Latest videos
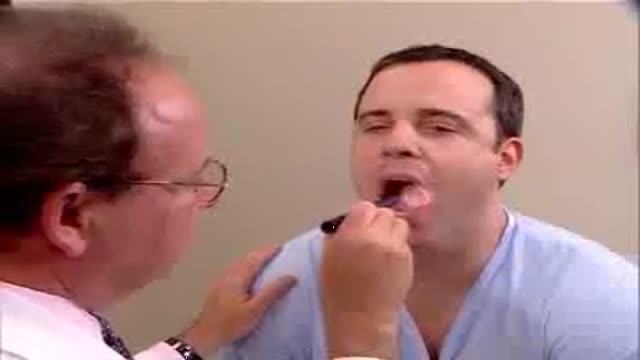
Clinical complete examination of the mouth and throat
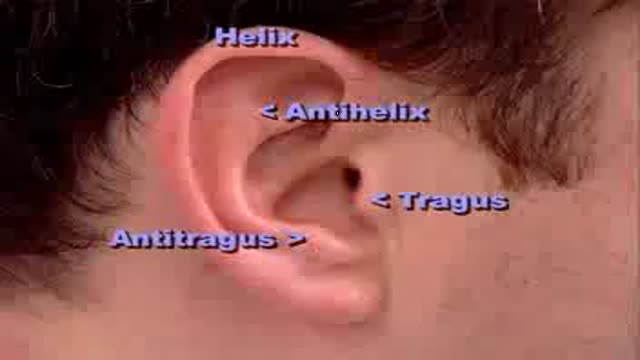
Complete clinical examination of the ears with all the associated tests
Examination of the eye,vision,retina and field of vision
It is very important to instruct your patients about how to self exam their breasts for any abnormalities or masses for early detection of any changes
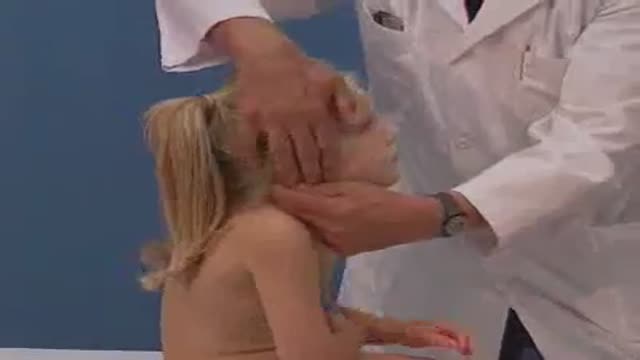
Examination of the lymph nodes of the head
Optimal blood pressure typically is defined as 120 mm Hg systolic — which is the pressure as your heart beats — over 80 mm Hg diastolic — which is the pressure as your heart relaxes. For your resting heart rate, the target is between 60 and 100 beats per minute (bpm)
Breast masses are broadly classified as benign or malignant. Common causes of a benign breast mass include fibrocystic disease, fibroadenoma (see the image below), intraductal papilloma, and abscess.
surgical examination of intra abdominal lump or mass
Surgical Examination of an ulcer in a proper way
Video showing normal vagina delivery and child birth
aricose veins are gnarled, enlarged veins. Any vein may become varicose, but the veins most commonly affected are those in your legs and feet. That's because standing and walking upright increases the pressure in the veins of your lower body. For many people, varicose veins and spider veins — a common, mild variation of varicose veins — are simply a cosmetic concern. For other people, varicose veins can cause aching pain and discomfort. Sometimes varicose veins lead to more-serious problems.
Fertilization of the egg with sperm generally occurs during the two weeks following the first day of your last menstrual period.1 The week of pregnancy that you are entering is dated from the first day of your last period. This means that in the first two weeks or so, you are not actually pregnant - your body will be preparing for ovulation as normal.
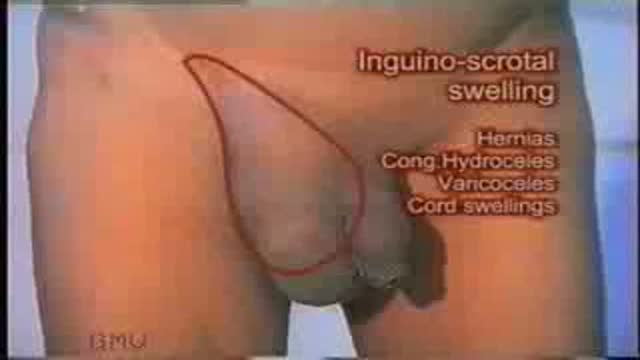
examination of a case of inguino-scrotal swelling as in cases of oblique inguinal hernia..etc
A testicular examination is mainly performed on male patients who present with testicular pathology e.g. pain, swelling, a lump. Although titled testicular examination it involves the examination of the penis, scrotum and testes. As this is an intimate examination it is pertinent to gain a good rapport with your patient, maintain good communication and ensure the patient’s dignity at all times. Remember to offer a chaperone for this skill. For the purposes of your exam, you will most likely be examining a mannequin.
Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism Symptoms: Swollen Neck. A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland. As shown here, an enlarged thyroid can be seen as a swelling in the front of the neck. A goiter can occur with either hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism
ost of us come across this particular sign quite often. Of course, you can just jump to the numerous investigations and one after another, rule out the possible causes, finally getting to the diagnosis. For me, that’s no fun at all. Although I still don’t know whether I am going to become a surgeon or not (embarassing for me, since I’m going to be done with med-school this year), its pretty fascinating. If I were to work in a country whether investigations aren’t that expensive, I would definitely just perform a small examination and take a short history, sending off my patient to get a myriad of investigations, reporting to me after a while, with the diagnosis in his reports.
Peripheral vascular disease, also called PVD, refers to any disease or disorder of the circulatory system outside of the brain and heart. The term can include any disorder that affects any blood vessels. It is, though, often used as a synonym for peripheral artery disease. PVD is the most common disease of the arteries. The build-up of fatty material inside the vessels, a condition called atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries, is what causes it. The build up is a gradual process. Over time, the artery becomes blocked, narrowed, or weakened.
full pediatric examination of lymph nodes