Top videos

Vial medication administration nursing skill. Learn techniques to withdraw medication from a vial using a syringe with a needle.
Medications can come in different forms, such as ampules, vials, tablets, capsules, and so forth. When withdrawing medication from a vial, there are a few things you'll want to know as a nursing student or nurse.
First, there are different needles that can be attached to the syringe. You can use a traditional needle with a beveled tip; you can use a blunt-tip needle to reduce the risk of needle sticks; or you can use a filter needle, which is sometimes required or recommended when drawing medication from a vial, particularly in cases of reconstituted medication.
When withdrawing from a vial, you'll want to do these things (assuming they fit with the protocols and manufacturer's instructions):
NOTE: Some medications or vaccines may require a different technique, so always consult with the manufacturer's instructions.
-gather your supplies
-perform hand hygiene
-clean the vial's top with alcohol prep
-attach the appropriate needle
-stick the needle using a technique to prevent coring of the rubber on the vial (start with 45 degree angle, and as you puncture the vial, rotate the needle to a 90 degree angle in one smooth motion).
-push air into the vial equal to the amount of medication you plan to draw
-invert the vial to withdraw medication
-remove air bubbles
-and much more
See more Nursing Skills: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLQrdx7rRsKf
Notes: https://www.registerednursern.....com/how-to-withdraw-
Website: https://www.registerednursern.com/
More Videos: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R2XMro13dD0&list=UUPyMN8DzkFl2__xnTEiGZ1w
Nursing Gear: https://teespring.com/stores/registerednursern
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/registerednursern_com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/RegisteredNurseRNs
Twitter: https://twitter.com/NursesRN
Popular Playlists:
NCLEX Reviews: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLQrdx7rRsKf
Fluid & Electrolytes: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLQrdx7rRsKf
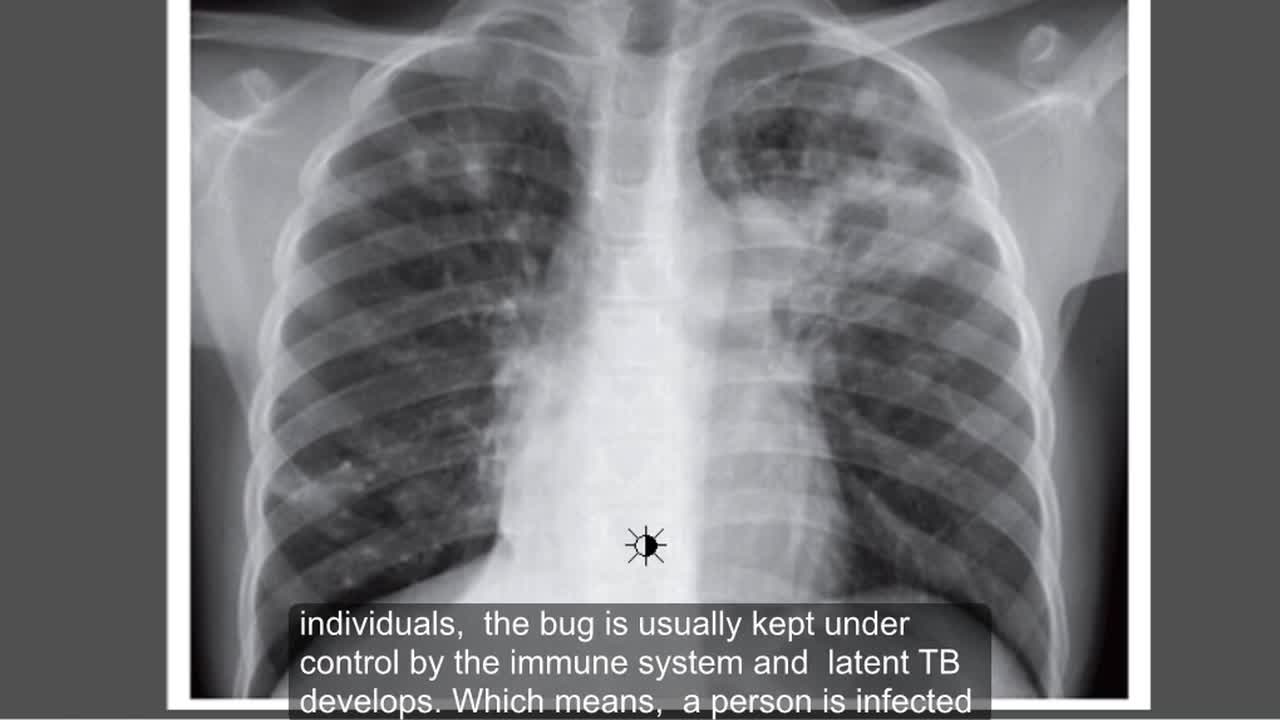
Tuberculosis (TB) is a potentially serious infectious disease that mainly affects your lungs. The bacteria that cause tuberculosis are spread from one person to another through tiny droplets released into the air via coughs and sneezes.
Pyogenic liver abscess Email this page to a friend Email this page to a friend Facebook Twitter Google+ Pyogenic liver abscess is a pus-filled area in the liver. Causes There are many potential causes of liver abscesses, including: Abdominal infection, such as appendicitis, diverticulitis, or a perforated bowel Infection in the blood Infection of the bile draining tubes Recent endoscopy of the bile draining tubes Trauma that damages the liver The most common bacteria that cause liver abscesses are: Escherichia coli Bacteroides Enterococcus Klebsiella pneumoniae Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus In most cases, more than one type of bacteria is found.

