Top videos
Ewing's sarcoma typically occurs in children and young adults. It often begins in the legs, bones of the pelvis, and arms. Bone pain, localized swelling, and tenderness are symptoms. In rare cases bone fractures may also be found. Treatments include chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation.

Head to SimpleNursing’s OFFICIAL website here: https://bit.ly/3TzGwF0
SimpleNursing memberships have 1,200+ animated videos, 900+ colorful study guides, 3,000+ practice questions, and more! See why SimpleNursing is trusted by over 1,000,000 nursing students.
Today’s video is all about peritoneal dialysis vs hemodialysis for Nursing Students and NCLEX Review.
Two common treatments for kidney failure are hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. With the right nursing assessments and interventions, your kidney failure patient can have a better chance at recovery.
We’re going over the roles that potassium plays in each of these two types of dialysis, as well as how stenosis monitoring can be used to prevent complications.
00:00 Introduction
01:10 Hyperkalemia in Hemodialysis
02:27 Assessing Fluid Status
03:35 Medications to Hold Before Hemodialysis
04:50 Medications Removed During Hemodialysis
05:45 Dialysis Disequilibrium Syndrome
07:20 Caring for a Fistula
09:12 Avoiding Fistula Complications
10:35 Peritoneal Dialysis
11:23 Peritonitis Risk
12:31 Respiratory Distress With Peritoneal Dialysis
13:39 Repositioning With Outflow Problems
#KidneyFailure #Dialysis #Hemodialysis #Peritonealdialysis

While the incidence of most sports-related injuries has been holding steady for the past two decades, injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) continue to increase significantly, particularly in female athletes. In fact, on many college teams, as many as 30 to 50 percent of young women have had an ACL injury during their high school careers in certain sports, such as basketball, soccer and gymnastics.
Watch pediatric orthopedic surgeons at Akron Children's Hospital perform arthroscopic surgery to replace a young athlete's ACL
Intramedullary nailing of the tibia with suprapatellar entry and semi-extended positioning makes it technically easier to nail the proximal and distal fractures. The purpose of this article was to describe a simple method for suprapatellar nailing (SPN). A step-by-step run through of the surgical technique is described, including positioning of the patient. There are as yet only a few clinical studies that illustrate the complications with this method, and there has been no increased frequency of intraarticular damage. Within the body of the manuscript, information is included about intraarticular damage and comments with references about anterior knee pain.
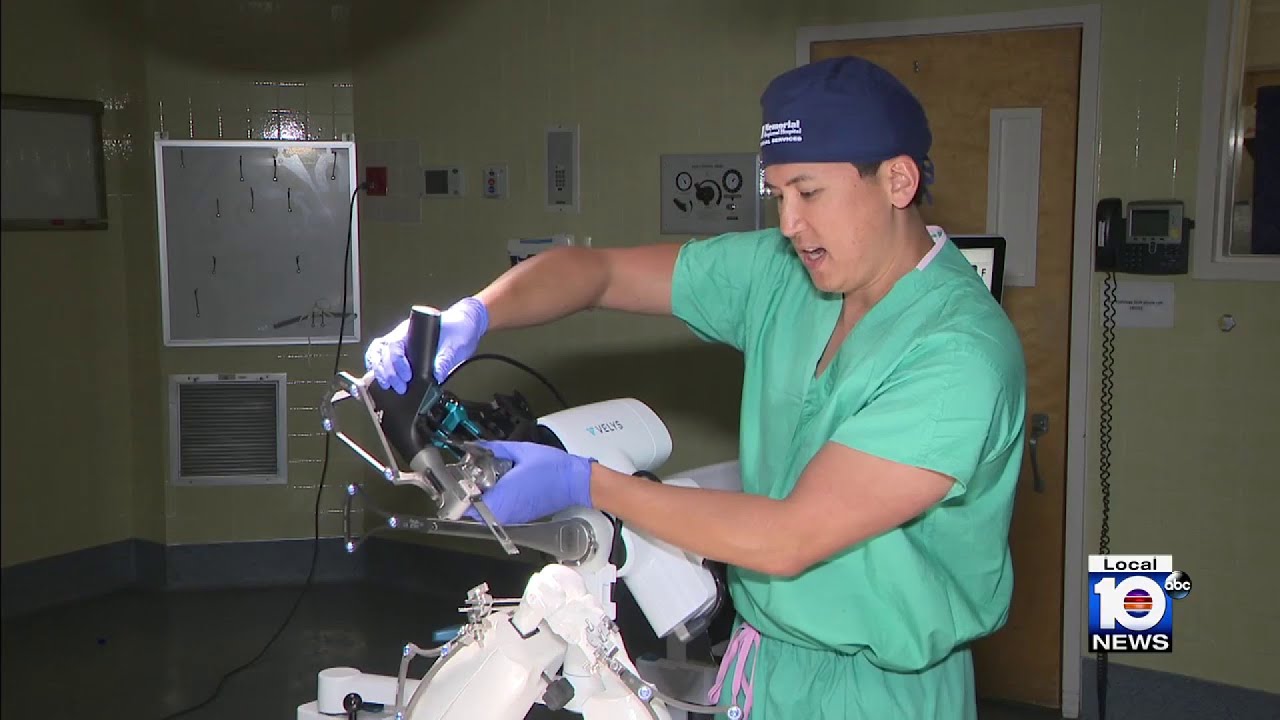

