Top videos

The ACL is one of the four main ligaments within the knee that connect the femur to the tibia. The knee is essentially a hinged joint that is held together by the medial collateral (MCL), lateral collateral (LCL), anterior cruciate (ACL) and posterior cruciate (PCL) ligaments.
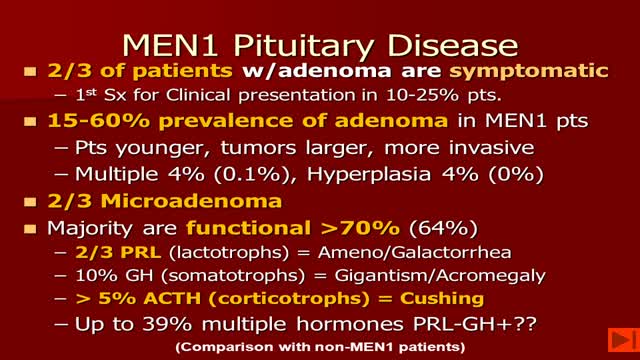
-MEN1 syndrome is composed of hyperparathyroidism, gastrinoma (pancreatic tumor) and pituitary tum or(remember the 3 Ps). Hyperparathyroidism in MEN1 is caused by hyperplasia of the parathyroid glands. Removal of 3 1/2 glands or total parathyroidectomy with autotransplantation is necessary.

Radiosurgery: Radiosurgery devices, such as the CyberKnife Robotic Radiosurgery System, offer patients a new option for the treatment of lung cancer. The CyberKnife® System is used to treat lung cancer patients who cannot tolerate surgery, have an inoperable tumor, or are seeking an alternative to surgery.
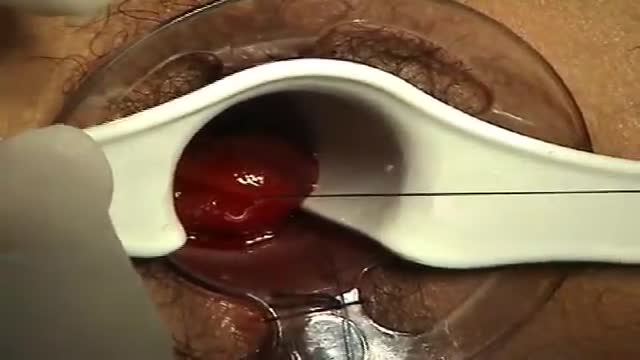
A surgeon begins the PPH stapled hemorrhoidectomy by inserting a circular anal dilator and obturator into the anal canal and then securing the dilator in place with four sutures. The surgeon then inserts a PPH anoscope into the obturator. Next, he places a circumferential purse-string suture of 2-0 Monocryl on a UR-6 needle 4 cm proximal to the dentate line. The surgeon opens a PPH stapler and places its anvil across the purse string. The stapler is then closed and fired; it is held closed for two minutes to improve hemostasis. Prior to firing the stapler in a female patient, the surgeon places a gloved finger in the vagina to ensure the vaginal mucosa and rectal-vaginal septum are not trapped within the jaws of the closed stapler. The surgeon then opens and removes the stapler.
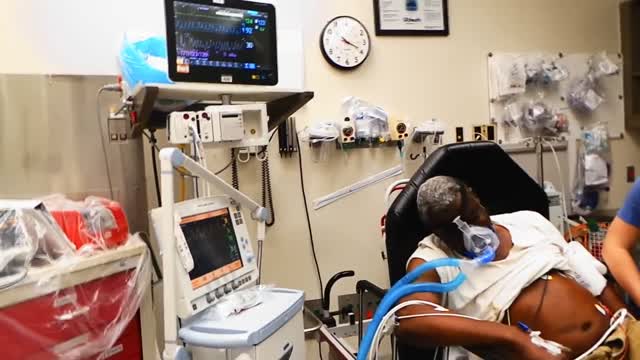
Pulmonary edema is almost always treated in the emergency room or hospital. You may need to be in an intensive care unit (ICU). Oxygen is given through a face mask or tiny plastic tubes are placed in the nose. A breathing tube may be placed into the windpipe (trachea) so you can be connected to a breathing machine (ventilator) if you cannot breathe well on your own. The cause of edema should be identified and treated quickly. For example, if a heart attack has caused the condition, it must be treated right away. Medicines that may be used include: Diuretics that remove excess fluid from the body Medicines that strengthen the heart muscle, control the heartbeat, or relieve pressure on the heart

How do you make a working human heart? Scientists can turn stem cells into beating heart cells, but getting them to organize into a 3D heart requires a scaffold. At the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, Harald Ott and his team are reusing the scaffold that nature provides. They’re stripping away all the living cells from dead hearts, before filling in the leftover matrix with healthy new cells. In this video, Brendan Maher finds out how the technique could be used to develop parts of the heart, like the aortic root and valve, for transplant.