Vitiligine Cura, Vitiligine Rimedi Naturali, Vitiligine Omeopatia, Rimedi Per La Vitiligine -- http://vitiligine-cura.good-info.co --- Vitiligine Cura, Vitiligine Rimedi Naturali, Vitiligine Omeopatia, Rimedi Per La Vitiligine. Soffri Di Uno Qualunque Dei Seguenti Sintomi Emotivi O Fisici? Qualsiasi tipo di vitiligine (qualsiasi livello di gravità) su viso, schiena, guance, palmi delle mani, gambe o piedi? Sei affetto da macchie o scoloramento della pelle? Provi ansia nel doverti togliere la maglia in pubblico? Provi costantemente insicurezza? Provi esasperazione per il disturbo della vitiligine? Spendi molti soldi in farmaci o parafarmaci che sembrano non funzionare? Vuoi curare la vitiligine ma non sai quale sia la giusta cura a causa di un sovraccarico di informazioni? "Una Presentazione Video Gratuita Spiega Un Singolare Consiglio Per Eliminare La Vitiligine Per Sempre In 45-60 Giorni - Garantito!" http://vitiligine-cura.good-info.co
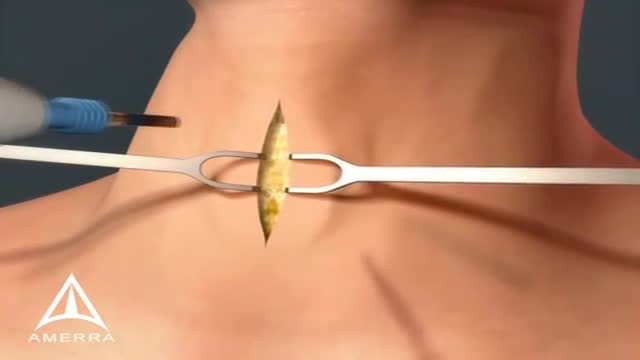
A tracheotomy or a tracheostomy: is simply an opening surgically created through the neck into the trachea (windpipe) to allow direct access to the breathing tube and is commonly done in an operating room under general anesthesia. A tube is usually placed through this opening to provide an airway and to remove secretions from the lungs. Breathing is done through the tracheostomy tube rather than through the nose and mouth. The term “tracheotomy” refers to the incision into the trachea (windpipe) that forms a temporary or permanent opening, which is called a “tracheostomy,” however; the terms are sometimes used interchangeably.

Dermatomyositis (dur-muh-toe-my-uh-SY-tis) is an uncommon inflammatory disease marked by muscle weakness and a distinctive skin rash. Dermatomyositis affects adults and children alike. In adults, dermatomyositis usually occurs from the late 40s to early 60s. In children, the disease most often appears between 5 and 15 years of age. Dermatomyositis affects more females than males. There's no cure for dermatomyositis, but periods of remission — when symptoms improve spontaneously — may occur. Treatment can clear the skin rash and help you regain muscle strength and function. Symptoms ShareTweet June 17, 2014 References Products and Services Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter See also Dysphagia Electromyography Fatigue MRI Muscle pain Peptic ulcer Prednisone risks, benefits Show more Advertisement Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Advertising & Sponsorship PolicyOpportunitiesAd Choices Mayo Clinic Store Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic. NEW! – The Mayo Clinic Diet, Second Edition Treatment Strategies for Arthritis Mayo Clinic on Better Hearing and Balance Keeping your bones healthy and strong The Mayo Clinic Diet Online