Top videos
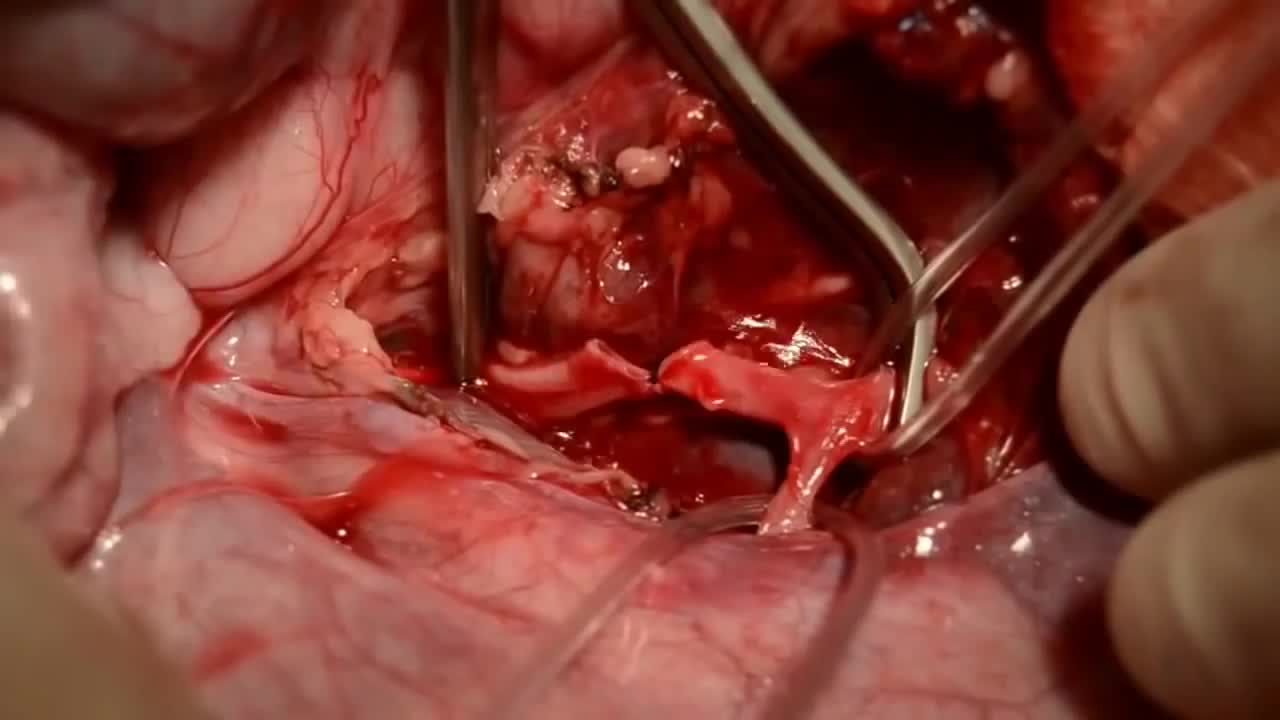
Throughout the body, there are several points at which blood vessels unite. The junctions are termed anastomoses. In the simplest sense, an anastomosis is any connection (made surgically or occurring naturally) between tube-like structures. Naturally occurring arterial anastomoses provide an alternative blood supply to target areas in cases where the primary arterial pathway is obstructed. They are most abundant in regions of the body where the blood supply may can be easily damaged or blocked (such as the joints or intestines). This article focuses on the arterial anastomotic networks of the upper limb.

