Top videos
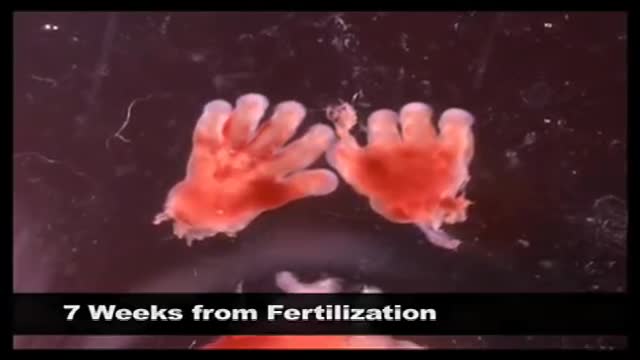
Childbirth (also called labour, birth, partus or parturition) is the culmination of a human pregnancy or gestation period with the birth of one or more newborn infants from a woman's uterus. The process of normal human childbirth is categorized in three stages of labour: the shortening and dilation of the cervix, descent and birth of the infant, and birth of the placenta. In many cases, with increasing frequency, childbirth is achieved through caesarean section, the removal of the neonate through a surgical incision in the abdomen, rather than through vaginal birth. In the U.S. and Canada it represents nearly 1 in 3 (31.8%) and 1 in 4 (22.5%) of all childbirths, respectively.
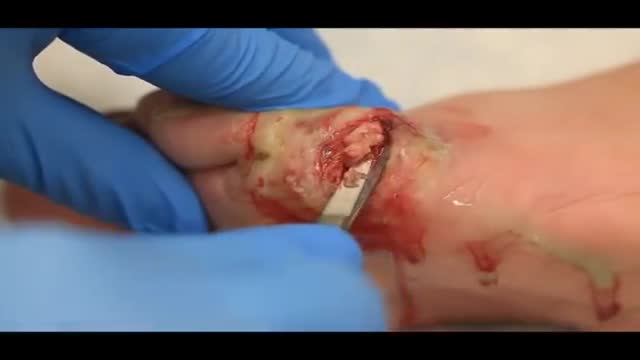
Treatment may not be needed for an eschar if it is part of the natural healing process. However, if an eschar looks like it may have a wound infection – symptoms can include oozing fluid such as pus or blood, your clinician will likely recommend topical treatment or debridement to help control and remove the infection.

White stretch marks are unsightly marks that are found along the thighs, abdomen and upper arms. These are marks that could be due to a recent weight loss, trauma or pregnancy. Stretch marks can affect your confidence if you wear revealing outfits and so you should do all you can to remove them.

Morning erections have colloquially been termed as “morning wood” while scientifically it is called nocturnal penile tumescence. It is a normal and healthy physiological reaction and response that most men experience in their lives. Morning erections are really the ending of a series of erections that happen to men during the night. Healthy men can, on average, have anywhere between three to five erections in a full night of sleep, each of which lasts from 25-35 minutes.
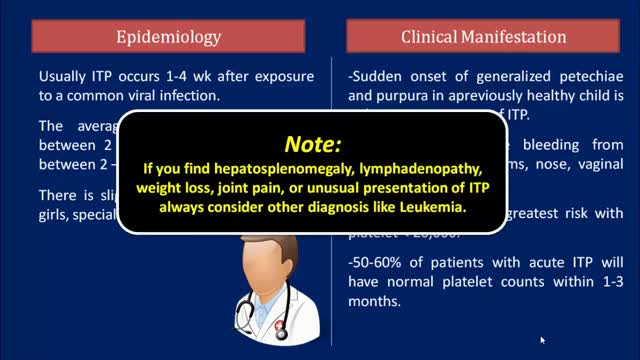
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is a disorder that can lead to easy or excessive bruising and bleeding. The bleeding results from unusually low levels of platelets — the cells that help blood clot. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, which is also called immune thrombocytopenia, affects children and adults. Children often develop ITP after a viral infection and usually recover fully without treatment. In adults, the disorder is often long term. If you don't have signs of bleeding and your platelet count isn't too low, you may not need any treatment. In rare cases, the number of platelets may be so low that dangerous internal bleeding occurs. Treatment options are available.

