Latest videos

Curious about physiotherapy or wanting to know how to properly perform an exercise? Check us out on Social Media! Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/striveptandperformance/ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/striveptandperf/ Twitter: https://twitter.com/StrivePTandPerf Blog: http://www.strivept.ca/blog

Hair Transplant Results Before and After Photos who undergone Hair Transplant. View our patient's successful results with the FUE, Bio - FUE and B.E.S.T FUE hair transplant technique. Comparable before & after photos! For More Visit Here:- https://www.hairtransplantchennai.org/hair-transplant-results-chennai.php or call us:- +91-8939636222
o you have an exercise routine that makes you feel absolutely awesome when you stick to it? Or a healthy eating pattern that makes you crackle with energy and vitality when you actually follow it. Well, today I’m sharing with you what makes me feel even more alive, energetic and vibrant than both of those… My daily sexual self-care practice.

Cervicitis is an inflammation of the cervix, the lower, narrow end of the uterus that opens into the vagina. Possible symptoms of cervicitis include bleeding between menstrual periods, pain with intercourse or during a cervical exam, and abnormal vaginal discharge. However, it's also possible to have cervicitis and not experience any signs or symptoms. Often, cervicitis results from a sexually transmitted infection, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea. Cervicitis can develop from noninfectious causes, too. Successful treatment of cervicitis involves treating the underlying cause of the inflammation.

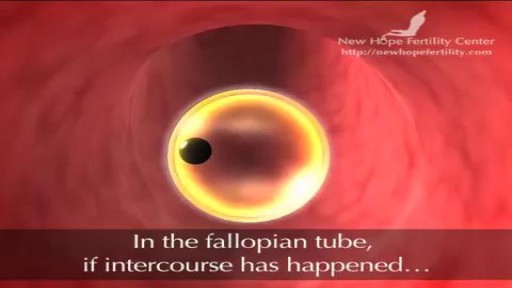
The journey of egg and sperm. There are a lot of casualties (deaths) among the sperm as they swim toward the egg. First, many get lost in the maze of a woman's uterus where they also have to contend with acidic vaginal secretions.
The male orgasm is a common subject but usually misunderstood at the same time. Men are sometimes led to believe that ejaculating often is a bad thing, particularly if you masturbate. The truth is that ejaculation is important to every man due to a number of reasons. The main goal of this post is to shed some light on reasons why men need to ejaculate.
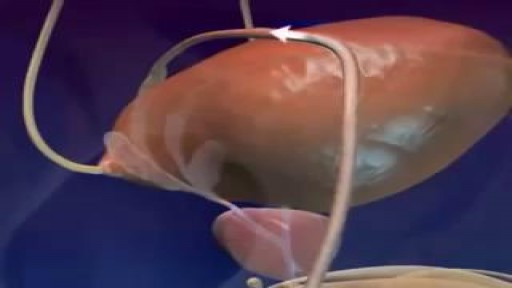
Nuclear Transfer is a form of cloning. The steps involve removing the DNA from an oocyte and while(unfertilized egg), and injecting the nucleus which contains the DNA to be cloned. In rare instances, the newly constructed cell will divide normally, replicating the new DNA while remaining
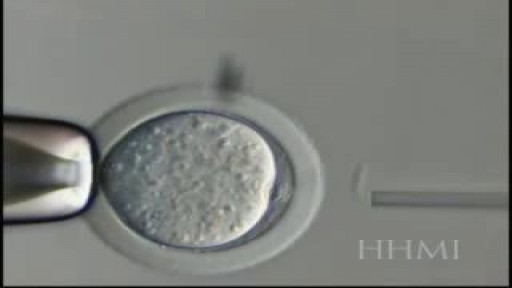
Almost all the cells in your body were produced by mitosis. The only exception is sperm or eggs which are produced by a different type of cell division called meiosis. During fertilization the sperm and egg unite to form a single cell called the zygote which contains chromosomes from both the sperm and egg.
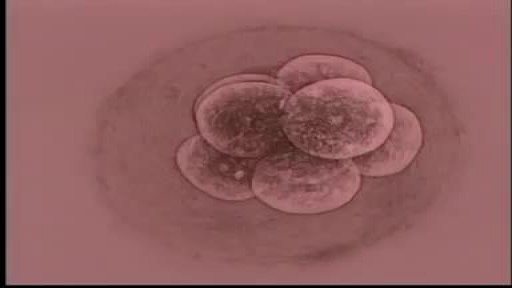
Sperm Meets Egg: Weeks 1 to 3 of Pregnancy. Something magical is about to happen! Watch as the ovulation process occurs, and then millions of sperm swim upstream on a quest to fertilize an egg. Your due date is calculated from the first day of your last menstrual period
Before ovulation occurs, the average diameter of the dominant follicle is 22 to 24 mm (range 18-36 mm). It is the only marker that can predict ovulation with ease. * In stimulated cycle (hormonal treatment), generally, all or most of the antral follicles grow. The growth rate will be different for each of them.

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural change that occurs in the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of oocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy.

Normal sperm densities range from 15 million to greater than 200 million sperm per milliliter of semen. You are considered to have a low sperm count if you have fewer than 15 million sperm per milliliter or less than 39 million sperm total per ejaculate.

A semen analysis, also called "seminogram" evaluates certain characteristics of a male's semen and the sperm contained therein. It is done to help evaluate male fertility, whether for those seeking pregnancy or verifying the success of vasectomy