Top videos
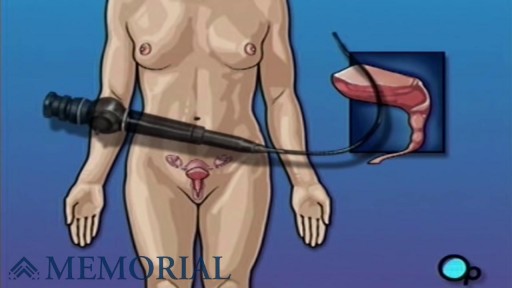
Cystoscopy (sis-TOS-kuh-pee) is a procedure that allows your doctor to examine the lining of your bladder and the tube that carries urine out of your body (urethra). A hollow tube (cystoscope) equipped with a lens is inserted into your urethra and slowly advanced into your bladder.

Men and women have anatomical differences when it comes to genitals, but orgasms are fundamentally very similar. The female orgasm lasts longer than the male, ranging about 20 seconds compared to 3 to 10 seconds, but men do experience more orgasms.

Macrobiopsy of breast lesions is a complicated procedure when performed with vacuum assisted biopsy tools. The Spirotome is a hand-held needle set that doesn't need capital investment, is ready to use and provides tissue samples of high quality in substantial amounts. In this way quantitative molecular biology is possible with one tissue sample. The Coramate is an automated version of this direct and frontal technology.
CORRECTION: After review of this video, it is clear that this video is of a baby who is near full term (40 weeks) based on the size. Late trimester "abortions" are defined only to viability of a baby (24 weeks) A 24 week baby is much smaller than this baby shown and by definition this is not a late "abortion" procedure. The proper labeling of this video should be management of a deceased breech baby with "head entrapment" as this was almost certainly a naturally occuring delivery and an OB nightmare (Reviewed by Dr. Frederick Bright)

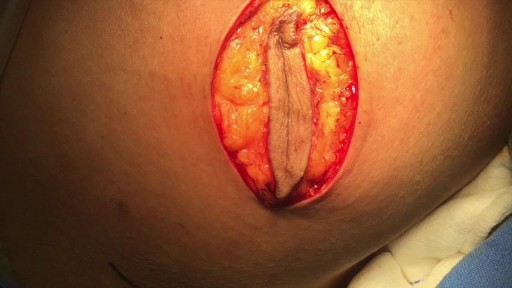
Vasectomy is a minor surgical procedure wherein the vasa deferentia of a man are severed, and then tied or sealed in a manner such to prevent sperm from entering the seminal stream (ejaculate). Typically done in an outpatient setting, a traditional vasectomy involves numbing (local anesthetic) of the scrotum after which 1 (or 2) small incisions are made, allowing a surgeon to gain access to the vas deferens.