Latest videos
Meningitis is a common life-threatening medical emergency caused by infectious and non-infectious agents. Rapid and accurate evaluation by history and clinical examination is helpful to guide further specific investigation and treatment. Kernig's sign, Brudzinski's sign, and nuchal rigidity are bedside diagnostic signs used to evaluate suspected cases of meningitis. The presence of meningeal irritation, however, is not pathognomonic for meningitis.
In a normal person, when a muscle tendon is tapped briskly, the muscle immediately contracts due to a two-neuron reflex arc involving the spinal or brainstem segment that innervates the muscle. The afferent neuron whose cell body lies in a dorsal root ganglion innervates the muscle or Golgi tendon organ associated with the muscles; the efferent neuron is an alpha motoneuron in the anterior horn of the cord. The cerebral cortex and a number of brainstem nuclei exert influence over the sensory input of the muscle spindles by means of the gamma motoneurons that are located in the anterior horn; these neurons supply a set of muscle fibers that control the length of the muscle spindle itself. Hyporeflexia is an absent or diminished response to tapping. It usually indicates a disease that involves one or more of the components of the two-neuron reflex arc itself. Hyperreflexia refers to hyperactive or repeating (clonic) reflexes. These usually indicate an interruption of corticospinal and other descending pathways that influence the reflex arc due to a suprasegmental lesion, that is, a lesion above the level of the spinal reflex pathways.
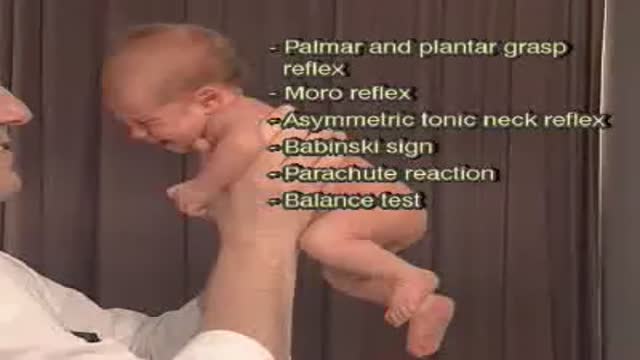
Primitive reflexes are reflex actions originating in the central nervous system that are exhibited by normal infants, but not neurologically intact adults, in response to particular stimuli. These reflexes are absent due to the development of the frontal lobes as a child transitions normally into child development.

Psychomotor learning is demonstrated by physical skills such as movement, coordination, manipulation, dexterity, grace, strength, speed; actions which demonstrate the fine motor skills such as use of precision instruments or tools. Psychomotor ability refers to a wide range of actions involving physical movement related to conscious cognitive processing. Psychomotor ability may be measured by accuracy or speed (reaction time)

For open hernia repair surgery, a single long incision is made in the groin. If the hernia is bulging out of the abdominal wall (a direct hernia), the bulge is pushed back into place. If the hernia is going down the inguinal canal (indirect), the hernia sac is either pushed back or tied off and removed.

When a ventral hernia occurs, it usually arises in the abdominal wall where a previous surgical incision was made. In this area the abdominal muscles have weakened; this results in a bulge or a tear. In the same way that an inner tube pushes through a damaged tire, the inner lining of the abdomen pushes through the weakened area of the abdominal wall to form a balloon-like sac. This can allow a loop of intestines or other abdominal contents to push into the sac. If the abdominal contents get stuck within the sac, they can become trapped or “incarcerated.” This could lead to potentially serious problems that might require emergency surgery.
Laparoscopic ventral hernia repair is a technique to fix tears or openings in the abdominal wall using small incisions, laparoscopes (small telescopes inserted into the abdomen) and a patch (screen or mesh) to reinforce the abdominal wall.

The words “laparoscopic” and “open” appendectomy describes the techniques a surgeon uses to gain access to the internal surgery site. Most laparoscopic appendectomies start the same way. Using a cannula (a narrow tube-like instrument), the surgeon enters the abdomen. A laparoscope (a tiny telescope connected to a video camera) is inserted through a cannula, giving the surgeon a magnified view of the patient’s internal organs on a television monitor. Several other cannulas are inserted to allow the surgeon to work inside and remove the appendix. The entire procedure may be completed through the cannulas or by lengthening one of the small cannula incisions. A drain may be placed during the procedure. This will be removed later by your surgeon.
Appendicitis is one of the most common surgical problems. One out of every 2,000 people has an appendectomy sometime during their lifetime. Treatment requires an operation to remove the infected appendix. Traditionally, the appendix is removed through an incision in the right lower abdominal wall. In most laparoscopic appendectomies, surgeons operate through 3 small incisions (each ¼ to ½ inch) while watching an enlarged image of the patient’s internal organs on a television monitor. In some cases, one of the small openings may be lengthened to complete the procedure.
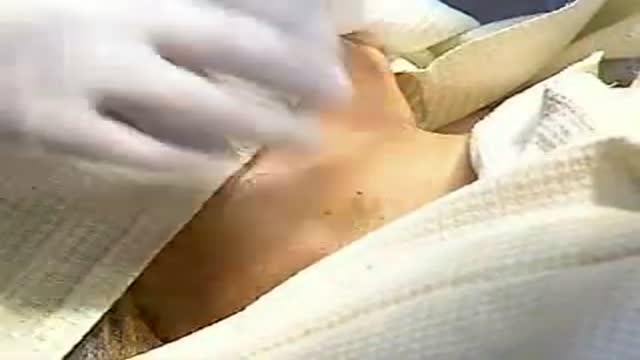
Central venous access is essential in providing quality medical care to many patients for whom intensive therapy is required. In many situations, a semipermanent tunneled central line is preferred (see Indications). An anterior approach to the internal jugular vein (IJV) is the best option in this situation because it offers the easiest route with a low risk of complications. In this procedure, a tunneled catheter is surgically inserted into a vein in the neck or chest and passed under the skin. Only the end of the catheter is brought through the skin; medicines and intravenous (IV) fluid can be administered through this catheter; other tasks, such as blood sampling, can also be performed. The fact that the catheter is passed under the skin helps secure the catheter, reduces the rate of infection, and permits free movement of the catheter port. The placement of a tunneled catheter should be carried out by practitioners with specific experience in the procedure.

he appendix is a long narrow tube (a few inches in length) that attaches to the first part of the colon. It is usually located in the lower right quadrant of the abdominal cavity. The appendix produces a bacteria destroying protein called immunoglobulins, which help fight infection in the body. Its function, however, is not essential. People who have had appendectomies do not have an increased risk toward infection. Other organs in the body take over this function once the appendix has been removed.