There are lots of fallacies about the missionary position being the best position for getting pregnant. With the woman on her back and her partner on top, it is thought that gravity will assist the sperm to swim upwards towards the egg.
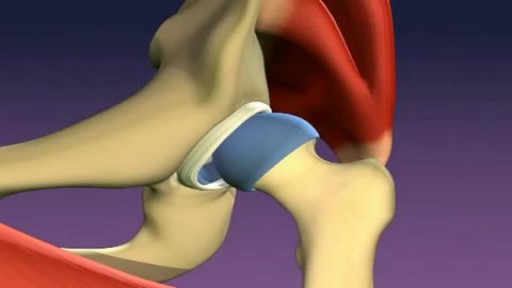
In a normal hip, the ball at the upper end of the thighbone (femur) fits firmly into the socket, which is part of the large pelvis bone. In babies and children with developmental dysplasia (dislocation) of the hip (DDH), the hip joint has not formed normally.

A spontaneous vaginal delivery (SVD) occurs when a pregnant woman goes into labor with or without use of drugs or techniques to induce labor, and delivers her baby in the normal manner, without forceps, vacuum extraction, or a cesarean section. Assisted vaginal delivery (AVD) occurs when a pregnant woman goes into labor with or without the use of drugs or techniques to induce labor, and requires the use of special instruments such as forceps or a vacuum extractor to deliver her baby vaginally.
The male orgasm is a common subject but usually misunderstood at the same time. Men are sometimes led to believe that ejaculating often is a bad thing, particularly if you masturbate. The truth is that ejaculation is important to every man due to a number of reasons. The main goal of this post is to shed some light on reasons why men need to ejaculate.

Macrobiopsy of breast lesions is a complicated procedure when performed with vacuum assisted biopsy tools. The Spirotome is a hand-held needle set that doesn't need capital investment, is ready to use and provides tissue samples of high quality in substantial amounts. In this way quantitative molecular biology is possible with one tissue sample. The Coramate is an automated version of this direct and frontal technology.
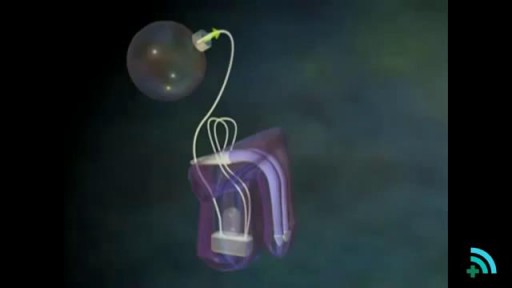
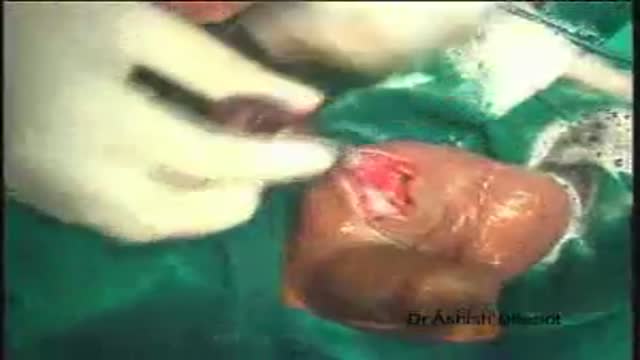
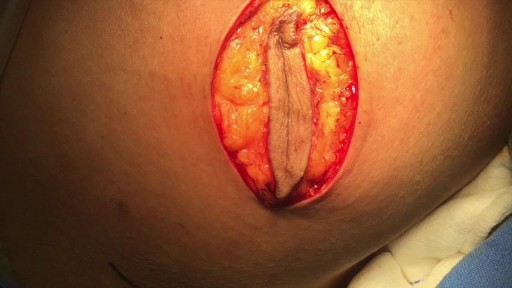
he inflatable penile prosthesis consists of two attached cylinders -- a reservoir and a pump -- which are placed surgically in the body. The two cylinders are inserted in the penis and connected by tubing to a separate reservoir of saline. The reservoir is implanted under the rectus muscles in the lower abdomen.

Heart failure, sometimes known as congestive heart failure, occurs when your heart muscle doesn't pump blood as well as it should. Certain conditions, such as narrowed arteries in your heart (coronary artery disease) or high blood pressure, gradually leave your heart too weak or stiff to fill and pump efficiently.