Top videos
Routine pelvic exams are important for good reproductive health. A woman should have her first GYN exam when she first thinks about becoming sexually active, when she becomes sexually active or when she turns 18.
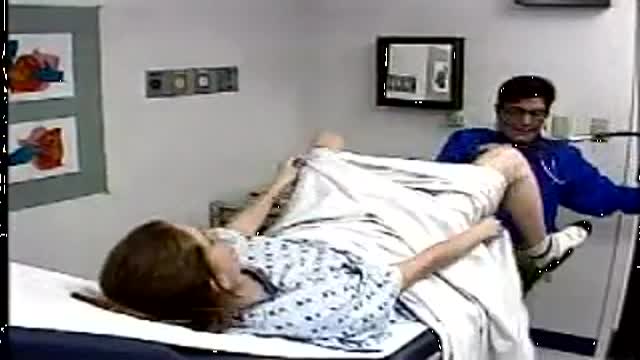
At the gynecologist, you will have a short general physical exam, including a breast exam. You will wear a hospital gown and nothing else. For the actual pelvic examination, you will lie down on an examination table with your feet resting in elevated “stirrups” (props that support your legs in the air). Stirrups might look a little scary, but they are there to keep you comfortable. Your legs will be spread apart, with your knees falling to each side so that your vagina is exposed. You may feel uncomfortable, but relax and realize that everyone goes through this.
External Exam
The practitioner will visually examine your vulva for discoloration, irritation, swelling and other abnormalities, and will gently feel for glands.
Internal Exam
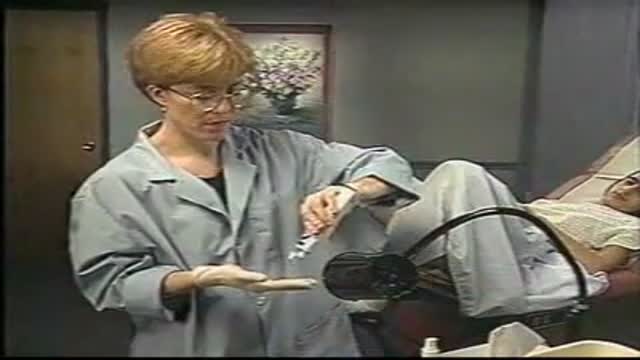
There are two parts to the internal exam. The first involves a speculum, a metal or plastic instrument that the practitioner inserts into the vagina. The speculum is shaped like a duck’s bill, and once it is inserted into the vaginal canal, it is gently widened to spread the interior vaginal walls (this is not painful). As the vaginal walls are spread, the practitioner is able to see the walls of the vagina itself, and up the vaginal canal to the cervix. When viewing the vaginal canal and the cervix, the practitioner can look for discoloration, abnormal discharge, lesions, growths and signs of infection. It is possible for you to look at your own cervix during this process by propping yourself up on your elbows and using a mirror. Some practitioners ask if you would like to do this, but feel free to ask to if she doesn’t mention it first.
Pap Smear
Next the practitioner will take a pap smear. She/he uses a long-stemmed cotton swab to collect a sample of cells in the cervix. Some women feel a slight cramping sensation when their cervix is touched. The collected cells are smeared onto a slide and sent to a lab for testing and examination. The pap smear is extremely important for spotting abnormalities in the cervix which may indicate infection or disease.
STD Testing
If you are sexually active, the practitioner will test for STDs. The gynecologist will swab the inside of the cervix with a long cotton swab. The speculum is then taken out of the vagina. The samples are sent to a laboratory for various STD testing. The tests will probably take a couple days. Ask when your results will be available so you can call. If you want to be tested for HIV, syphilis, genital herpes or hepatitis you need to have blood taken. They can do that as well, but you will need to ask since it is not usually routine.
