Top videos

A parasitic twin (also known as an asymmetrical or unequal conjoined twin) is the result of the processes that produce vanishing twins and conjoined twins, and may represent a continuum between the two. Parasitic twins occur when a twin embryo begins developing in utero, but the pair does not fully separate, and one embryo maintains dominant development at the expense of the other. Unlike conjoined twins, one ceases development during gestation and is vestigial to a mostly fully-formed, otherwise healthy individual twin. The undeveloped twin is defined as parasitic, rather than conjoined, because it is incompletely formed or wholly dependent on the body functions of the complete fetus. The independent twin is called the autosite.

Video giving an overview of histology, slide preparation, histological stains, and types of microscopy. This video is a part of our Histology Video Course (https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDynxT
Specific topics: what is histology, general composition of tissues, histotechnology: how histology slides are prepared, histology stains, immunohistochemistry, light microscopy vs electron microscopy, and pro tips for learning histology
Additional YouTube Content
Anatomy Videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDz2dK
Biochemistry videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDzCUC
DaVinci Cases Videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDyJUl
The DaVinci Hour Podcast: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDwSm9
DaVinci Academy Website: https://www.dviacademy.com/
The heart weighs between 7 and 15 ounces (200 to 425 grams) and is a little larger than the size of your fist. By the end of a long life, a person's heart may have beat (expanded and contracted) more than 3.5 billion times. In fact, each day, the average heart beats 100,000 times, pumping about 2,000 gallons. Your heart is located between your lungs in the middle of your chest, behind and slightly to the left of your breastbone (sternum). A double-layered membrane called the pericardium surrounds your heart like a sac. The outer layer of the pericardium surrounds the roots of your heart's major blood vessels and is attached by ligaments to your spinal column, diaphragm, and other parts of your body. The inner layer of the pericardium is attached to the heart muscle. A coating of fluid separates the two layers of membrane, letting the heart move as it beats. Your heart has 4 chambers. The upper chambers are called the left and right atria, and the lower chambers are called the left and right ventricles. A wall of muscle called the septum separates the left and right atria and the left and right ventricles. The left ventricle is the largest and strongest chamber in your heart. The left ventricle's chamber walls are only about a half-inch thick, but they have enough force to push blood through the aortic valve and into your body.
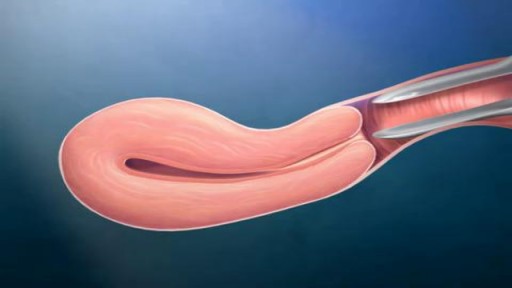
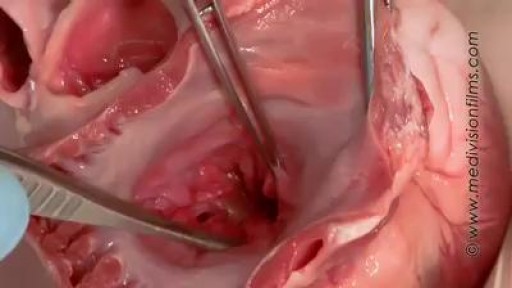
An intrauterine device (IUD), also known as intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD or ICD) or coil, is a small, often T-shaped birth control device that is inserted into a woman's uterus to prevent pregnancy. IUDs are one form of long-acting reversible birth control (LARC).
