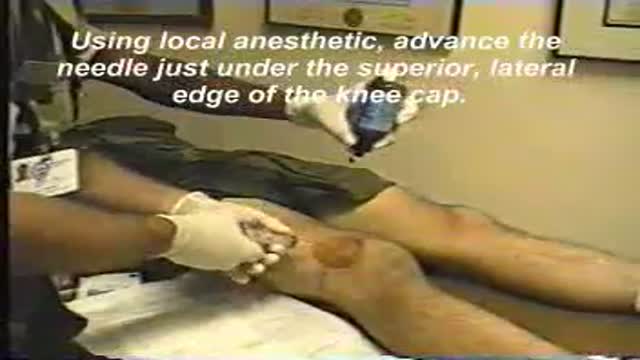
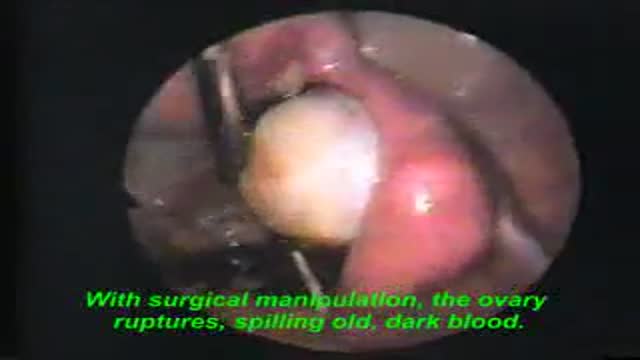
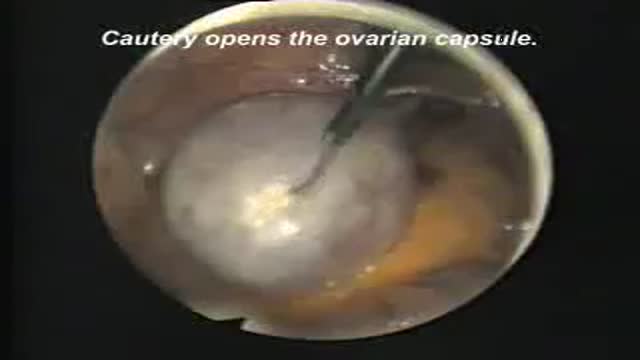
Latest videos
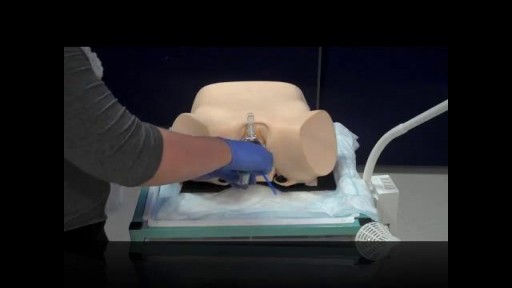
Pelvic Exam During Labor
Mohamed Ibrahim
706,020 Views • 2 years ago
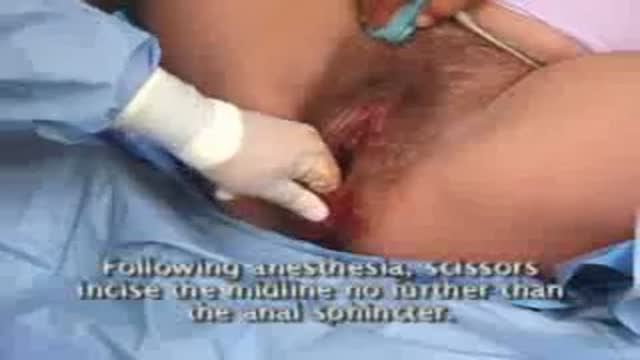
Pelvic examinations during labor are used for several purposes, among them assessment of cervical dilatation, effacement, station of the presenting part, presentation, position, and pelvic capacity.Instruction in these techniques is particularly important for those health care providers involved in labor management, including physicians, nurses, midwives, paramedics and EMT personnel.
Showing 370 out of 371