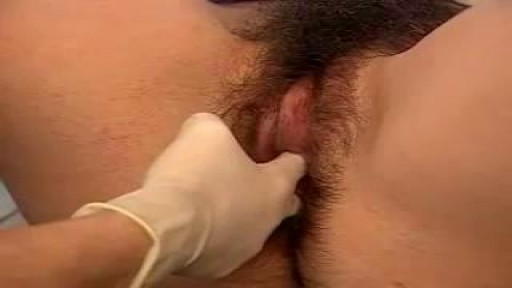
Manual Exam
The second part of the pelvic exam is called the manual or bi-manual exam. The practitioner will insert one or two fingers into your vagina and press with her/his other hand on the outside of your lower abdomen. They will use a lubricant on their fingers so it is more comfortable. The person can then feel the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries, and check for any swelling or tenderness. Once the doctor is finished checking your uterus and ovaries, the exam is complete. The entire pelvic exam (the parts involving your vagina, cervix, uterus, and ovaries) takes 3 to 5 minutes to complete.
Watch that Full Female Body Medical Anatomy Autopsy
http://www.proctoscopeexam.com This is a demonstration of a proctoscope examination of the rectum.
Traditional African treatment for infertility
Dr Chris Steele demonstrates a breast examination on a live model. This shows how to check yourself for early signs of tumours, cysts and other symptoms of breast cancer.
Pelvic Exam Video
Child birth in squatting positions. The most comfortable position for the mother
ectal exam is an internal examination of the rectum such as by a physician or other healthcare professional.
The digital rectal examination (DRE, Latin palpatio per anum or PPA) is a relatively simple procedure. The patient is placed in a position where the anus is accessible and relaxed (lying on the side, squatting on the examination table, bent over the examination table, etc). The physician inserts a gloved and lubricated finger into the rectum through the anus and palpates the insides.
The DRE is inadequate as a screening tool for colorectal cancer because it examines less than 10% of the colorectal mucosa; colonoscopy is preferred. However, it's an important part of a general examination, as many tumors or other diseases are made manifest in the distal part of the rectum.
This examination may be used: * for the diagnosis of rectal tumors and other forms of cancer; * in males, for the diagnosis of prostatic disorders, notably tumors and benign prostatic hyperplasia; * for the diagnosis of appendicitis or other examples of an acute abdomen (i.e. acute abdominal symptoms indicating a serious underlying disease); * for the estimation of the tonicity of the anal sphincter, which may be useful in case of fecal incontinence or neurologic diseases, including traumatic spinal cord injuries; * in females, for gynecological palpations of internal organs * for examination of the hardness and color of the feces (ie. in cases of constipation, and fecal impaction); * prior to a colonoscopy or proctoscopy. * to evaluate haemorrhoids
The DRE is frequently combined with an FOBT (fecal occult blood test), which may be useful for diagnosing the etiology of an anemia and/or confirming a gastrointestinal bleed.
Sometimes proctoscopy may also be part of a rectal examination.
Inguinal hernia Diagram of an indirect, scrotal inguinal hernia ( median view from the left). Diagram of an indirect, scrotal inguinal hernia ( median view from the left). By far the most common hernias (up to 75% of all abdominal hernias) are the so-called inguinal hernias. For a thorough understanding of inguinal hernias, much insight is needed in the anatomy of the inguinal canal. Inguinal hernias are further divided into the more common indirect inguinal hernia (2/3, depicted here), in which the inguinal canal is entered via a congenital weakness at its entrance (the internal inguinal ring), and the direct inguinal hernia type (1/3), where the hernia contents push through a weak spot in the back wall of the inguinal canal. Inguinal hernias are more common in men than women while femoral hernias are more common in women.
Position the patient with her buttocks just at the edge or just over the edge of the exam table. If she is not down far enough, inserting the speculum can be more difficult for you and uncomfortable for her.
http://www.hypodermic-injection.com This is a demonstration of an IM hypodermic injection administered in the gluteus maximus muscle. The patient is in the prone position.
Physical exam by a urologist including kidney, testicular and prostate exam.
Watch that Female Recto-vaginal Exam Video
http://www.hypodermic-injection.com This is a demonstration of an IM injection being administered in the patient's buttocks while bending over the edge of the exam table.
A digital rectal examination (DRE) is a simple procedure doctors use to examine the lower rectum and other internal organs. A DRE is done for a number of reasons. It's a quick, easy way to check the health of a man's prostate gland. It can detect conditions like an enlarged prostate
Bimanual pelvic exam of a female, using two fingers inside the vagina and one hand on the outside of the abdomen.
Orgasmic childbirth is a new variant of water birth delivery.
http://www.vaginal-ultrasound.com A demonstration of a vaginal ultrasound.