The Epley Maneuver for Vertigo can be very effective at relieving vertigo symptoms, but it’s a procedure that should be performed by a physical therapist or other health care professional. This video is for demonstration purposes only. See Doctor Jo’s blog post about the Epley

To treat your tinnitus, your doctor will first try to identify any underlying, treatable condition that may be associated with your symptoms. If tinnitus is due to a health condition, your doctor may be able to take steps that could reduce the noise. Examples include: Earwax removal.

If levels of both vitamins are extremely high, there is more than a 17-fold greater risk that a child will develop autism, the researchers said. Most of the women in the study said they took multivitamins — which would include folic acid and vitamin B12 — throughout their pregnancy.
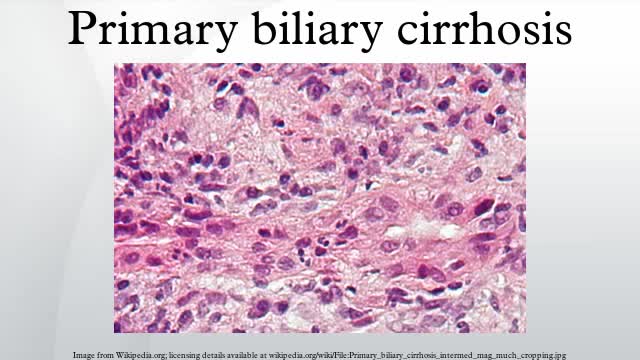
Primary biliary cirrhosis, sometimes called PBC, is a disease in which the bile ducts in your liver are slowly destroyed. Bile, a fluid produced in your liver, plays a role in digesting food and helps rid your body of worn-out red blood cells, cholesterol and toxins. When bile ducts are damaged, as in primary biliary cirrhosis, harmful substances can build up in your liver and sometimes lead to irreversible scarring of liver tissue (cirrhosis). Primary biliary cirrhosis is considered an autoimmune disease, in which the body turns against its own cells. Researchers think it is triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Primary biliary cirrhosis usually develops slowly and medication can slow its progression, especially if treatment begins early.
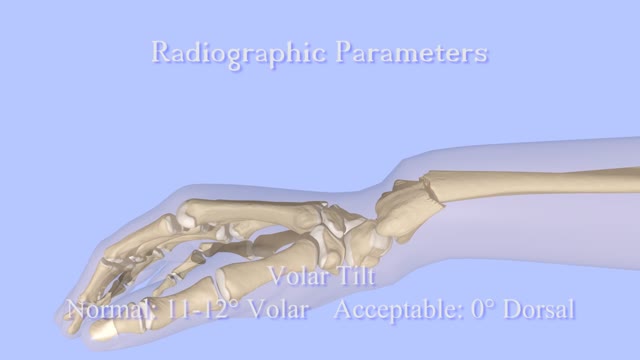
Closed Reduction of Distal Radius Fractures - Discussion: (distal radius fracture menu) - closed reduction & immobilization in plaster cast remains accepted method of treatment for majority of stable distal radius frx; - unstable fractures will often lose reduction in the cast and will slip back to the pre-reduction position; - patients should be examined for carpal tunnel symptoms before and after reduction; - carpal tunnel symptoms that do not resolve following reduction will require carpal tunnel release; - cautions: - The efficacy of closed reduction in displaced distal radius fractures. - Technique: - anesthesia: (see: anesthesia menu) - hematoma block w/ lidocaine; - w/ hematoma block surgeon should look for "flash back" of blood from hematoma, prior to injection; - references: - Regional anesthesia preferable for Colles' fracture. Controlled comparison with local anesthesia. - Neurological complications of dynamic reduction of Colles' fractures without anesthesia compared with traditional manipulation after local infiltration anesthesia. - methods of reduction: - Jones method: involves increasing deformity, applying traction, and immobilizing hand & wrist in reduced position; - placing hand & wrist in too much flexion (Cotton-Loder position) leads to median nerve compression & stiff fingers; - Bohler advocated longitudinal traction followed by extension and realignment; - consider hyper-extending the distal fragment, and then translating it distally (while in extended position) until it can be "hooked over" proximal fragment; - subsequently, the distal fragment can be flexed (or hinged) over the proximal shaft fragment; - closed reduction of distal radius fractures is facilitated by having an assistant provide counter traction (above the elbow) while the surgeon controls the distal fragment w/ both hands (both thumbs over the dorsal surface of the distal fragment); - flouroscopy: - it allows a quick, gentle, and complete reduction; - prepare are by prewrapping the arm w/ sheet cotton and have the plaster or fibroglass ready; - if flouroscopy is not available, then do not pre-wrap the extremity w/ cotton; - it will be necessary to palpate the landmarks (outer shaped of radius, radial styloid, and Lister's tubercle, in order to judge success of reduction; - casting: - generally, the surgeon will use a pre-measured double sugar sugar tong splint, which is 6-8 layers in thickness; - more than 8 layers of plaster can cause full thickness burns: - reference: Setting temperatures of synthetic casts. - position of immobilization - follow up: - radiographs: - repeat radiographs are required weekly for 2-3 weeks to ensure that there is maintenance of the reduction; - a fracture reduction that slips should be considered to be unstable and probably require fixation with (pins, or ex fix ect.) - there is some evidence that remanipulation following fracture displacement in cast is not effective for these fractures; - ultimately, whether or not a patient is satisfied with the results of non operative treatment depends heavily on th
6 987 24 MORE How Does Anesthesia Work? Credit: itsmejust | Shutterstock If you’ve ever had surgery, unless you are super tough, you’ve gone through it with the benefit of anesthetics. But, how do these body-numbing elixirs work? Prior to the invention of anesthesia in the mid-1800s, surgeons had to hack off limbs, sew up wounds and remove mysterious growths with nothing to dull the patient's pain but opium or booze. While these drugs may have numbed the patient, they didn’t always completely block the pain, or erase the memory of it. Since then, doctors have gotten much better at putting us out with drug combinations that ease pain, relax muscles and, in some cases, put us in a deep state of hypnosis that gives us temporary amnesia. Today, there are two primary types of anesthesia drugs: those that knockout the whole body (general) and those that only numb things up locally.

