Top videos
Key facts
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic disease.
The virus is transmitted through contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person - not through casual contact.
About 2 billion people worldwide have been infected with the virus and about 350 million live with chronic infection. An estimated 600 000 persons die each year due to the acute or chronic consequences of hepatitis B.
About 25% of adults who become chronically infected during childhood later die from liver cancer or cirrhosis (scarring of the liver) caused by the chronic infection.
The hepatitis B virus is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
Hepatitis B virus is an important occupational hazard for health workers.
Hepatitis B is preventable with a safe and effective vaccine.
-----------------------------------
Hepatitis B is a potentially life-threatening liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. It is a major global health problem and the most serious type of viral hepatitis. It can cause chronic liver disease and puts people at high risk of death from cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer.
Worldwide, an estimated two billion people have been infected with the hepatitis B virus (HBV), and more than 350 million have chronic (long-term) liver infections.
A vaccine against hepatitis B has been available since 1982. Hepatitis B vaccine is 95% effective in preventing HBV infection and its chronic consequences, and is the first vaccine against a major human cancer.
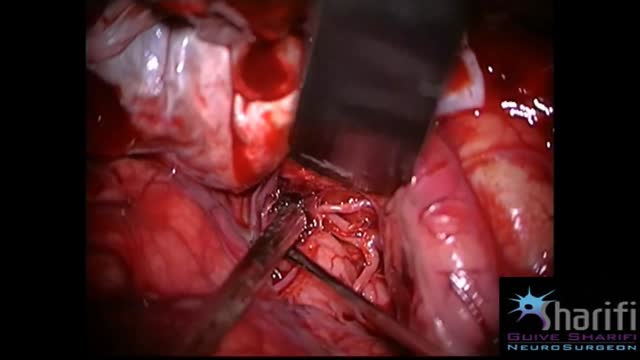
The goal of surgical clipping is to isolate an aneurysm from the normal circulation without blocking off any small perforating arteries nearby. Under general anesthesia, an opening is made in the skull, called a craniotomy. The brain is gently retracted to locate the aneurysm. A small clip is placed across the base, or neck, of the aneurysm to block the normal blood flow from entering. The clip works like a tiny coil-spring clothespin, in which the blades of the clip remain tightly closed until pressure is applied to open the blades. Clips are made of titanium and remain on the artery permanently.

White stretch marks are unsightly marks that are found along the thighs, abdomen and upper arms. These are marks that could be due to a recent weight loss, trauma or pregnancy. Stretch marks can affect your confidence if you wear revealing outfits and so you should do all you can to remove them.

https://bit.ly/3HIStRc #shorts
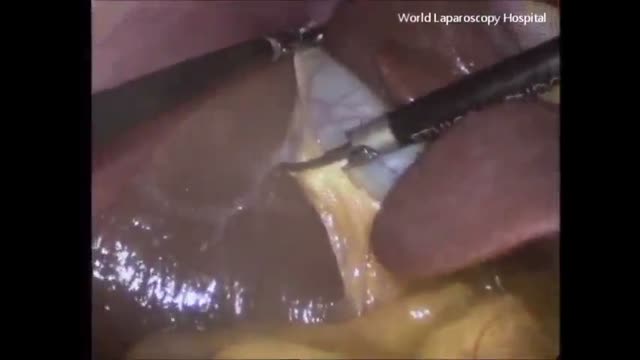
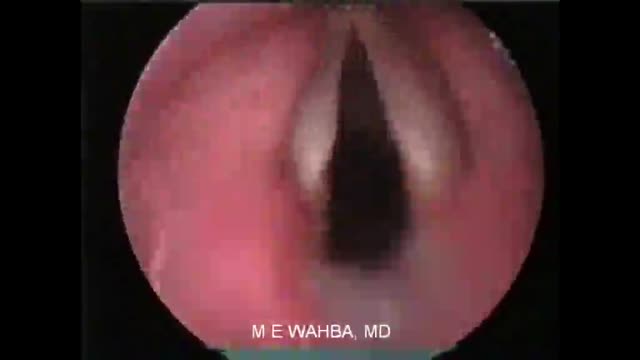
Coloscopy | Colon Polyp Resection | Polypectomy
Colonoscopies are essential for detecting colorectal abnormalities, including colon polyps. Polypectomy, the surgical removal of these growths, can prevent them from becoming cancerous. This article offers a brief overview of colonoscopies, colon polyps, and polypectomy procedures.
A colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination allowing healthcare providers to visualize the colon and rectum using a colonoscope. The colonoscope, a flexible tube with a camera and light source, helps detect abnormalities, including polyps or tumors.
Colon polyps are abnormal growths arising from the colon's inner lining. While most polyps are benign, some can become malignant. Adenomatous polyps have a higher potential to become cancerous, whereas hyperplastic and inflammatory polyps pose a lower risk.
Polypectomy involves removing colon polyps during a colonoscopy. Two primary techniques include snare polypectomy, using a wire loop to cut the polyp, and cold forceps polypectomy, which employs forceps to grasp and remove smaller polyps.
Following a polypectomy, patients may experience mild discomfort or bleeding. Regular surveillance is crucial to minimize colorectal cancer risk. The frequency of surveillance colonoscopies depends on the number, size, and type of polyps found, as well as the patient's overall risk factors.
Colonoscopies and polypectomies play vital roles in detecting and removing colon polyps, reducing the risk of colorectal cancer, and maintaining optimal colon health.
Do you want to learn more about colon polyps and colonoscopy? check our:
Article @ https://bit.ly/41w5Ooq
For more free resources, find us on Pinterest & Facebook pages:
https://www.pinterest.ca/medicalartsofficial/
https://www.facebook.com/Medicalartsofficial
https://www.youtube.com/@medic....alarts?sub_confirmat
https://www.instagram.com/medicalartsofficial/
https://www.tiktok.com/@medicalarts
#endoscopicsurgery #digestivesystem
coloscopy
polyp
colon polyp
polypectomy
colonoscopy
colon polyp animation
gi endoscopy
@MedicalArts , 2023.

