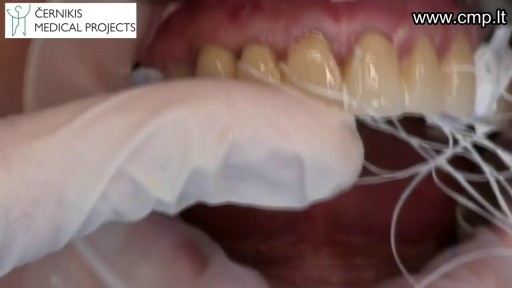
Top videos
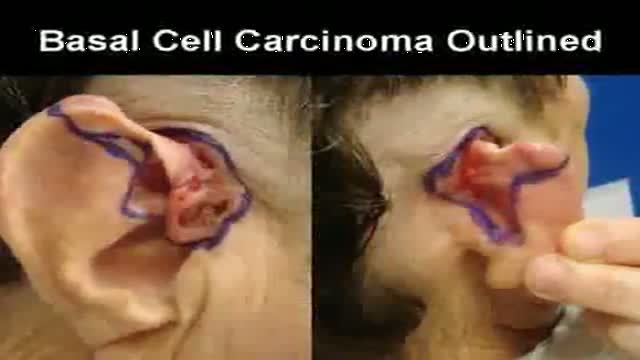
Graphic images focusing on the reconstruction of an ear after the removal of a long-standing skin cancer that this patient allowed to slowly grow over many years because he was afraid of what the surgery to remove might entail. Go to www.skincancercentre.com to learn more about the importance of the early diagnosis of skin cancer. BTW, when you put on your sunscreen, don't forget your ears, and wear a broad brimmed hat to cover this very vulnerable area of your anatomy. www.skincancercentre.com
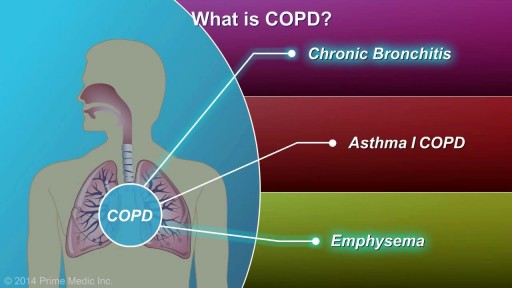
COPD, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, is a progressive disease that makes it hard to breathe. Progressive means the disease gets worse over time. COPD can cause coughing that produces large amounts of a slimy substance called mucus, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and other symptoms. Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of COPD. Most people who have COPD smoke or used to smoke. However, up to 25 percent of people with COPD never smoked. Long-term exposure to other lung irritants—such as air pollution, chemical fumes, or dusts—also may contribute to COPD. A rare genetic condition called alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency can also cause the disease.
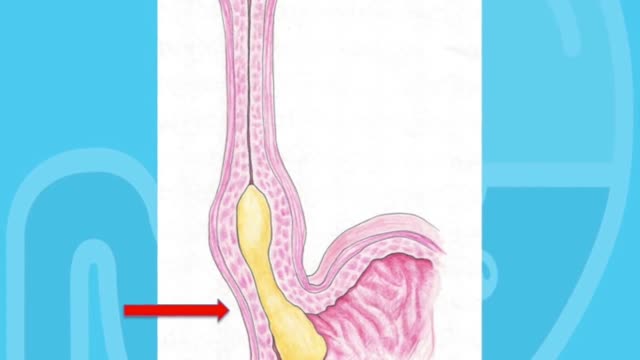
Achalasia is a neurogenic esophageal motility disorder characterized by impaired esophageal peristalsis and a lack of lower esophageal sphincter relaxation during swallowing. Symptoms are slowly progressive dysphagia, usually to both liquids and solids, and regurgitation of undigested food. Evaluation typically includes manometry, barium swallow, and endoscopy. Treatments include dilation, chemical denervation, surgical myotomy, and peroral endoscopic myotomy.

Que Es Bueno Para La Diabetes Medicina Natural. Porque Con Este Método Que Voy a Revelarte que es 10 Veces Más Efectivo Que Cualquier Otro Podrás Vencer A Tu Diabetes RÁPIDAMENTE. Si no hubiera sido por el poderoso método inusual pero PROBADO que usé para obtener RESULTADOS rápidos y controlar la diabetes. La genialidad de este gran descubrimiento es que está diseñado para controlar, frenar y vencer a la diabetes. con la “complicidad” de tu propio cuerpo que se auto regenera si se le instalan los comando correctos en el metabolismo. Sin importar si tienes 7 ó 90 años. Sin importar si tu nivel de azúcar es más incontrolable que un caballo salvaje, o tu tipo de diabetes. Sin importar cuantas veces tu doctor te ha dicho que la diabetes no tiene cura. Sin importar si has fallado una docena de veces con tratamientos, medicamentos o métodos convencionales que NO SIRVEN. Estás a punto de descubrir cómo controlar la diabetes usando la Solución Natural más exitosa jamás revelada que transformará tu cuerpo en una máquina generadora de salud y energía – ¡en tan solo unos pocos días! haciendo click aqui. http://vencer-la-diabetes-rapido.info-pro.co

There are several reasons that your doctor may recommend that you have your spleen removed. These include having: a spleen that’s damaged from injury an enlarged spleen or ruptured spleen, which can occur from trauma certain rare blood disorders cancer or large cysts of the spleen infection

Will you still love me if I have herpes? About 1 in 6 Americans between the ages of 14 and 49 is infected with herpes simplex virus type 2, according to a health survey released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If you’re living with herpes, HSV, HPV or other STDs, you're recommended to check out the largest STD support site STDdatings.

