical lance is used to create a small incision on the side of an infant's heel in order to collect small amounts of blood for screening. As with a Fingerstick, the incision should be made perpendicular to the heel lines, and it should be made far enough to the left or right side of the heel to avoid patient agitation. Before performing a Heelstick, the infant's heel should be warmed to about 42 degrees Celsius in order to stimulate capillary blood and gas flow. Therapeutic Phlebotomy: This involves the actual letting of blood in order to relieve chemical and pressure imbalances within the blood stream. Making use of a butterfly needle, this therapy provides a slow removal of up to one pint of blood. Though the blood removed is not used for blood transfusions, the procedure and concerns are the same as with routine blood donation. As with any phlebotomy procedure, one should pay close attention to the patient in order to prevent a blood overdraw. Bleeding Time: A simple diagnostic test that is used to determine abnormalities in blood clotting and platelet production. A shallow laceration is made, followed by sterile swabbing of the wound every 30 seconds until the bleeding stops. Average bleed times range between one and nine minutes. As a phlebotomist, you should familiarize yourself with the application and cross-application of these procedures in order to recognize when a procedure is necessary, and what the risks are for each.
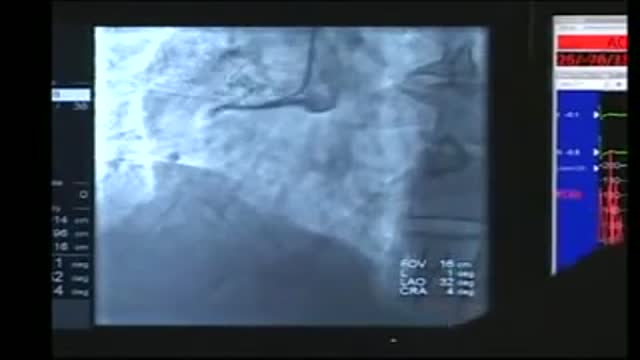
Cardiac catheterization (kath-uh-tur-ih-ZAY-shun) is a procedure used to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions. During cardiac catheterization, a long thin tube called a catheter is inserted in an artery or vein in your groin, neck or arm and threaded through your blood vessels to your heart. Using this catheter, doctors can then do diagnostic tests as part of a cardiac catheterization. Some heart disease treatments, such as coronary angioplasty, also are done using cardiac catheterization. Usually, you'll be awake during cardiac catheterization, but given medications to help you relax. Recovery time for a cardiac catheterization is quick, and there's a low risk of complications.
Pulmonary edema is a condition caused by excess fluid in the lungs. This fluid collects in the numerous air sacs in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. In most cases, heart problems cause pulmonary edema. But fluid can accumulate for other reasons, including pneumonia, exposure to certain toxins and medications, trauma to the chest wall, and exercising or living at high elevations. Pulmonary edema that develops suddenly (acute pulmonary edema) is a medical emergency requiring immediate care. Although pulmonary edema can sometimes prove fatal, the outlook improves when you receive prompt treatment for pulmonary edema along with treatment for the underlying problem. Treatment for pulmonary edema varies depending on the cause but generally includes supplemental oxygen and medications.
Cardiac tamponade Email this page to a friend Print Facebook Twitter Bookmark & Share Cardiac tamponade is pressure on the heart that occurs when blood or fluid builds up in the space between the heart muscle (myocardium) and the outer covering sac of the heart (pericardium). Causes In this condition, blood or fluid collects in the pericardium, the sac surrounding the heart. This prevents the heart ventricles from expanding fully. The excess pressure from the fluid prevents the heart from working properly. As a result, the body does not get enough blood. Cardiac tamponade can occur due to: Dissecting aortic aneurysm (thoracic) End-stage lung cancer Heart attack (acute MI) Heart surgery Pericarditis caused by bacterial or viral infections Wounds to the heart
A pneumothorax (noo-moe-THOR-aks) is a collapsed lung. A pneumothorax occurs when air leaks into the space between your lung and chest wall. This air pushes on the outside of your lung and makes it collapse. In most cases, only a portion of the lung collapses. A pneumothorax can be caused by a blunt or penetrating chest injury, certain medical procedures, or damage from underlying lung disease. Or it may occur for no obvious reason. Symptoms usually include sudden chest pain and shortness of breath. On some occasions, a collapsed lung can be a life-threatening event. Treatment for a pneumothorax usually involves inserting a flexible tube or needle between the ribs to remove the excess air. However, a small pneumothorax may heal on its own.
