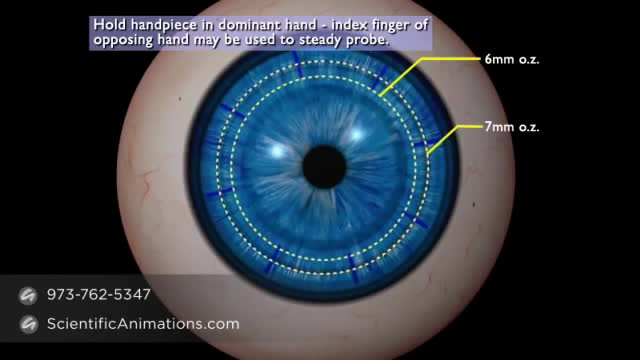
Top videos
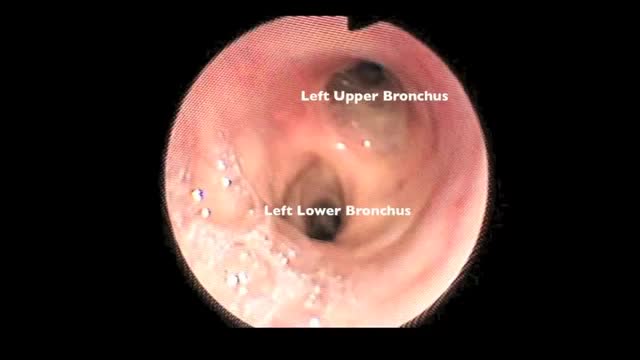
Flexible bronchoscopy is a procedure that allows a clinician to examine the breathing passages (airways) of the lungs (figure 1). Flexible bronchoscopy can be either a diagnostic procedure (to find out more about a possible problem) or a therapeutic procedure (to try to treat an existing problem or condition).
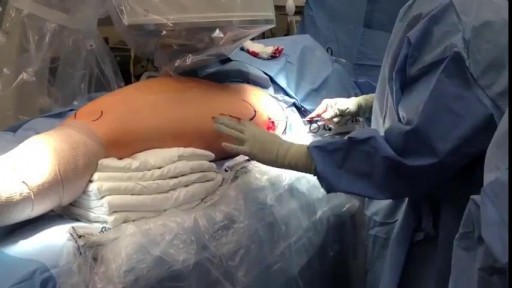
This is an example of a surgery to fix a femur (thigh bone) fracture utilizing an intramedullary nail. This is a minimally invasive way of fixing this surgical problem and allows for immediate range of motion and full weight-bearing.
Key facts
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic disease.
The virus is transmitted through contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person - not through casual contact.
About 2 billion people worldwide have been infected with the virus and about 350 million live with chronic infection. An estimated 600 000 persons die each year due to the acute or chronic consequences of hepatitis B.
About 25% of adults who become chronically infected during childhood later die from liver cancer or cirrhosis (scarring of the liver) caused by the chronic infection.
The hepatitis B virus is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
Hepatitis B virus is an important occupational hazard for health workers.
Hepatitis B is preventable with a safe and effective vaccine.
-----------------------------------
Hepatitis B is a potentially life-threatening liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. It is a major global health problem and the most serious type of viral hepatitis. It can cause chronic liver disease and puts people at high risk of death from cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer.
Worldwide, an estimated two billion people have been infected with the hepatitis B virus (HBV), and more than 350 million have chronic (long-term) liver infections.
A vaccine against hepatitis B has been available since 1982. Hepatitis B vaccine is 95% effective in preventing HBV infection and its chronic consequences, and is the first vaccine against a major human cancer.