The word enuresis is derived from a Greek word (enourein) that means “to void urine.” It can occur either during the day or at night (though some restrict the term to bedwetting that occurs at night). Enuresis can be divided into primary and secondary forms.

Rotator cuff pain commonly causes local swelling and tenderness in the front of the shoulder. You may have pain and stiffness when you lift your arm. There may also be pain when the arm is lowered from an elevated position. Beginning symptoms may be mild. Patients frequently do not seek treatment at an early stage. These symptoms may include: Minor pain that is present both with activity and at rest Pain radiating from the front of the shoulder to the side of the arm Sudden pain with lifting and reaching movements Athletes in overhead sports may have pain when throwing or serving a tennis ball As the problem progresses, the symptoms increase: Pain at night Loss of strength and motion Difficulty doing activities that place the arm behind the back, such as buttoning or zippering If the pain comes on suddenly, the shoulder may be severely tender. All movement may be limited and painful.
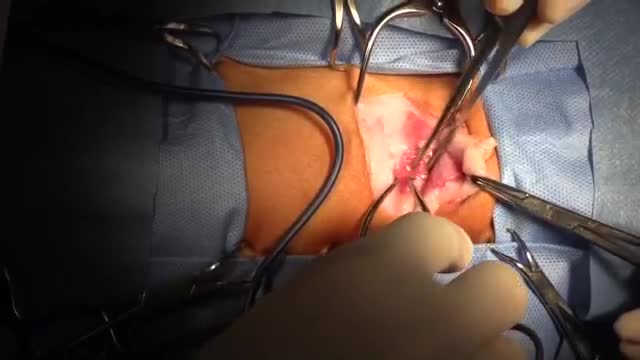
This video: Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a persistent opening between two major blood vessels leading from the heart. The opening, called the ductus arteriosus, is a normal part of a baby's circulatory system before birth that usually closes shortly after birth. If it remains open, however, it's called a patent ductus arteriosus. A small patent ductus arteriosus often doesn't cause problems and might never need treatment. However, a large patent ductus arteriosus left untreated can allow poorly oxygenated blood to flow in the wrong direction, weakening the heart muscle and causing heart failure and other complications. Treatment options for a patent ductus arteriosus include monitoring, medications and closure by cardiac catheterization or surgery.

EART (Health Education and Rescue Training) Wilderness First Aid is an intensive course that covers patient examination and evaluation, body systems and anatomy, wound care, splinting, environmental emergencies, and backcountry medicine. Hands-on simulations provide first-hand training in treating patients. This is an excellent course taught by experienced Wilderness First Responders and Emergency Medical Technicians and is highly recommended to all wilderness travelers. People who pass the courses will receive a Wilderness First Aid certification from the Emergency Care and Safety Institute (ECSI) which is good for 2 years. Participants who successfully pass CPR and HEART Wilderness First Aid will have met the First Aid requirements for OA Leader Training.