Latest videos

Wernickes Aphasia Interview with a Patient
Alicia Berger
8,378 Views • 2 years ago
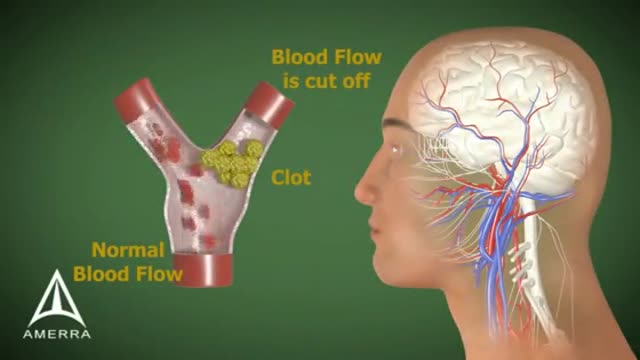
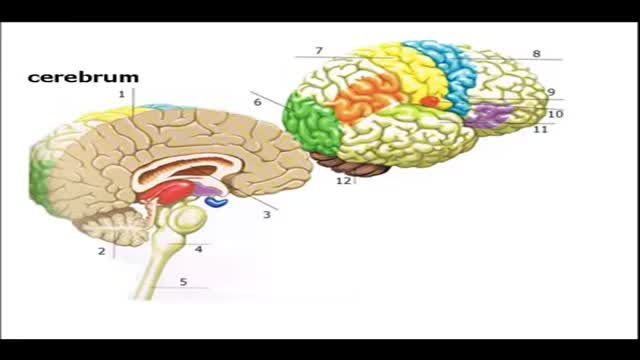
Wernicke's aphasia is a neurological disorder typically caused by stroke. It affects the Wernicke's region in the brain's left hemisphere which is reasoned to be responsible for processing of meaning, especially as it relates to verbal communication, hence the problems with speech witnessed in these patients
Showing 264 out of 265