Dr. David L. Sneed discusses the Austin Threadlift procedure, commonly referred to as the non-surgical facelift. This minimally-invasive skin rejuvenation procedure uses non-absorbable sutures to gently lift and tighten sagging, facial tissue and drooping skin, while at the same time stimulating further collagen growth over time. If you would like to find out more about the Silhouette Suture ThreadLift procedure offered in Austin, TX, please visit http://www.amedspa.com/silhouette-threadlift.php
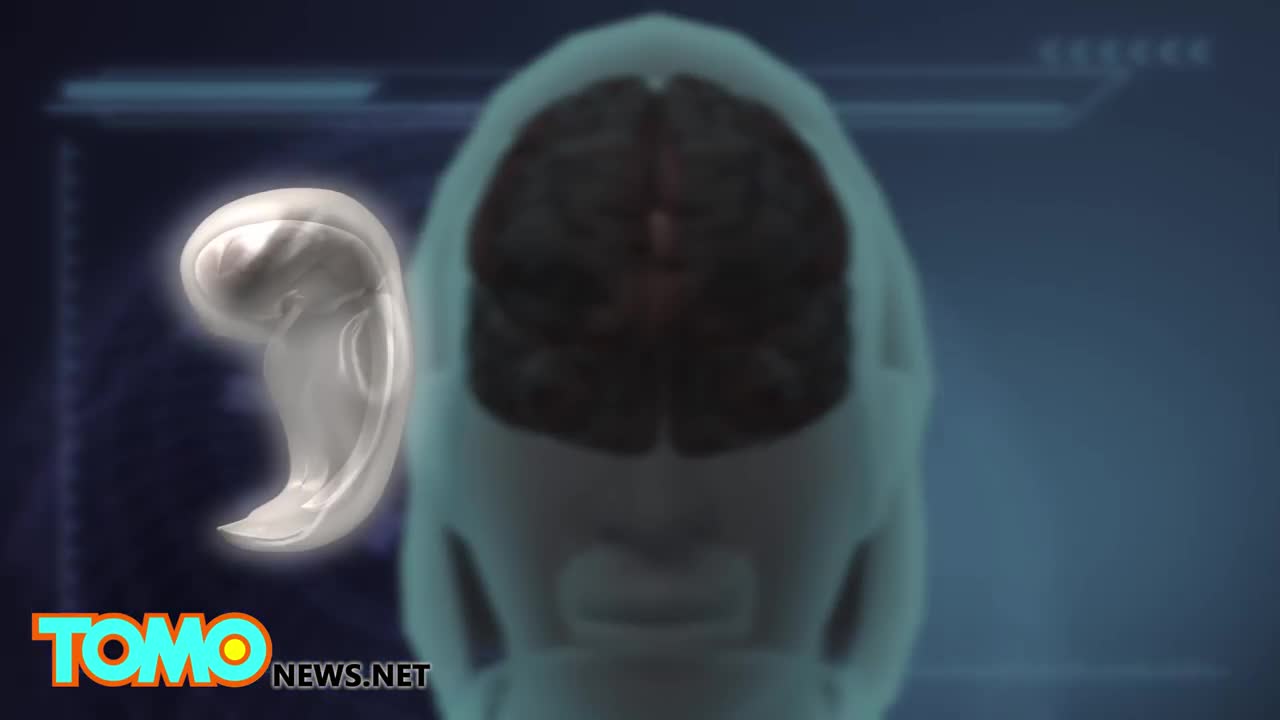
A man set to become the world’s first head transplant patient has scheduled the procedure for December 2017. Valery Spiridonov, 30, was diagnosed with a genetic muscle-wasting condition called Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, and volunteered for the procedure despite the risks involved, Central European News (CEN) reported. “When I realized that I could participate in something really big and important, I had no doubt left in my mind and started to work in this direction,” Spiridonov, a Russian computer scientist, told CEN. “The only thing I feel is the sense of pleasant impatience, like I have been preparing for something important all my life and it is starting to happen.”
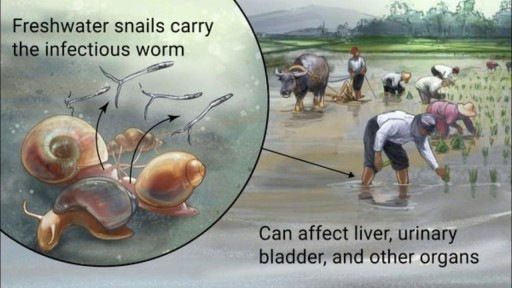
Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by flukes (trematodes) of the genus Schistosoma. After malaria and intestinal helminthiasis, schistosomiasis is the third most devastating tropical disease in the world, being a major source of morbidity and mortality for developing countries in Africa, South America, the Caribbean, the Middle East, and Asia. (See Epidemiology and Prognosis.) [1] More than 207 million people, 85% of who live in Africa, are infected with schistosomiasis, [1] and an estimated 700 million people are at risk of infection in 76 countries where the disease is considered endemic, as their agricultural work, domestic chores, and recreational activities expose them to infested water. [1, 2] Globally, 200,000 deaths are attributed to schistosomiasis annually. [3] Transmission is interrupted in some countries. [2] (See Etiology and Epidemiology.)