Latest videos
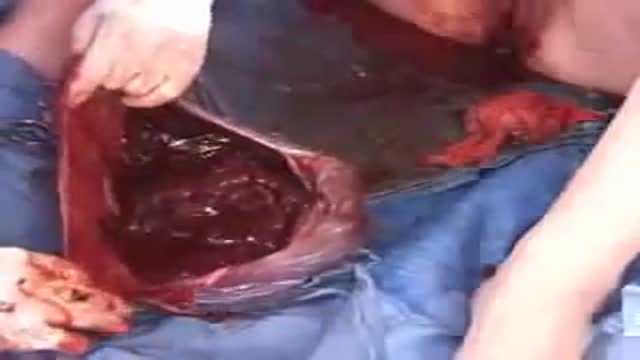
Intestinal malrotation is a developmental anomaly that occasionally causes an unusual array of symptoms in adults. The delay in diagnosis that is common in patients with malrotation frequently results in a ruptured appendix. Appendicitis should be considered when characteristic signs and symptoms are present, even if the location of abdominal pain is atypical.
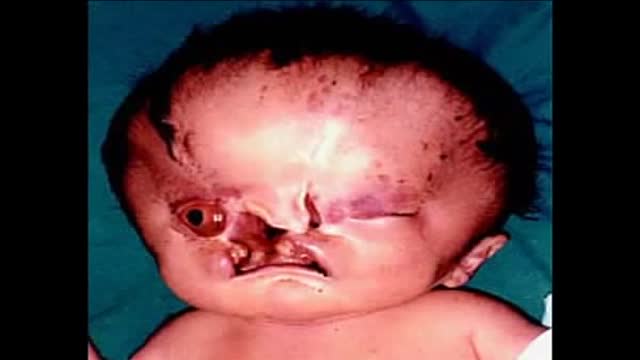
Holoprosencephaly (HPE, once known as arhinencephaly) is a cephalic disorder in which the prosencephalon (the forebrain of the embryo) fails to develop into two hemispheres. Normally, the forebrain is formed and the face begins to develop in the fifth and sixth weeks of human pregnancy. The condition also occurs in other species, as with Cy, the Cyclops kitten.

Debulking is the surgical removal of part of a malignant tumour which cannot be completely excised, so as to enhance the effectiveness of radiation or chemotherapy. It is used only in specific malignancies, as generally partial removal of a tumor is not considered a worthwhile intervention. Ovarian carcinoma and some types of brain tumor are debulked prior to commencing radio- or chemotherapy. It may also be used in the case of slow growth tumors to shift tumor cells from phase of cell cycle to replicative pool.
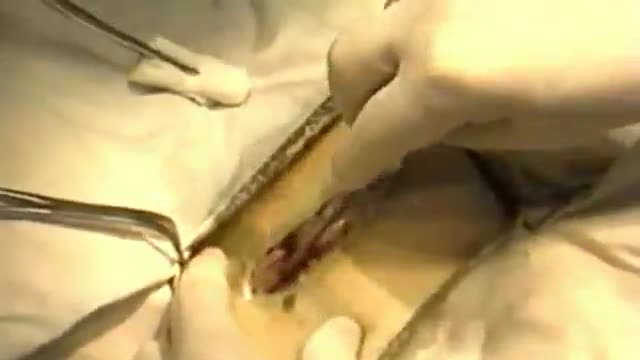
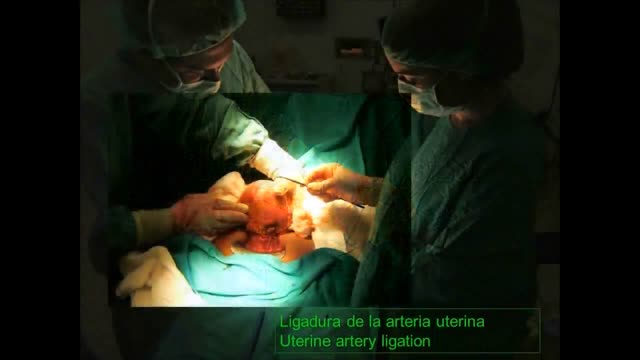
An appendectomy (sometimes called appendisectomy or appendicectomy (British English)) is the surgical removal of the vermiform appendix. This procedure is normally performed as an emergency procedure, when the patient is suffering from acute appendicitis. In the absence of surgical facilities, intravenous antibiotics are used to delay or prevent the onset of sepsis; it is now recognized that many cases will resolve when treated perioperatively. In some cases the appendicitis resolves completely; more often, an inflammatory mass forms around the appendix, causing transruptural flotation. This is a relative contraindication to surgery.
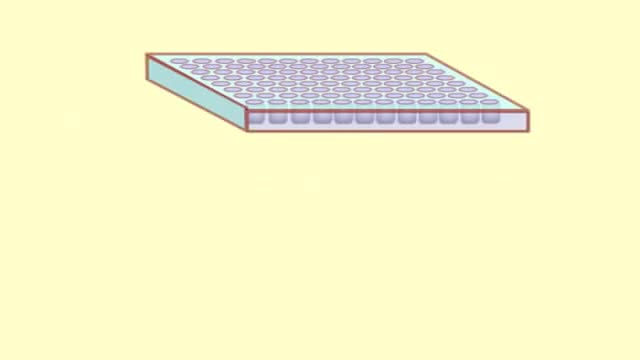
The purpose of an ELISA is to determine if a particular protein is present in a sample and if so, how much. There are two main variations on this method: you can determine how much antibody is in a sample, or you can determine how much protein is bound by an antibody. The distinction is whether you are trying to quantify an antibody or some other protein. In this example, we will use an ELISA to determine how much of a particular antibody is present in an individuals blood.
ELISAs are performed in 96-well plates which permits high throughput results. The bottom of each well is coated with a protein to which will bind the antibody you want to measure. Whole blood is allowed to clot and the cells are centrifuged out to obtain the clear serum with antibodies (called primary antibodies). The serum is incubated in a well, and each well contains a different serum (see figure below). A positive control serum and a negative control serum would be included among the 96 samples being tested.