An estimated 900,000 knee replacements are performed in the U.S. every year, but experts say about 15% of patients aren’t totally pleased with the outcome. An advancement in technology is focused on improving those outcomes.
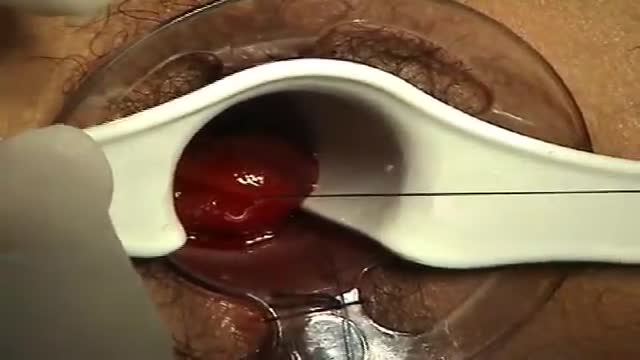
A surgeon begins the PPH stapled hemorrhoidectomy by inserting a circular anal dilator and obturator into the anal canal and then securing the dilator in place with four sutures. The surgeon then inserts a PPH anoscope into the obturator. Next, he places a circumferential purse-string suture of 2-0 Monocryl on a UR-6 needle 4 cm proximal to the dentate line. The surgeon opens a PPH stapler and places its anvil across the purse string. The stapler is then closed and fired; it is held closed for two minutes to improve hemostasis. Prior to firing the stapler in a female patient, the surgeon places a gloved finger in the vagina to ensure the vaginal mucosa and rectal-vaginal septum are not trapped within the jaws of the closed stapler. The surgeon then opens and removes the stapler.

Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. The main symptoms of arthritis are joint pain and stiffness, which typically worsen with age. The most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis causes cartilage — the hard, slippery tissue that covers the ends of bones where they form a joint — to break down. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that first targets the lining of joints (synovium). Uric acid crystals, infections or underlying disease, such as psoriasis or lupus, can cause other types of arthritis. Treatments vary depending on the type of arthritis. The main goals of arthritis treatments are to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.

Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome, an extra electrical pathway between your heart's upper and lower chambers causes a rapid heartbeat. The extra pathway is present at birth and fairly rare. The episodes of fast heartbeats usually aren't life-threatening, but serious heart problems can occur. Treatment can stop or prevent episodes of fast heartbeats. A catheter-based procedure (ablation) can permanently correct the heart rhythm problems. Most people with an extra electrical pathway experience no fast heartbeat. This condition, called Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern, is discovered only by chance during a heart exam. Although WPW pattern is often harmless, doctors might recommend further evaluation before children with WPW pattern participate in high-intensity sports.
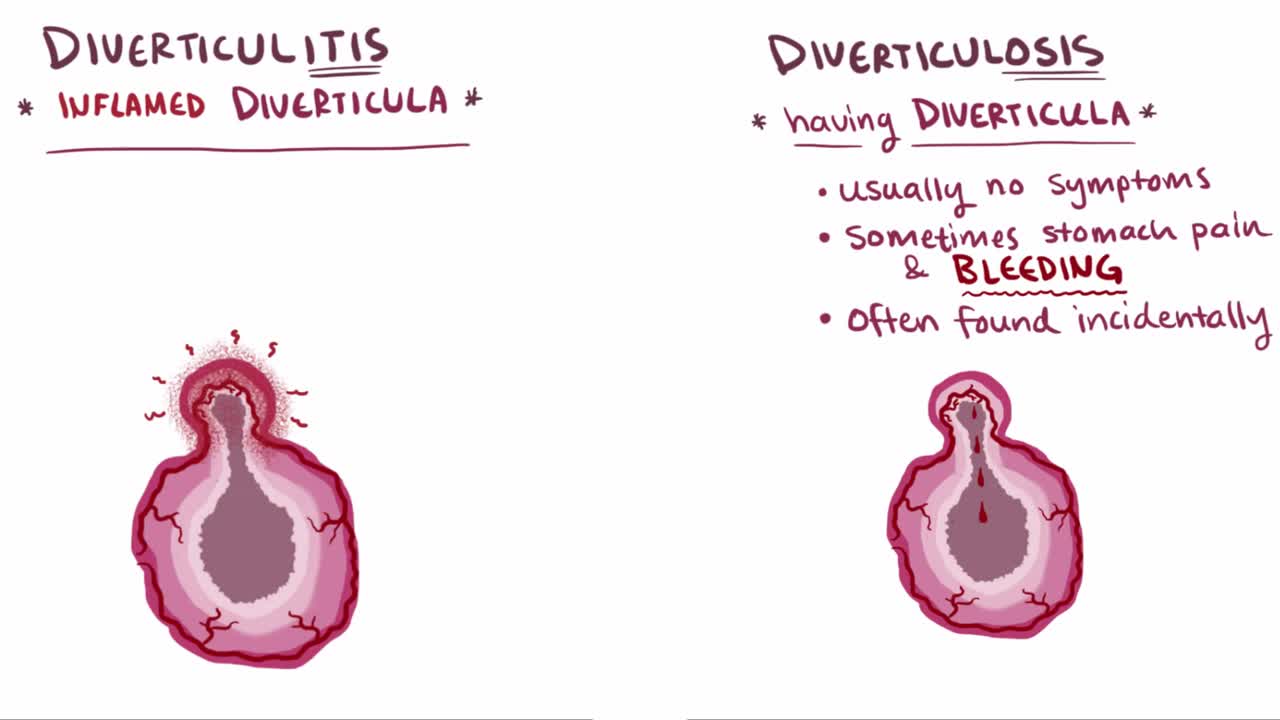
What are diverticula? Diverticula are outpouchings that most commonly happen in the sigmoid colon of the large intestine. The presence of a diverticulum is defined as diverticulosis, whereas diverticulitis describes an inflamed diverticulum

http://control-blood-sugar.good-info.co Normal Blood Sugar, Normal Blood Glucose, Low Blood Glucose, Foods That Lower Blood Sugar. happy to tell you that all these conditions of your uncontrollable blood sugar can be completely thrown away for good! Without expensive and dangerous surgery. Without leaving embarrassing pricking scars on your fingers. Without spending hundreds or even thousands of dollars on prescription drugs that not only empty your bank account. but leave big pharmaceutical executives richer from preying off your condition. The truth is, all of the blood sugar problems you’re having are completely reversible and curable. All of the frustrations and anxiety that comes with your condition can be a thing of the past. Plus, keep reading and you’ll find out the real truth to why prescription drugs are not helping your body control your blood sugar, but are guaranteed to ruin your body’s functions over time. you how to naturally and safely control your uncontrollable blood sugar in as little as 3 weeks. click here. http://control-blood-sugar.good-info.co