Top videos

Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the uterus that often appear during childbearing years. Also called leiomyomas (lie-o-my-O-muhs) or myomas, uterine fibroids aren't associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer and almost never develop into cancer. Fibroids range in size from seedlings, undetectable by the human eye, to bulky masses that can distort and enlarge the uterus. You can have a single fibroid or multiple ones. In extreme cases, multiple fibroids can expand the uterus so much that it reaches the rib cage. Many women have uterine fibroids sometime during their lives. But most women don't know they have uterine fibroids because they often cause no symptoms. Your doctor may discover fibroids incidentally during a pelvic exam or prenatal ultrasound.
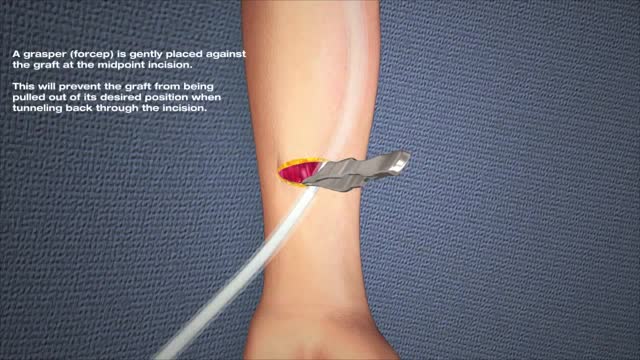
arteriovenous hemodialysis access has been the "gold standard" for patients needing hemodialysis for the past 30 years. Despite the reported advantages of autologous access, the availability of prosthetic graft material, coupled with the challenging dialysis candidate, has led to a trend of primary prosthetic graft dialysis access in the 1980s and 1990s. In recognition of this unfortunate trend, the National Kidney Foundation Dialysis Outcomes Quality Initiative (DOQI) used evidence from published studies and summary articles to generate clinical practice guidelines, emphasizing a shift back to autologous arteriovenous fistula (AVF) as the key to long-term successful hemodialysis.[1,2] These initial guidelines proposed a goal of 50% autologous AVF as the initial access, with a 40% prevalence of autologous access for a given practice or unit.
Pulmonary edema is almost always treated in the emergency room or hospital. You may need to be in an intensive care unit (ICU). Oxygen is given through a face mask or tiny plastic tubes are placed in the nose. A breathing tube may be placed into the windpipe (trachea) so you can be connected to a breathing machine (ventilator) if you cannot breathe well on your own. The cause of edema should be identified and treated quickly. For example, if a heart attack has caused the condition, it must be treated right away. Medicines that may be used include: Diuretics that remove excess fluid from the body Medicines that strengthen the heart muscle, control the heartbeat, or relieve pressure on the heart

An undescended testicle (cryptorchidism) is a testicle that hasn't moved into its proper position in the bag of skin hanging below the penis (scrotum) before birth. Usually just one testicle is affected, but about 10 percent of the time both testicles are undescended. An undescended testicle is uncommon in general, but common among baby boys born prematurely. The vast majority of the time, the undescended testicle moves into the proper position on its own, within the first few months of life. If your son has an undescended testicle that doesn't correct itself, surgery can relocate the testicle into the scrotum.

Cluster headaches, which occur in cyclical patterns or clusters, are one of the most painful types of headache. A cluster headache commonly awakens you in the middle of the night with intense pain in or around one eye on one side of your head. Bouts of frequent attacks, known as cluster periods, can last from weeks to months, usually followed by remission periods when the headaches stop. During remission, no headaches occur for months and sometimes even years. Fortunately, cluster headache is rare and not life-threatening. Treatments can make cluster headache attacks shorter and less severe. In addition, medications can reduce the number of cluster headaches.

The Ortolani method is an examination method that identifies a dislocated hip that can be reduced into the socket (acetabulum). Ortolani described the feeling of reduction as a “Hip Click” but the translation from Italian was interpreted a sound instead of a sensation of the hip moving over the edge of the socket when it re-located. After the age of six weeks, this sensation is rarely detectable and should not be confused with snapping that is common and can occur in stable hips when ligaments in and around the hip create clicking noises. When the Ortolani test is positive because the hip is dislocated, treatment is recommended to keep the hip in the socket until stability has been established
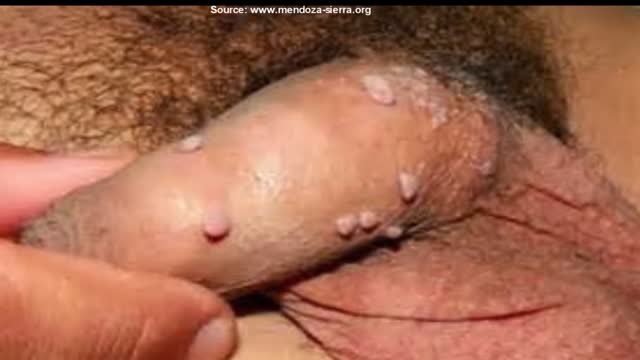
Genital warts are one of the most common types of sexually transmitted infections. At least half of all sexually active people will become infected with human papillomavirus (HPV), the virus that causes genital warts, at some point during their lives. Women are somewhat more likely than men to develop genital warts. As the name suggests, genital warts affect the moist tissues of the genital area. Genital warts may look like small, flesh-colored bumps or have a cauliflower-like appearance. In many cases, the warts are too small to be visible. Like warts that appear elsewhere on your body, genital warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Some strains of genital HPV can cause genital warts, while others can cause cancer. Vaccines can help protect against certain strains of genital HPV

