Top videos

Dialysis services at UC San Diego Health: https://health.ucsd.edu/care/kidney/dialysis
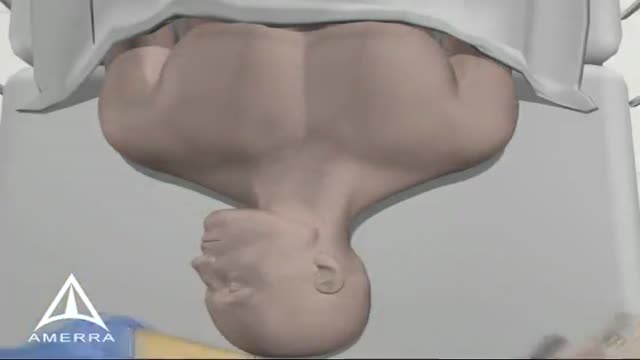
UC San Diego Health Licensed Clinical Social Worker, Norma Reggev, discusses hemodialysis as a treatment option for failing kidneys with patient testimonials. Discussion includes In Center Hemodialysis and Home Hemodialysis.
0:00 - Hemodialysis
1:34 - When Should Dialysis Begin?
2:00 - What is Dialysis?
2:25 - How Hemodialysis Works
3:15 - In-Center Hemodialysis Considerations
3:42 - Patient Shares Their Experience With In-Center Hemodialysis
7:30 - Home Hemodialysis Considerations
8:35 - Patient Shares Their Experience With Home Hemodialysis
12:23 - Types of Vascular Access

Ischemic colitis occurs when blood flow to part of the large intestine (colon) is reduced, usually due to narrowed or blocked blood vessels (arteries). The diminished blood flow doesn't provide enough oxygen for the cells in your digestive system. Ischemic colitis can cause pain and may damage your colon. Any part of the colon can be affected, but ischemic colitis usually causes pain on the left side of the belly area (abdomen). The condition can be misdiagnosed because it can easily be confused with other digestive problems. Ischemic colitis may heal on its own. But you may need medication to treat ischemic colitis or prevent infection, or you may need surgery if your colon has been damaged. Symptoms ShareTweet Oct. 13, 2015 References Products and Services Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter See also Abdominal pain Colonoscopy Color Blue Detects Colon Cancer CT scan CT scans: Are they safe? Diarrhea Ultrasound Advertisement Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Advertising & Sponsorship PolicyOpportunitiesAd Choices Mayo Clinic Store Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic. NEW! – The Mayo Clinic Diet, Second Edition Treatment Strategies for Arthritis Mayo Clinic on Better Hearing and Balance Keeping your bones healthy and strong The Mayo Clinic Diet Online Ads by Swoop Psoriasis Treatment www.informationaboutpsoriasis.com Explore a Treatment Option for Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis Immune Biomarker PD-L1 - Discover the Science iobiomarkers.bmsinformation.com Understanding Assay Results for PD-L1 is Crucial for Treatment Decisions. Biomarker PD-L1 Information - Easy to Download Resources iobiomarkers.bmsinformation.com Explore the Role of PD-L1 in Immuno-Oncology & the Evolving Biomarker Landscape.

Results Sinusitis was characterized as acute in 26 patients, subacute in 5 (including 1 pyocele), and chronic in 8 (including 2 fungal infections). No tumors were found. Isolated sinus cysts were excluded from the study. Headache, the main symptom in 32 patients (82%), was localized most commonly on the vertex. Other common complaints were rhinitis, dizziness, eye symptoms, and fever. In 2 patients, the finding was occult. Eight patients (21%) presented with cranial nerve deficits, and 1 patient had an intracranial complication. Sinus irrigation was performed in 16 patients (41%) and sphenoidotomy was performed in 10 (26%). Fifteen patients (38%) were treated with antibiotic drugs alone. Within 3 months, 31 (84%) of 37 patients had recovered from the illness; 5 still experienced headaches despite having normalized radiographic findings; and 1 had permanent unilateral visual loss. Two patients were lost to follow-up.