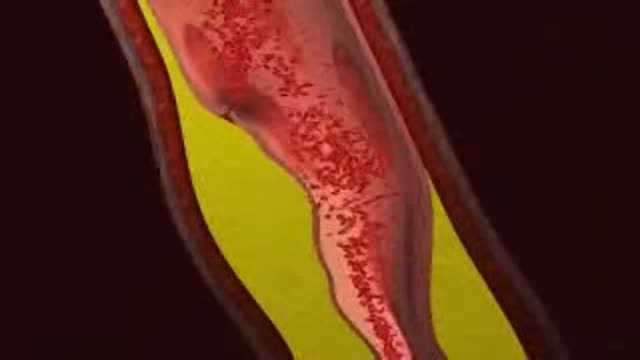
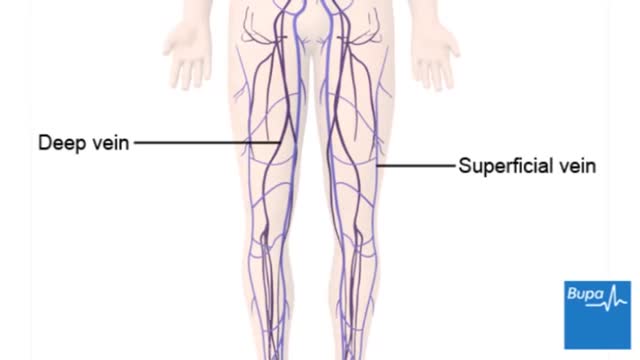
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in your legs. Deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling, but may occur without any symptoms. Deep vein thrombosis can develop if you have certain medical conditions that affect how your blood clots. Deep vein thrombosis can also happen if you don't move for a long time, such as after surgery, following an accident, or when you are confined to a hospital or nursing home bed.
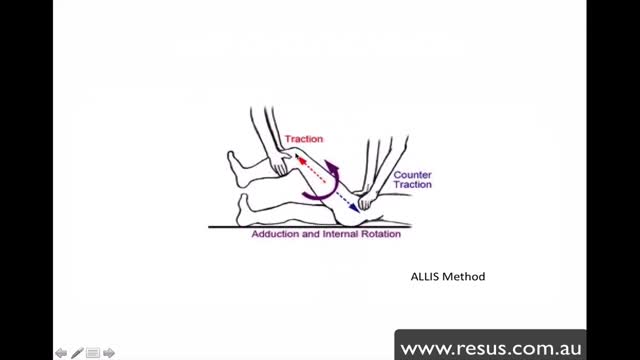
The hip joint is formed between the 'ball' of the femoral head and the 'socket' of the acetabulum and a cartilaginous labrum. Strong supporting muscles, the fibrous joint capsule and ischiofemoral ligament make this a stable joint. Hip dislocations are either congenital or traumatic. Congenital dislocation of the hip is caused by dysplasia of the femoral head or acetabulum and is covered in the separate article Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. This remainder of this article deals with traumatic dislocation. Traumatic hip dislocation is an orthopaedic emergency. Large forces are required to cause hip dislocation (except in prosthetic hips) and this means that such injury may be associated with other life-threatening injuries and other fractures. The condition is extremely painful. Accurate and swift diagnosis means appropriate management can reduce morbidity.