Alcoholic liver disease is a term that encompasses the liver manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with liver fibrosis or cirrhosis. It is the major cause of liver disease in Western countries.
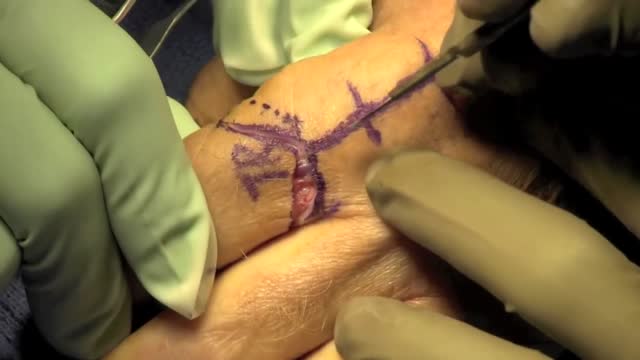
An amputation is the removal of an extremity or appendage from the body. Amputations in the upper extremity can occur as a result of trauma, or they can be performed in the treatment of congenital or acquired conditions. Although successful replantation represents a technical triumph to the surgeon, the patient's best interests should direct the treatment of amputations. The goals involved in the treatment of amputations of the upper extremity include the following : Preservation of functional length Durable coverage Preservation of useful sensibility Prevention of symptomatic neuromas Prevention of adjacent joint contractures Early return to work Early prosthetic fitting These goals apply differently to different levels of amputation. Treatment of amputations can be challenging and rewarding. It is imperative that the surgeon treat the patient with the ultimate goal of optimizing function and rehabilitation and not become absorbed in the enthusiasm of the technical challenge of the replantation, which could result in poorer outcome and greater financial cost due to lost wages, hospitalization, and therapy.

Human immunodeficiency virus infection / acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a disease of the human immune system caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).[1] During the initial infection a person may experience a brief period of influenza-like illness. This is typically followed by a prolonged period without symptoms. As the illness progresses it interferes more and more with the immune system, making people much more likely to get infections, including opportunistic infections, and tumors that do not usually affect people with working immune systems.
HIV is transmitted primarily via unprotected sexual intercourse (including anal and even oral sex), contaminated blood transfusions and hypodermic needles, and from mother to child during pregnancy, delivery, or breastfeeding.[2] Some bodily fluids, such as saliva and tears, do not transmit HIV.[3] Prevention of HIV infection, primarily through safe sex and needle-exchange programs, is a key strategy to control the spread of the disease. There is no cure or vaccine; however, antiretroviral treatment can slow the course of the disease and may lead to a near-normal life expectancy. While antiretroviral treatment reduces the risk of death and complications from the disease, these medications are expensive and may be associated with side effects.
Genetic research indicates that HIV originated in West-central Africa during the early twentieth century.[4] AIDS was first recognized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in 1981 and its cause—HIV infection—was identified in the early part of the decade.[5] Since its discovery, AIDS has caused nearly 30 million deaths (as of 2009).[6] As of 2010, approximately 34 million people have contracted HIV globally.[7] AIDS is considered a pandemic—a disease outbreak which is present over a large area and is actively spreading.[8]
HIV/AIDS has had a great impact on society, both as an illness and as a source of discrimination. The disease also has significant economic impacts. There are many misconceptions about HIV/AIDS such as the belief that it can be transmitted by casual non-sexual contact. The disease has also become subject to many controversies involving religion.

How To Get Pregnant, Ways To Get Pregnant, Best Days To Get Pregnant, Easiest Way To Get Pregnant.
http://how-to-get-pregnant.info-pro.co
Signs Of Infertility
What Exactly Is Infertility?
The problems with either conceiving a child, or with carrying out the pregnancy to its eventual fruitful end, fall under the definition of infertility. Infertility is the incapability of an individual to become pregnant, in case of females, or the incapability to induce pregnancy, in case of the males.
The inability of an individual to carry out a pregnancy to its full term is also dubbed infertility. How does one recognize infertility? What are the signs of infertility?
Signs of infertility in women:
Children At Age 43 After Years Of "Trying".
You Can Too! Here's How...": http://how-to-get-pregnant.info-pro.co
For More Information
http://how-to-get-pregnant.info-pro.co
http://natural-fertility-remedies.blogspot.com/
Subscribe To Our Channel
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R6gRskH4WxY
How To Get Pregnant, Ways To Get Pregnant, Best Days To Get Pregnant, Easiest Way To Get Pregnant, preparing for pregnancy, pills to get pregnant, tricks for getting pregnant, help with pregnancy, help me get pregnant faster, how you get pregnant fast, i really want to get pregnant, male infertility treatments, get me pregnant, natural tips to get pregnant, tips on getting pregnant, how to help get pregnant faster