Top videos

Routine pelvic exams are important for good reproductive health. A woman should have her first GYN exam when she first thinks about becoming sexually active, when she becomes sexually active or when she turns 18.
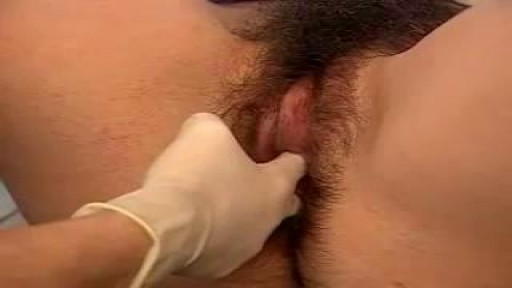
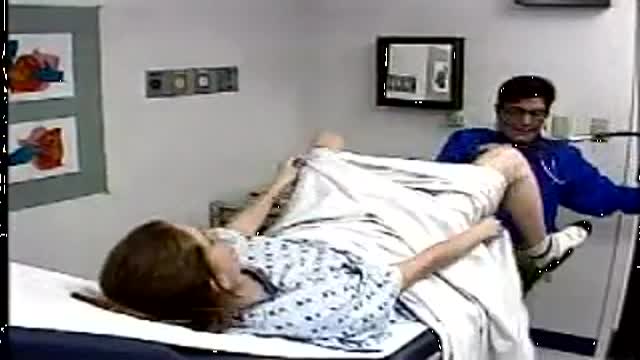
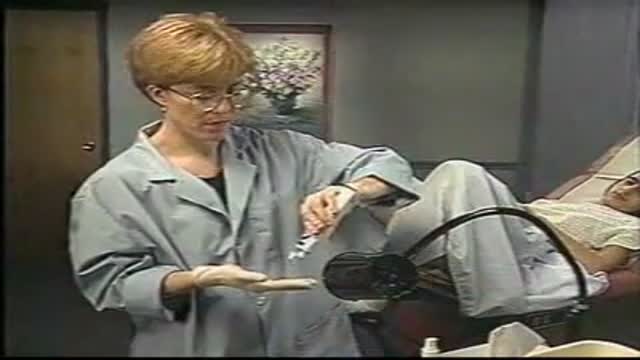
At the gynecologist, you will have a short general physical exam, including a breast exam. You will wear a hospital gown and nothing else. For the actual pelvic examination, you will lie down on an examination table with your feet resting in elevated “stirrups” (props that support your legs in the air). Stirrups might look a little scary, but they are there to keep you comfortable. Your legs will be spread apart, with your knees falling to each side so that your vagina is exposed. You may feel uncomfortable, but relax and realize that everyone goes through this.
External Exam
The practitioner will visually examine your vulva for discoloration, irritation, swelling and other abnormalities, and will gently feel for glands.
Internal Exam
There are two parts to the internal exam. The first involves a speculum, a metal or plastic instrument that the practitioner inserts into the vagina. The speculum is shaped like a duck’s bill, and once it is inserted into the vaginal canal, it is gently widened to spread the interior vaginal walls (this is not painful). As the vaginal walls are spread, the practitioner is able to see the walls of the vagina itself, and up the vaginal canal to the cervix. When viewing the vaginal canal and the cervix, the practitioner can look for discoloration, abnormal discharge, lesions, growths and signs of infection. It is possible for you to look at your own cervix during this process by propping yourself up on your elbows and using a mirror. Some practitioners ask if you would like to do this, but feel free to ask to if she doesn’t mention it first.
Pap Smear
Next the practitioner will take a pap smear. She/he uses a long-stemmed cotton swab to collect a sample of cells in the cervix. Some women feel a slight cramping sensation when their cervix is touched. The collected cells are smeared onto a slide and sent to a lab for testing and examination. The pap smear is extremely important for spotting abnormalities in the cervix which may indicate infection or disease.
STD Testing
If you are sexually active, the practitioner will test for STDs. The gynecologist will swab the inside of the cervix with a long cotton swab. The speculum is then taken out of the vagina. The samples are sent to a laboratory for various STD testing. The tests will probably take a couple days. Ask when your results will be available so you can call. If you want to be tested for HIV, syphilis, genital herpes or hepatitis you need to have blood taken. They can do that as well, but you will need to ask since it is not usually routine.
Manual Exam
The second part of the pelvic exam is called the manual or bi-manual exam. The practitioner will insert one or two fingers into your vagina and press with her/his other hand on the outside of your lower abdomen. They will use a lubricant on their fingers so it is more comfortable. The person can then feel the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries, and check for any swelling or tenderness. Once the doctor is finished checking your uterus and ovaries, the exam is complete. The entire pelvic exam (the parts involving your vagina, cervix, uterus, and ovaries) takes 3 to 5 minutes to complete.