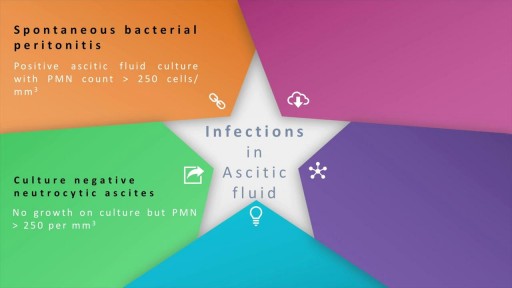
Ascites, the collection of fluid within the peritoneal space is caused due to a variety of causes including cirrhosis, cardiac causes, sinusoidal obstruction syndrome, tubercular peritonitis and pancreatitis, amongst others. Most commonly, the cause of ascots may be cirrhosis , which in turn, is most frequently causes by alcohol use, hepatitis C and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. At the heart of the ascitic fluid analysis is the serum albumin ascitic gradient, the differential diagnosis of which has been discussed in detail in this presentation. Both low SAAG and high SAAG ascites have been dealt with in some depth, with a brief overview of the management of these conditions

Shut the front door: Scientists have finally found the perfect breasts. No, they weren't hiding in the Amazon or roving solo across the Sahara (although we have no doubt there are women in both the Amazon and the Sahara who have magnificent mammaries); it turns out these perfect breasts were hiding in a plastic surgeon's office this whole time! Now, before you get all worked up, the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) would like you to know that the super-fake looking plastic breasts of yore are not actually what people think are most attractive now. According to a study published in the Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery—which involved asking over 1,300 people to look at pictures of naked boobies and rank them by hotness (stop laughing, this is serious research!)—people preferred a more "real" and "normal" look from their silicone, with the ideal breast shape having a 45:55 ratio. People said the best chests have 45 percent of the fullness above the nipple line and 55 percent of the fullness below, in a slightly teardrop shape. Researchers noted this preference remained consistent across gender, racial, and ethnic groups with the 45:55 ratio favored by 87 percent of women in their 30s, 90 percent of men, and 94 percent of plastic surgeons.

This video shows Prof Dan Reinstein, MD MA(Cantab) FRCSC DABO FRCOphth FEBO performing a ReLEx SMILE keyhole LASIK procedure using the latest surgical instrument that he helped to develop (Malosa MMSU1297 - Reinstein Lenticule Separator: http://www.malosa.com/en/reinstein-le...). This instrument enables the procedure to be performed with one instrument, through one 2mm incision, using only one sweep per plane, and taking about 30 seconds to separate and withdraw the lenticule, improving day 1 uncorrected vision over other lenticule extraction techniques that require more corneal manipulation.
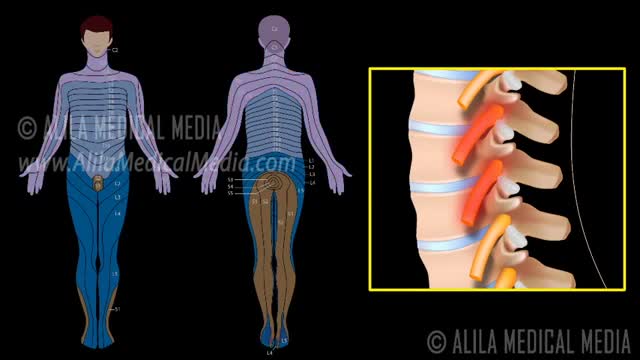
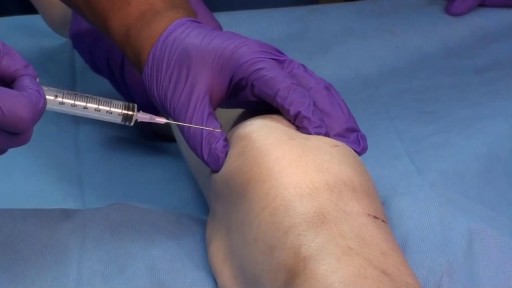
A nerve root block is an injection of local anesthetic (numbing medicine) and steroid injected under X-ray guidance into the area where the nerve exits the spinal column. A nerve root block is usually ordered by your doctor for pain in the arm or leg that follows the path of a single nerve. A nerve root block may be diagnostic (a test to determine the source of your pain) and/or therapeutic (to relieve your pain). If you get a period of sustained pain relief from the injection, the block may be repeated. Sometimes the block is done to help identify whether or not surgery might be helpful and at what level such surgery might be most helpful.

Today I will discuss about hemodialysis.
Start with a free 3-day trial at ReMarNurse.com/FREE
Follow & Subscribe for more weekly nursing and NCLEX content every Monday and Wednesday with Regina MSN, RN!
00:00 Introduction
02:53 Hemodialysis
06:06 Dialysis Apparatus
07:59 Dialysis Mechanism
13:27 Vascular Access
18:55 Nursing Considerations
25:07 Nursing Management for HD
27:57 NCLEX Practice Questions
Hemodialysis is a procedure where a dialysis machine and a special filter called an artificial kidney, or a dialyzer, are used to clean your blood.
I will also discuss about hemodialysis procedure, how hemodialysis machine works and its benefits for patients.
If you're interested in learning more about hemodialysis, or if this just seems like something you should know for nursing school or for the NCLEX exam, check out this video!