http://eliminar-celulite.plus101.com --- Eliminar Celulite, O Que Fazer Para Acabar Com A Celulite, Como Tirar Celulite Das Pernas. Mas as razões que vou compartilhar são diferentes das que a maioria das outras fontes está tentando fazê-la acreditar. Há um mito fazendo com que algumas mulheres acreditem que certos alimentos e nutrientes irão “eliminar as toxinas que estão causando a celulite”. ISSO É TOTALMENTE FALSO, porque não há toxinas em ou sob sua pele. Se houvesse toxinas se acumulando e ficando presas sob sua pele, você estaria morta. Simples assim. Nosso corpo foi feito para remover toxinas com muita eficácia. Este processo fisiológico acontece 24 horas por dia, 7 dias por semana, sem parar, o tempo todo. Então, a ideia não comprovada de que “toxinas” são a causa de sua celulite significa que a celulite não pode ser revertida ao “eliminá-las” com alguns alimentos, porque elas não estão lá, para começar. Mas não se preocupe, porque eis o que o planejamento alimentar apropriado pode fazer para reverter, ou prevenir, a raiz da causa da celulite em suas pernas, bumbum, quadris e coxas. Uma verdadeira dieta contra a celulite fornece nutrientes em quantidades que impactam positivamente a regulagem e equilíbrio dos hormônios femininos. Esta é a razão principal de o Planejamento Alimentar/Dieta Contra Celulite do "Adeus Celulite" só estar disponível para mulheres que começam com o Método de Exercícios SYMULAST do programa Adeus Celulite. Então se você estiver interessada, vá para: http://eliminar-celulite.plus101.com
Possible causes are a blocked milk duct or bacteria entering the breast. It usually occurs within the first three months of breast-feeding. Symptoms include breast pain, swelling, warmth, fever, and chills. Antibiotics are required. Mild pain relievers can help with discomfort.

Timothy Lovell, MD, an orthopedic surgeon, talks to Spokane, WA knee replacement surgery patients about the procedure, possible risks and complications of surgery, and about your recovery time.
Dr. Lovell addresses anesthesia, the size and location of the incision, and shows you what the knee replacement ball and socket joint looks like. He'll talk about the recovery process; using a crutches, a walker or a cane to get around; movements to avoid; and how long it takes to feel better and return to your normal, active life.
To learn more about Dr. Lovell, visit http://washington.providence.o....rg/find-a-provider/l
And, to learn more about having orthopedic surgery in Spokane, WA, visit http://washington.providence.o....rg/clinics/providenc

Most folks remember puberty – and not always in a good way. It can be an awkward stage of budding breasts, unwanted hair, acne and unexpected body odor. Puberty, when a child undergoes physical changes and becomes sexually mature, typically begins around age 8 in girls and age 9 in boys. But imagine, say, a 6- or 7-year-old undergoing such changes? Studies are showing that the onset of puberty for both boys and girls is occurring earlier and earlier, a phenomenon defined as precocious puberty. A study published in Pediatrics in 2010 found that among a population of 1,200 American girls, about 23 percent of African-Americans,15 percent of Latinas and 10 percent of Caucasian girls had begun puberty (marked by breast development) at age 7. In 2012, another study published in Pediatrics found that puberty in American boys – measured by testicular enlargement and pubic hair growth – was beginning six months to two years earlier than what research in previous decades had documented, particularly among African-American children.

A flail chest occurs when a segment of the thoracic cage is separated from the rest of the chest wall. This is usually defined as at least two fractures per rib (producing a free segment), in at least two ribs. A segment of the chest wall that is flail is unable to contribute to lung expansion. Large flail segments will involve a much greater proportion of the chest wall and may extend bilaterally or involve the sternum. In these cases the disruption of normal pulmonary mechanics may be large enough to require mechanical ventilation.
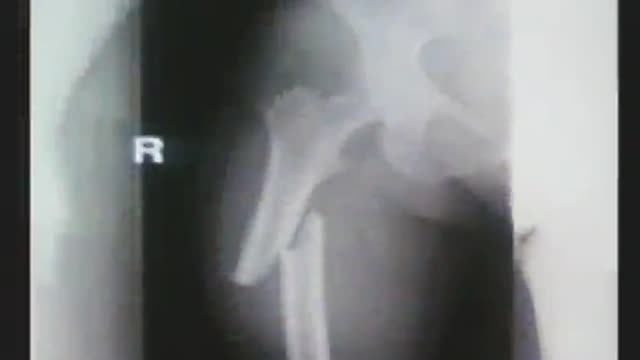
Treating osteoporosis with bisphosphonates, particularly for more than five years, has been linked to some side effects, including atypical femur fractures. Osteoporosis medications are supposed to prevent bone breaks. But if they are taken for too long, the opposite can happen. This video highlights what you need to know as a healthcare professional to educate patients