Dialysis patients need to choose their heart medicine carefully, as Canadian researchers say that some beta blockers are easily removed from the blood during treatment. Also, people who eat a Mediterranean diet may decrease their risk of developing kidney problems. Eboni Williams reports on the day's top health news.
Cervical cancer occurs when abnormal cells on the cervix camera.gif grow out of control. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina. Cervical cancer can often be successfully treated when it's found early. It is usually found at a very early stage through a Pap test.
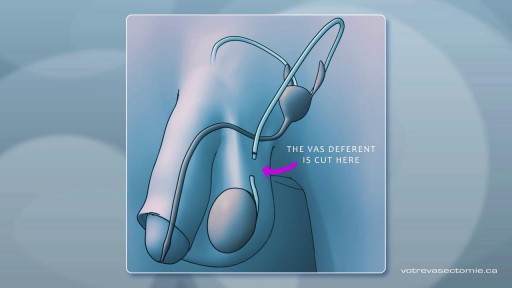
A vasectomy is one of the most effective kinds of birth control out there, and THE most effective method for people with penises and testicles. Vasectomies are almost 100% effective at preventing pregnancy — but not right away. It takes about 3 months for your semen to become sperm-free

You may have a lot of questions about epilepsy. We will help you understand the basics, answer the most common questions, and help you find resources and other information you may need. However, information alone won’t help you manage your epilepsy and find a way to cope with the effects on your daily life. You’ll need to learn how to use the information and make it work for you.
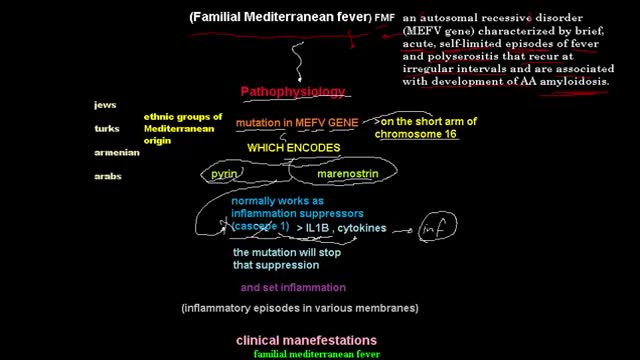
Familial Mediterranean fever is an inflammatory disorder that causes recurrent fevers and painful inflammation of your abdomen, lungs and joints. Familial Mediterranean fever is an inherited disorder that usually occurs in people of Mediterranean origin — including Sephardic Jews, Arabs, Greeks, Italians, Armenians and Turks. But it may affect any ethnic group. Familial Mediterranean fever is typically diagnosed during childhood. While there's no cure for this disorder, you may be able to relieve signs and symptoms of familial Mediterranean fever — or even prevent them altogether — by sticking to your treatment plan.

Réduire La Cellulite, Meilleure Creme Anti Cellulite, Programme Anti Cellulite, Cuisse Cellulite http://perdre-sa-cellulite.plus101.com Une Bonne Alimentation Pour Lutter Contre la Cellulite. Certains aliments ont des composants naturels antioxydants et draineurs qui éliminent naturellement la cellulite. Parmi eux se trouvent le céleri branche. Il s’agit d’un légume un peu amère mais qui aide beaucoup à accélérer le métabolisme des graisses afin de débarrasser la cellulite. Coupé en bâtonnet, il peut être consommé en apéro ou en plat de crudités. Le poireau figure également dans la liste des meilleurs aliments anticellulite. Légume anti-rétention d’eau, il chasse les toxines tout en luttant contre la cellulite. Enfin, n’oubliez pas de consommer de l’ananas si vous voulez combattre votre cellulite. Il a pour principal mission de réduire la rétention d’eau. Selon des experts en physiologie, les femmes ont 90 muscles dans les membres inférieurs et en les stimulant doucement, ces muscles des fesses, jambes, hanches et cuisses, 76,3% des femmes peuvent inverser la cause de la peau d’orange et des capitons pour avoir une peau tonifiée et lisse. CLIQUEZ ICI: http://perdre-sa-cellulite.plus101.com

A water birth means at least part of your labor, delivery, or both happen while you’re in a birth pool filled with warm water. It can take place in a hospital, a birthing center, or at home. A doctor, nurse-midwife, or midwife helps you through it. In the U.S., some birthing centers and hospitals offer water births. Birthing centers are medical facilities that offer a more homelike setting than a hospital and more natural options for women having babies. The use of a birthing pool during the first stage of labor might: Help ease pain Keep you from needing anesthesia Speed up your labor The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), which sets guidelines for pregnancy and childbirth care in the U.S., says a water birth during the first stage of labor may have some benefits but delivering your baby underwater should be considered an experimental procedure with risks. The first stage is from when contractions start until your cervix is fully dilated.