Join the #1 community of nursing students on the planet with 12,000+ students studying now inside of the NCLEX Virtual Trainer review on sale now at http://www.ReMarNurse.com
► Subscribe to JOIN the ReMar YouTube Channel: http://bit.ly/ReMar-Subscription
Your NCLEX RN & LPN Study Tools:
► Get NCLEX Virtual Trainer: http://www.ReMarNurse.com/NCLEXVT
► Get the Question Bank: http://www.ReMarNurse.com/NCLEXQBank
► Get Quick Facts for NCLEX: http://bit.ly/QuickFactsNCLEX
Get MORE from Regina MSN, RN:
► WATCH MORE: http://bit.ly/PassNCLEXPlayList/
► GET THE PODCAST: https://remarnurse.podbean.com/
► WATCH LESSONS: http://bit.ly/ReMarNCLEXLectures/
► FOLLOW ReMar on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/ReMarNurse/
► LIKE ReMar on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ReMarReview/
#nursingstudent #hemodialysis #nursing #remarreview
ReMar Review features weekly NCLEX review questions and lectures from Regina M. Callion MSN, RN. ReMar is the #1 content-based NCLEX review and has helped thousands of repeat-testers pass NCLEX with a 99.2% student success rate!
ReMar focuses on 100% core nursing content and as a result, has the best review to help nursing students pass boards - fast!
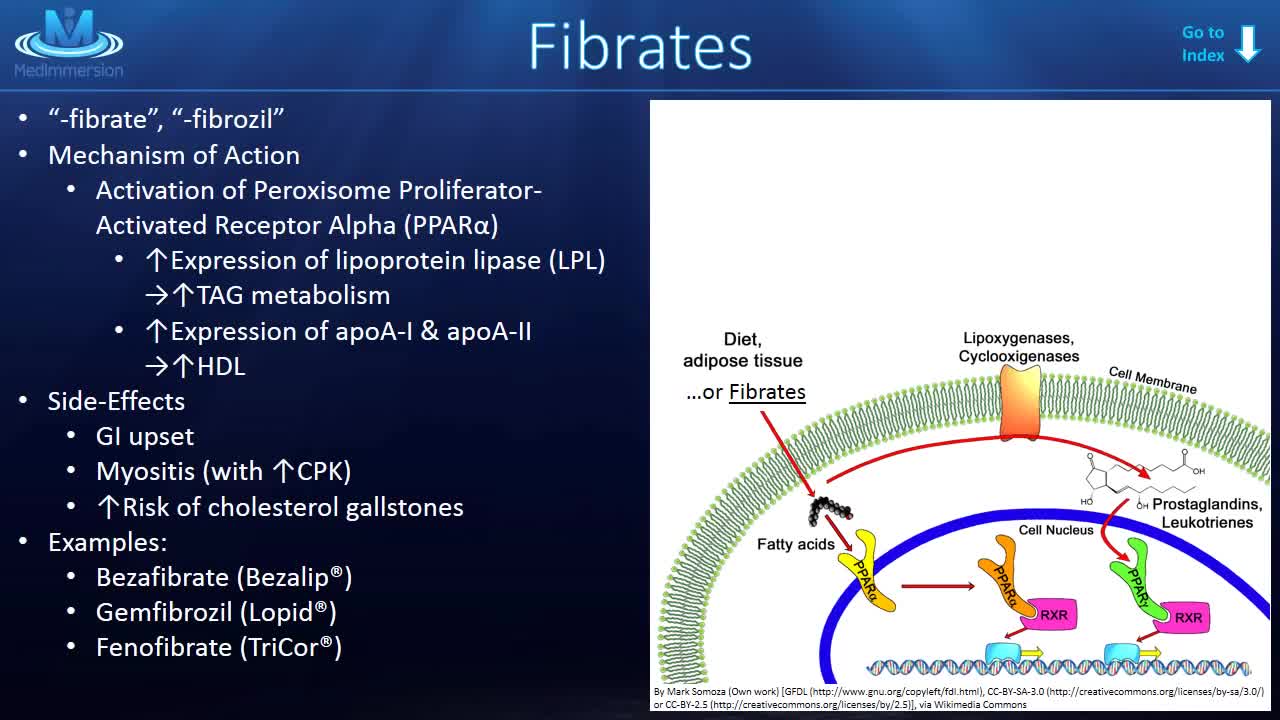
Lipid-Lowering Agents HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) These agents inhibit the rate-limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis by competitively inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase. Note the following: Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) reduction of 25%-60% Examples include Atorvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, pitavastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin Contraindications include hypersensitivity, active liver disease, pregnancy, lactation, coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (selected statins) Vitamin B3 Vitamin B3 inhibits very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) synthesis. Note the following: LDL reduction of 10% High-density lipoprotein (HDL) increase of 20% Example includes Niacin (nicotinic acid) Contraindications include hypersensitivity, liver disease, active peptic ulcer, severe hypotension, arterial bleeding Fibrates Fibrates enhance lipoprotein lipase, resulting in increased VLDL catabolism, fatty acid oxidation, and triglycerides elimination. They decrease hepatic extraction of free fatty acids. Note the following: LDL reduction of 15% Triglyceride reduction of 35% Examples include Gemfibrozil, fenofibrate, fenofibrate (micronized), fenofibric acid Contraindications include active liver disease, renal disease, primary biliary cirrhosis, gallbladder disease 2-Azetidiones These agents inhibit sterol transporter at brush border and, consequently, intestinal absorption of