#tummytucksurgery #tummytuckcost #tummytuckresult #drprashantyadav #dezireclinicindia #cosmeticsurgery #plasticsurgery #weightloss #tummytuck #abdominoplasty
Tummy tuck surgery | Weight Loss
Tummy Tuck Marking before surgery
Tummy Tuck Surgery , Tummy Tuck Surgery Cost, Weight Loss with Tummy tuck surgery, tummy tuck surgery result , tummy tuck cost, Abdominoplasty
📞 Delhi - +91 8956880644 | Pune - +91 9222122122 | Bangalore- 8971224700 | Gurugram - 9272007896 | Ahmedabad - 9711162746
Subscribe to our Channel https://www.youtube.com/dezireclinic
💸Cost: call for free consultation | Zero % interest finance options
Subscribe on YouTube : https://youtube.com/dezireplas....ticsurgerycenter?sub
Subscribe on YouTube https://youtube.com/dezireclin....ic?sub_confirmation=
📸 https://www.instagram.com/drprashantdezireclinic/
🌐 http://dezireclinic.in/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/drprashantmch/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/drprashantmch
Email: dezireclinicindia@gmail.com
WHY choose Dezire plastic surgery center?
We are leading cosmetic surgery centre in India leading by Dr Prashant Yadav . See hundreds of various cosmetic surgery and real feedback videos. Watch live surgery to gain confidence before deciding surgery
Dr. Prashant Yadav
M.S., M.Ch. (Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery)
#plasticsurgery #cosmeticsurgery #dezireclinicindia #drprashantyadav #dezireplasticsurgerycenter
ectal exam is an internal examination of the rectum such as by a physician or other healthcare professional.
The digital rectal examination (DRE, Latin palpatio per anum or PPA) is a relatively simple procedure. The patient is placed in a position where the anus is accessible and relaxed (lying on the side, squatting on the examination table, bent over the examination table, etc). The physician inserts a gloved and lubricated finger into the rectum through the anus and palpates the insides.
The DRE is inadequate as a screening tool for colorectal cancer because it examines less than 10% of the colorectal mucosa; colonoscopy is preferred. However, it's an important part of a general examination, as many tumors or other diseases are made manifest in the distal part of the rectum.
This examination may be used: * for the diagnosis of rectal tumors and other forms of cancer; * in males, for the diagnosis of prostatic disorders, notably tumors and benign prostatic hyperplasia; * for the diagnosis of appendicitis or other examples of an acute abdomen (i.e. acute abdominal symptoms indicating a serious underlying disease); * for the estimation of the tonicity of the anal sphincter, which may be useful in case of fecal incontinence or neurologic diseases, including traumatic spinal cord injuries; * in females, for gynecological palpations of internal organs * for examination of the hardness and color of the feces (ie. in cases of constipation, and fecal impaction); * prior to a colonoscopy or proctoscopy. * to evaluate haemorrhoids
The DRE is frequently combined with an FOBT (fecal occult blood test), which may be useful for diagnosing the etiology of an anemia and/or confirming a gastrointestinal bleed.
Sometimes proctoscopy may also be part of a rectal examination.
![Female Foley Insertion (Urinary Catheter) [How to Insert Nursing Skills]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Mq4Yh0-iozY/maxresdefault.jpg)
Pass your tests and improve your grades with the below FREE resources:
1) A FREE 140 Must Know Meds book
Click here to get your FREE copy of the 140 Must Know Meds Book: https://bit.ly/41rxSt0
2) A FREE test-taking tips webinar
Join us for our free test-taking tips webinar to boost your exam scores: https://bit.ly/nursingtesttaking
You can now test your knowledge with a free lesson quiz on NURSING.com!
Click here to take a free quiz: https://bit.ly/3HwJr8t
FREE Nursing School Cheat Sheets at: http://www.NURSING.com
Get the full lesson on Female Foley Insertion here:
https://nursing.com/lesson/ski....lls-03-01-inserting-
Get the Male Foley Insertion lesson here:
https://nursing.com/lesson/ski....lls-03-02-inserting-
Get the Sterile glove application lesson here:
https://nursing.com/lesson/ski....lls-01-04-sterile-gl
Check out our new Nurse Care Plan Lessons here:
https://bit.ly/3BPRfPL
Get Access to Thousands of Lessons here:
https://nursing.com/courses/
Welcome to the NURSING Family, we call it the most supportive nursing cohort on the planet.
At NURSING.com, we want to help you remove the stress and overwhelm of nursing school so that you can focus on becoming an amazing nurse.
Check out our freebies and learn more at: (http://www.nursing.com)
Female Foley Insertion (Urinary Catheter)- Nursing Skills
In this video, we’re going to look at inserting a Foley catheter in a female. Of course make sure you’ve verified your order and told the patient what’s happening. You’ll also typically want to perform perineal care before you start. Then, you’ll want to assist the patient into the appropriate position. For females, that’s supine with their knees bent and feet close to their hips – allowing their knees to fall to the side. You may need a helper to help hold the patient in this position. We love you guys! Go out and be your best selves today! And, as always, happy nursing!
Bookmarks:
0.05 Female Foley insertion introduction
0.15 Patient positioning
0.27 Opening the sterile kit
1.41 Setting up the sterile field
2.25 Prepping the remaining Foley kit items
2.34 Catheter lubrication
3.00 Saline syringe attachment
3.10 Iodine, swabs and cleansing the area
3.52 Catheter insertion (into urethra)
4.06 Balloon inflation
4.25 Final catheter setting
4.31 Securing the catheter and bag
4.48 Discarding your supplies
5.00 Documentation
5.08 Foley insertion outro
Visit us at https://nursing.com/medical-disclaimer/ for disclaimer information.
NCLEX®, NCLEX-RN® are registered trademarks of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, INC. and hold no affiliation with NURSING.com.

EART (Health Education and Rescue Training) Wilderness First Aid is an intensive course that covers patient examination and evaluation, body systems and anatomy, wound care, splinting, environmental emergencies, and backcountry medicine. Hands-on simulations provide first-hand training in treating patients. This is an excellent course taught by experienced Wilderness First Responders and Emergency Medical Technicians and is highly recommended to all wilderness travelers. People who pass the courses will receive a Wilderness First Aid certification from the Emergency Care and Safety Institute (ECSI) which is good for 2 years. Participants who successfully pass CPR and HEART Wilderness First Aid will have met the First Aid requirements for OA Leader Training.