Top videos

Furosemide is used to reduce extra fluid in the body (edema) caused by conditions such as heart failure, liver disease, and kidney disease. This can lessen symptoms such as shortness of breath and swelling in your arms, legs, and abdomen. This drug is also used to treat high blood pressure. Lowering high blood pressure helps prevent strokes, heart attacks, and kidney problems. Furosemide is a "water pill" (diuretic) that causes you to make more urine. This helps your body get rid of extra water and salt.

360 tour videos are the latest video marketing trend all industries can be taking advantage of! VR and 360 medical videos, like this one, provide patients with a full understanding of the service. Whether you need a medical VR training video and a VR surgery video or medical videos for students to learn, these healthcare and medical videos will instill trust in your company and services.
Get a quote for your project here: https://epicproductionsllc.com/video-production/
Don't forget to follow us...
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/epicproductionsllc/
Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/epicprodllc
Connect with us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/compa....ny/epic-productions-
Follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/epicproductionsllc/
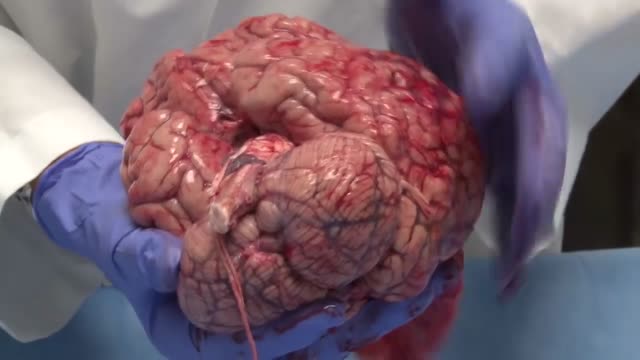
The human brain is the command center for the human nervous system. It receives input from the sensory organs and sends output to the muscles. The human brain has the same basic structure as other mammal brains, but is larger in relation to body size than any other brains.

Vitiligine Cura, Vitiligine Rimedi Naturali, Vitiligine Omeopatia, Rimedi Per La Vitiligine -- http://vitiligine-cura.good-info.co --- Vitiligine Cura, Vitiligine Rimedi Naturali, Vitiligine Omeopatia, Rimedi Per La Vitiligine. Soffri Di Uno Qualunque Dei Seguenti Sintomi Emotivi O Fisici? Qualsiasi tipo di vitiligine (qualsiasi livello di gravità) su viso, schiena, guance, palmi delle mani, gambe o piedi? Sei affetto da macchie o scoloramento della pelle? Provi ansia nel doverti togliere la maglia in pubblico? Provi costantemente insicurezza? Provi esasperazione per il disturbo della vitiligine? Spendi molti soldi in farmaci o parafarmaci che sembrano non funzionare? Vuoi curare la vitiligine ma non sai quale sia la giusta cura a causa di un sovraccarico di informazioni? "Una Presentazione Video Gratuita Spiega Un Singolare Consiglio Per Eliminare La Vitiligine Per Sempre In 45-60 Giorni - Garantito!" http://vitiligine-cura.good-info.co
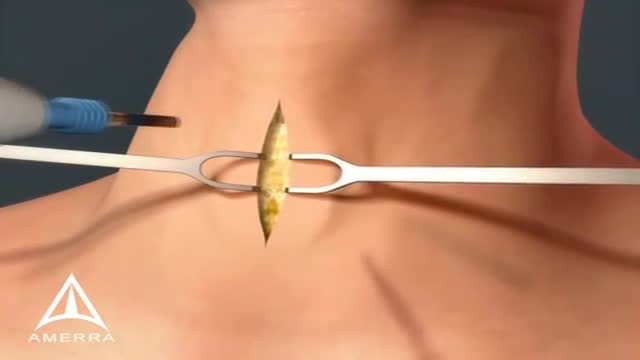
A tracheotomy or a tracheostomy: is simply an opening surgically created through the neck into the trachea (windpipe) to allow direct access to the breathing tube and is commonly done in an operating room under general anesthesia. A tube is usually placed through this opening to provide an airway and to remove secretions from the lungs. Breathing is done through the tracheostomy tube rather than through the nose and mouth. The term “tracheotomy” refers to the incision into the trachea (windpipe) that forms a temporary or permanent opening, which is called a “tracheostomy,” however; the terms are sometimes used interchangeably.

Ankle and Foot Clinical Examination - Clinical Skills - Dr Gill
When it comes to joints of the body, the ankle is one of the joints most commonly injured. This is vitally important to be able to effectively examine a patient who is complaining of pain in the ankle and foot.
In this video we will perform a demonstration of the ankle and foot examination.
Examination of the foot, and the ankle joint, follows the standard orthopaedic approach of look, feel, move.
There is a connected video to the foot and ankle examination, on the causes of carpal tunnel syndrome - here
https://youtu.be/aXx6NfBWDSs
________
Please note that there is no ABSOLUTE way to perform a clinical examination. Different institutions and even clinicians will have differing degrees of variations - the aim is the effectively identify medically relevant signs.
However during OSCE assessments. Different medical schools, nursing colleges, and other health professional courses will have their own preferred approach to a clinical assessment - you should concentrate on THEIR marks schemes for your assessments.
The examination demonstrated here is derived from Macleod's Clinical Examination - a recognized standard textbook for clinical skills.
#footpain #clinicalexamination #DrGill

The thyroid gland lies in the midline of the anterior neck, just caudal to the thyroid cartilage. To inspect the thyroid gland, the examiner stands in front of the patient. The examiner asks the seated patient to dorsiflex (extend) the neck and swallow a sip of water. Minor enlargement of the gland may only become apparent on inspection in this position. Palpation of the thyroid gland is typically performed with the examiner standing behind the patient. Both lobes and the isthmus of the thyroid gland should be palpated for any nodules or diffuse enlargement. Mobility of the thyroid gland with swallowing should be assessed with palpation. Nodules arising from the thyroid gland typically move with swallowing. A hard, fixed thyroid gland could indicate malignancy. If a central nodule is identified, the patient is asked to protrude the tongue. Upward movement of the central nodule on protrusion of the tongue indicates a thyroglossal cyst. Auscultation is performed at the superior poles of bilateral lobes as this is where the superior thyroid artery is most superficial and bifurcates into its terminal branches. A bilateral bruit over the superior poles suggests Graves disease. Examination of the thyroid gland is completed by palpating the regional cervical lymph nodes for any enlargement.
Subscribe to AMBOSS YouTube for the latest clinical examination videos, medical student interviews, study tips and tricks, and live webinars!
Free 5 Day Trial: https://go.amboss.com/amboss-YT
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/amboss_med/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/AMBOSS.Med/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ambossmed
Blog: https://blog.amboss.com/us
#AMBOSSMed #ClinicalExamination #USMLE

Clonidine lowers blood pressure by decreasing the levels of certain chemicals in your blood. This allows your blood vessels to relax and your heart to beat more slowly and easily. The Catapres brand of clonidine is used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). The Kapvay brand is used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Clonidine is sometimes given with other medications