cholesterol. LDL reduction of 15% Example includes Ezetimibe Contraindications include hypersensitivity, coadministration with statins (if active liver disease) Bile acid sequestrants These agents lower cholesterol and LDL via bile duct sequestration. Note the following: LDL reduction of 15% Examples include Cholestyramine, colesevelam, colestipol Contraindications include biliary/bowel obstruction, serum triglycerides >300-500 mg/dL, history of hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis
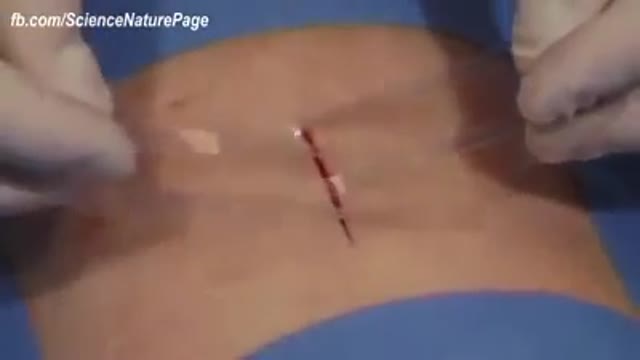
A fractured rib is usually a result of a fall or accident. Prolonged coughing and sports with repetitive movement, such as golf, also can cause a rib fracture. Symptoms include pain when taking a deep breath, pressing on the injured area, or bending or twisting the body. In most cases, fractured ribs usually heal on their own in one or two months. Pain relievers can make it easier to breathe deeply.

► Get a free NCLEX NGN sample test today: http://lectur.io/nclexrnsampletestyt
► Create your free account today: http://lectur.io/nurseregisteryt
► If you’re an nursing educator or faculty member, visit: http://lectur.io/nursytb2u
Want to know more about Clinical Skills?
Start watching our Clinical Skills course: http://lectur.io/fundamentalsclinical...
Lecturio is your smart tutor for nursing school: Learn the toughest NCLEX® topics with high-yield video lectures, integrated quiz questions, and more. Join Lecturio Nursing now: http://lectur.io/mg1
► INSTALL the free Lecturio app
iTunes Store: https://app.adjust.com/z21zrf
Play Store: https://app.adjust.com/b01fak
► CHECK OUT ALL NURSING COURSES:
Leadership Nursing: http://lectur.io/leadershipnursing
Dosage Calculation Nursing: http://lectur.io/dosagecalcnursing
Physiology Nursing: http://lectur.io/physiologynursing
Medical Surgical Nursing: http://lectur.io/medsurgnursing
Pharmacology Nursing: http://lectur.io/pharmacologynursing
NCLEX® Pharmacology Nursing: http://lectur.io/pharmnclexnursing
Pediatric Nursing: http://lectur.io/pediatricnursing
Study Skills Nursing: http://lectur.io/studyskillsnursing
Fundamentals of Nursing - Theory: http://lectur.io/fundamentalstheory
Fundamentals of Nursing - Clinical Skills: http://lectur.io/fundamentalsclinical...
Nursing Prerequisites: http://lectur.io/nursingprerequisites
Mental Health Nursing: http://lectur.io/mentalhealthnursing
Nursing Care of Childbearing Family: http://lectur.io/maternalnewbornnursing
► SUBSCRIBE to our YouTube channel: http://lectur.io/subscribenursing
► WATCH MORE ON YOUTUBE: http://lectur.io/nursingplaylists
► LET’S CONNECT:
Facebook: www.facebook.com/lecturio.nursing
Instagram: www.instagram.com/lecturio_nursing
TikTok: www.tiktok.com/@lecturio_nursing
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/lecturio-medical/