At Hutzel Women's Hospital, Dr. Giancarlo Mari performs breakthrough in-utero surgery to save the lives of high-risk twins developing with a rare "shared" circulatory problem. ~ Detroit Medical Center
The MORE subscribers we have the MORE unintentional ASMR videos we can post, so please SUBSCRIBE http://bit.ly/UASMR, hit that 🔔 and LIKE this video for more medical exam ASMR like this! So... here is the BEST medical exam ASMR on YouTube edited specifically for unintentional ASMR to become the best video to help fall asleep at night. Our medical exam ASMR playlist: http://bit.ly/MedicalASMR
🔴 Support the channel and get access to extra perks by becoming a member here: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCWCk81c_nQOsm5M-x
Try out the MOST comfortable sleep mask I've ever worn here ➜ https://bit.ly/MantaDiscount.
Prefer SOOTHING music for sleep? Here's what I use ➜ https://bit.ly/3lOPqe2
This hour long medical exam has a quiet doctor performing a routine medical exam with minimal talking. The video is 100% accidental ASMR and features a real doctor doing a head to toe assessment. This is honestly one of the best medical exam ASMR videos and on my all time favourite unintentional ASMR videos. This audio for this video has been significantly edited for maximum ASMR.
EXCLUSIVE: You can get 10% off any SleepPhones products with the code SLEEPNOW here: https://bit.ly/2YrrKQC
For the best unintentional ASMR and sleep aid videos we can't post here see http://ineedtosleepnow.com/
Medical ASMR: http://bit.ly/MedicalASMR
Female ASMR: http://bit.ly/FemaleASMR
Best of the best: http://bit.ly/BestUnintentionalASMR
Celeb ASMR: http://bit.ly/CelebASMR
Show and tell ASMR: http://bit.ly/ShowTellASMR
Relaxing interviews: http://bit.ly/InterviewsASMR
Original un-edited videos:
Part 1: https://youtu.be/S5tK3Ikb7ug
Part 2: https://youtu.be/m_-ALfUmmiA
WHAT IS UNINTENTIONAL ASMR?
https://ineedtosleepnow.com/what-is-u...
💤 For MORE of the Best (Intentional) ASMR videos on YouTube click here: https://goo.gl/mTsEBN
🙂 Finding, editing and uploading these videos does take some time and I try to upload a new video each night. If you find these videos useful, please consider supporting us by doing your Amazon shopping through our affiliate link: https://www.amazon.ca/shop/pur....eunintentionalasmrby
Best Microphone for recording ASMR: https://amzn.to/34WJhn2
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
WANT TO MAKE A RECOMMENDATION? Contact us via:
Facebook ► https://www.facebook.com/uASMR/
Twitter ► https://twitter.com/AccidentalASMR
Instagram ► https://www.instagram.com/pureunintentionalasmr/
See what's coming next by checking out our FB group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1649835798657192/
🔴 In case this channel is removed, please subscribe to our newsletter for updates on new videos locations: http://eepurl.com/ds-orr. We will never email you about anything other than a new channel.
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
More of the Pure ASMR channels:
Pure ASMR: http://bit.ly/PureASMR and hit that 🔔.
Pure Unintentional ASMR 2: https://bit.ly/PureUASMR2
Pure Natural ASMR: http://bit.ly/NatureASMR
Pure Audiobook ASMR: http://bit.ly/AudiobookChannel
Purr ASMR: http://bit.ly/CatASMR
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
NOTE: This video is being shared for #unintentionalASMR reasons only. The video has been edited from its original format for this purpose.
WHAT IS ASMR? http://ineedtosleepnow.com/what-is-asmr
ASMR definition: http://ineedtosleepnow.com/asmr-definition-what-is-the-definition-for-asmr
http://iNeedToSleepNow.com is a YouTube channel and website that curates calm softly spoken voices that serve as great unintentional #ASMR. This channel focuses primarily on soft speaking, calm softly spoken voices, unintentional ASMR interviews, relaxing voices, ASMR tingles and anything that helps you sleep.
Disclaimer: Some of these links are affiliate links where this channel could earn a small commission if you make a purchase. Shopping through these links is a great way to support the channel so we can keep making more videos for you. Thanks!