Knee pain location can often tell you what type of knee pain you have. If you confirm that with common symptoms and what aggravates it… you can get a pretty good idea of ‘why my knee hurts’. So, here’s a quick look at the most common type of knee problems.
‘The 3 Essential Exercises EVERYONE Should Do’ … Watch this EXCLUSIVE video, only here: https://stefan-becker.mykajabi.com/3-essentials
QUESTIONS? I answer questions here now: I’ve started a Facebook Group to help people achieve their musculo-skeletal goals. Join here… https://www.facebook.com/groups/bodyfixexercises
AND I’m developing a Coaching Program! Over 12 weeks, I help people with posture related issues—like neck, shoulder, & upper back pain—discover their root problem and correct it using science-backed mobilising, stretching, & strengthening exercises… so they can feel straight, strong, flexible, & pain free again (and get back to doing what they love). Find out more, and join the wait list here… https://stefan-becker.mykajabi.com/waiting-list
0:00 Intro
0:11 Pain at the front of the knee (Pain in kneecap)
0:42 Pain below kneecap
1:40 Pain on inside of knee
3:05 Pain below knee on inside
3:29 Pain on outside of knee
3:28 Pain above knee
3:28 Pain behind knee
---------------------------------------
Mentioned in this video...
How To Fix Pain In The Front Of The Knee… (Runner's Knee) https://youtu.be/g0qmx_0enAA
Looking to stop your knee problems? Do this...
Knee Strengthening Exercises To Prevent Knee Pain
https://youtu.be/Pk-ae_lyx7M
How To Treat Patellar Tendinopathy (Jumper’s Knee) & Quadriceps Tendinopathy
https://youtu.be/MkPwsb-rQwU
---------------------------------------
If you’re asking yourself ‘what’s the cause of my knee pain?’ or ‘what kind of knee pain do I have?’ (so that you can look up solutions to your knee pain on YouTube) the position of your knee pain will tell you a lot.
THE MOST COMMON KNEE PAIN TYPES?
Knee pain during running (or actually kneecap pain while running) is usually just that… Runner’s Knee (PATELLOFEMORAL PAIN SYNDROME, or it’s old name: Chondromalacia Patella) If you get knee pain while cycling it will often be the same thing. Same with knee pain with stairs.
Knee pain while squatting could be Runner’s Knee, but if you get pain in the tendon below the kneecap, it’s more likely to be Patellar Tendonitis or Jumper’s Knee.
Meniscus Tears will give you pain on the inside of the knee that is a localised pain, can feel as if it gets stuck, or feel like it’s going to give way, and often it’s hard to fully straighten or fully bend your knee.
Knee pain on the outside of the knee is usually Iliotibial Band Syndrome
ALSO COVERED:
Infrapatellar Fat Pad Syndrome (Hoffa's Syndrome)
Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Medial Collateral Ligament Tear
Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Osteoarthritic Knee Pain
Pes Anserine Bursitis.
Quadriceps Tendinopathy
Popliteus Strain
Baker’s Cyst
ACL Or PCL Tear/Rupture
------------------------------------
#bodyfixexercises #kneepainrelief #kneepain

http://www.HypothyroidismCure.blog300.com - Hypothyroidism Treatment Natural - Hypothyroidism Recipes Treatment
Let’s Get Something Straight…
* You’re here because you’re serious about overcoming your hypothyroidism…
* You’re here because you’re serious about and taking back your life…
* You know there’s no magic pill to cure your hypothyroidism and never will be…
Hypothyroidism Treatment Natural - Hypothyroidism Recipes Treatment

Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) Hip Joint Replacement is an advancement in hip replacement that offers important advantages over standard surgical procedures. Stryker has partnered with surgeons worldwide to develop MIS procedures and surgical instruments that are designed to help your surgeons do their very best to help you recover your lifestyle. These techniques bring together a wide variety of hip implants, new minimally invasive surgical techniques, and new instrumentation. The direct anterior approach is one of the minimally invasive techniques used in hip replacement surgery. Continuing orthopaedic experience suggests that this procedure may offer several advantages over the more traditional surgical approaches to hip replacement.1 Traditional hip replacement techniques involve operating from the side (lateral) or the back (posterior) of the hip, which requires a significant disturbance of the joint and connecting tissues and an incision approximately 8-12 inches long. In comparison, the direct anterior approach requires an incision that is only 3-4 inches in length and located at the front of the hip.1 In this position, the surgeon does not need to detach any of the muscles or tendons.

Best Gynecomastia surgeon in India is Dr. Ajaya Kashyap, with over 20 years experience in breast surgeries. He is the only active Indian member in American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Contact us to find out about your gynecomastia treatment in Delhi, India, maintaining high international standards, having a U.S. board certified surgeon, and latest technology and surgical techniques, our offices offer very economical costing. Contact us today inquire about gynecomastia surgery cost, in Delhi. You are sent query using WhatsApp and website.
For further information, are available visit our website: http://www.bestgynecomastiaindia.com/
Your Query for Chat and call +91-9818369662, 9958221983 (WhatsApp)

Most times, a pulmonary embolism is caused by blood clots that travel from the legs or, rarely, other parts of the body (deep vein thrombosis, or DVT). Symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain, and cough. Prompt treatment to break up the clot greatly reduces the risk of death. This can be done with blood thinners and drugs or procedures. Compression stockings and physical activity can help prevent clots from forming in the first place.