Morning erections have colloquially been termed as “morning wood” while scientifically it is called nocturnal penile tumescence. It is a normal and healthy physiological reaction and response that most men experience in their lives. Morning erections are really the ending of a series of erections that happen to men during the night. Healthy men can, on average, have anywhere between three to five erections in a full night of sleep, each of which lasts from 25-35 minutes.
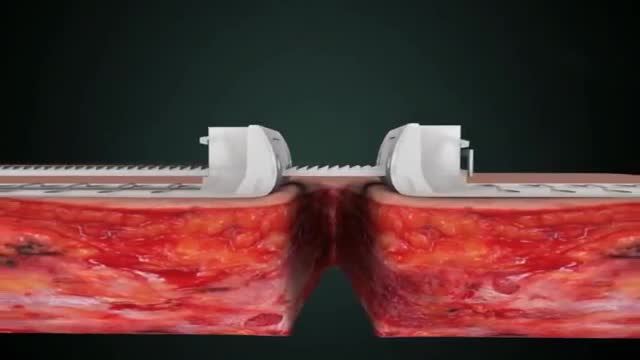
Wound closure techniques have evolved from the earliest development of suturing materials to comprise resources that include synthetic sutures, absorbables, staples, tapes, and adhesive compounds. The engineering of sutures in synthetic material along with standardization of traditional materials (eg, catgut, silk) has made for superior aesthetic results. Similarly, the creation of topical skin adhesives (the monomer 2-octyl cyanoacrylate), surgical staples, and tapes to substitute for sutures has supplemented the armamentarium of wound closure techniques. Aesthetic closure of a wound, whether traumatic or surgically induced, is based on knowledge of healing mechanisms and skin anatomy (see the image below), as well as an appreciation of suture material and closure technique. Choosing the proper materials and wound closure technique ensures optimal healing.[1]

Factitious disorder is the term used to describe a pattern of behavior centered on the exaggeration or outright falsifications of one’s own health problems or the health problems of others. Some people with this disorder fake or exaggerate physical problems; others fake or exaggerate psychological problems or a combination of physical and psychological problems. Factitious disorder differs from a pattern of falsified or exaggerated behavior called malingering. While malingerers make their claims out of a motivation for personal gain, people with factitious disorder have no such motivation.

Hoover's sign of leg paresis is one of two signs named for Charles Franklin Hoover. It is a maneuver aimed to separate organic from non-organic paresis of the leg. The sign relies on the principle of synergistic contraction. ... Feeling this would indicate an organic cause of the paresis.
Primary biliary cirrhosis, sometimes called PBC, is a disease in which the bile ducts in your liver are slowly destroyed. Bile, a fluid produced in your liver, plays a role in digesting food and helps rid your body of worn-out red blood cells, cholesterol and toxins. When bile ducts are damaged, as in primary biliary cirrhosis, harmful substances can build up in your liver and sometimes lead to irreversible scarring of liver tissue (cirrhosis). Primary biliary cirrhosis is considered an autoimmune disease, in which the body turns against its own cells. Researchers think it is triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Primary biliary cirrhosis usually develops slowly and medication can slow its progression, especially if treatment begins early.

This video: Polycythemia vera (pol-e-sigh-THEE-me-uh VEER-uh) is a slow-growing type of blood cancer in which your bone marrow makes too many red blood cells. Polycythemia vera may also result in production of too many of the other types of blood cells — white blood cells and platelets. These excess cells thicken your blood and cause complications, such as such as a risk of blood clots or bleeding. Polycythemia vera isn't common. It usually develops slowly, and you may have it for years without noticing signs or symptoms. Often, polycythemia vera is found during a blood test done for some other reason. Without treatment, polycythemia vera can be life-threatening. However, with proper medical care, many people experience few problems related to this disease. Over time, there's a risk of progressing to more-serious blood cancers, such as myelofibrosis or acute leukemia.

Before deciding how to treat one episode of high blood glucose, it is important to figure out why the number is high. Some possible causes include eating a heavy meal, not getting enough physical activity, forgetting to take diabetes medication, and dealing with illness and stress. Insulin is the medication that will bring blood glucose down the fastest. Someone who uses mealtime insulin can take correction doses to lower blood glucose. This requires a thorough understanding of when to inject, how often to give correction doses, and how much insulin to use. You will need to work with your doctor or diabetes educator to learn how to do this. Apart from administering insulin, the fastest way to lower your blood glucose is to engage in physical activity. Exercise results in an increased sensitivity to insulin. It causes your muscle cells to take up more glucose, leaving less of it to circulate in your bloodstream during and after the physical activity (which means a lower blood glucose when you test). Frequent, regular exercise is very important to good blood glucose control no matter what type of diabetes you have. Research has shown that it is vital in warding off long-term complications like neuropathy, retinopathy, and heart and kidney diseases. Don't forget to check with a doctor, though, before making any major changes to your exercise routine. And, if you have type 1 diabetes and your glucose is 250 mg/dl or higher, check for urine ketones. You should not exercise if ketones are present.