The Epley Maneuver for Vertigo can be very effective at relieving vertigo symptoms, but it’s a procedure that should be performed by a physical therapist or other health care professional. This video is for demonstration purposes only. See Doctor Jo’s blog post about the Epley
An aortic dissection is a serious condition in which the inner layer of the aorta, the large blood vessel branching off the heart, tears. Blood surges through the tear, causing the inner and middle layers of the aorta to separate (dissect). If the blood-filled channel ruptures through the outside aortic wall, aortic dissection is often fatal. Aortic dissection is relatively uncommon. The condition most frequently occurs in men in their 60s and 70s. Symptoms of aortic dissection may mimic those of other diseases, often leading to delays in diagnosis. However, when an aortic dissection is detected early and treated promptly, the chance of survival greatly improves.
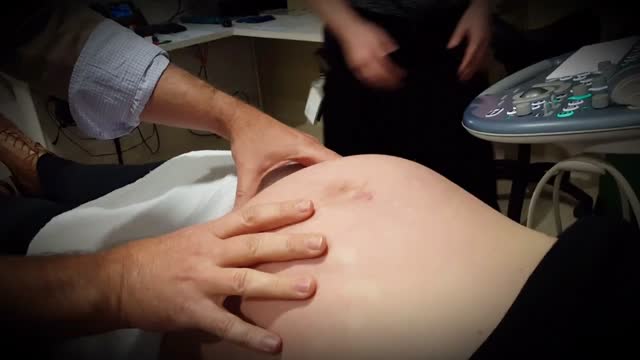
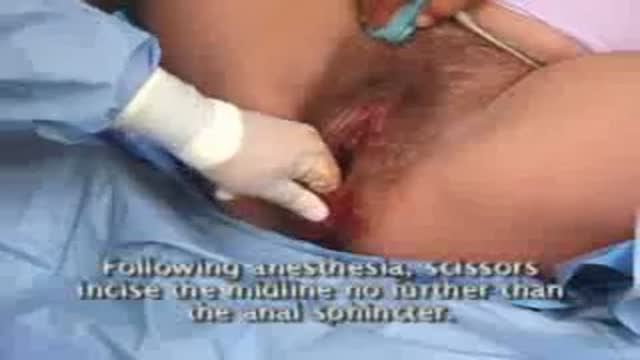
External cephalic version, or version, is a procedure used to turn a fetus from a breech position or side-lying (transverse) position into a head-down (vertex) position before labor begins. When successful, version makes it possible for you to try a vaginal birth.

Cannula are often introduced into blood vessels in 80% of patients in the hospital for treatment. This can be a daunting experience to patients and stressful to doctors as multiple attempts are used. This may result in introducing spreading MRSA, E Coli & Chlostredium living on your skin into blood and results in Invasive MRSA infection.
Skin is often not adequatly cleaned during subsequent atempts as doctors/nurses do not wait for 1 min after applying cleaning solution on the skin before they puncture your skin.
Multiple punctured sites allow CA-MRSA to enter blood stream resulting in bacteremia and death.
Our mission is to reduce spreading invasive CA-MRSA in the hospitals by developing alternative technique to introduce cannulae.
Medifix was created by doctors with a mission to reduce the threat of spreading antibiotic resustant bacteria to mankind.

To treat your tinnitus, your doctor will first try to identify any underlying, treatable condition that may be associated with your symptoms. If tinnitus is due to a health condition, your doctor may be able to take steps that could reduce the noise. Examples include: Earwax removal.

Patient Greg Grindley communicates with host Bryant Gumbel and his wife for the first time while undergoing deep brain stimulation surgery at University Hospital's Case Medical Center in Cleveland, Ohio.
➡ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/NatGeoSubscribe
About National Geographic:
National Geographic is the world's premium destination for science, exploration, and adventure. Through their world-class scientists, photographers, journalists, and filmmakers, Nat Geo gets you closer to the stories that matter and past the edge of what's possible.
Get More National Geographic:
Official Site: http://bit.ly/NatGeoOfficialSite
Facebook: http://bit.ly/FBNatGeo
Twitter: http://bit.ly/NatGeoTwitter
Instagram: http://bit.ly/NatGeoInsta
Greg's First In-Surgery Conversation | Brain Surgery Live
https://youtu.be/zvqV_2zncNU
National Geographic
https://www.youtube.com/natgeo