Top videos
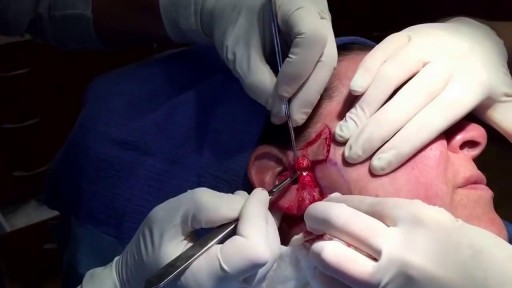
Hardware removals are among the most commonly performed surgical procedures worldwide. Current literature offers little data concerning postoperative patient satisfaction. The purpose of our study was to evaluate the patients’ point of view on implant removal. watch to learn more.

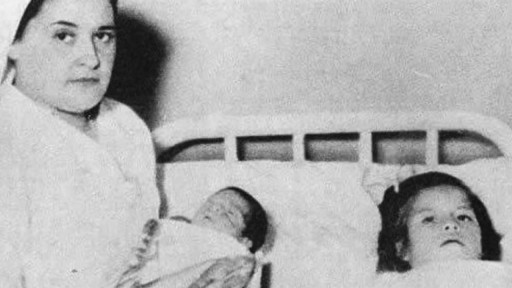
Rare condition disorder known as Diprosopus, also known as craniofacial duplication. Diprosopus is a congenital defect also known as craniofacial duplication. The exact description of diprosopus refers to a fetus with a single trunk, normal limbs, and facial features that are duplicated to a certain degree. A less severe instance is when the fetus has a duplicated nose and the eyes are spaced far apart. In the most extreme instances, the entire face is duplicated, hence the name diprosopus, which is Greek for two-faced. Fetuses with diprosopus often also lack brains (anencephaly), have neural tube defects, or heart malformations. In some cases, if the brain is formed, it may have duplicated structures. Most infants with diprosopus are stillborn and there are fewer than fifty cases documented since 1864.
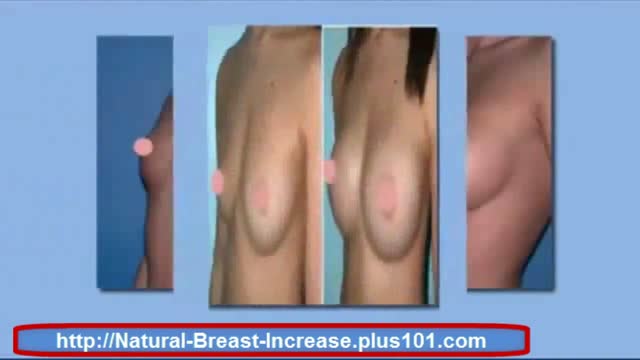
http://natural-breast-increase.plus101.com
---How To Make Bigger Breast. Can You Really Increase You Breast Size Naturally Without Surgery, Pills, Creams Etc Etc
Well a new website call natural-breast-increase.plus101.com says you can and thousands of women have already used there strategies.
And the best part about the this method is that you don't have to go through any expensive and painful surgery.
If you'd like to increase your own cup size then just visit the site below. I recommend the methods 100%
http://natural-breast-increase.plus101.com
How To Make Bigger Breast
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0cTQ3SZ4JIk
How To Make Bigger Breast,
can fenugreek increase breast size,
can i increase my breast size,
can i increase my breast size without surgery,
can i naturally increase breast size,
can we increase breast size naturally,
can women increase breast size naturally,
can you increase breast size,
can you increase breast size naturally,
can you make your breasts bigger,
cheap breast augmentation,
cheap breast implants,
cost of breast implants,
cream for breast enlargement,
cream to increase breast size,
curves breast enhancers,

A paralyzed teenager will make the first kick at the 2014 World Cup before the opening match between Brazil v. Croatia. The exoskeleton, which is enabling the paralyzed teen to walk and kick a soccer ball, has been designed by Duke University supported by the Walk Again Project. This monumental step in technology will make for a very exciting first kick, and let's not forget that this teenager will be walking when prior knowledge told us that was impossible. What are your thoughts on the opening kick?
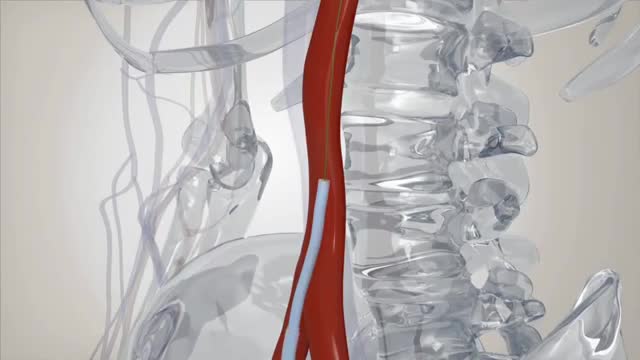
Aortic valve replacement is a procedure in which a patient's failing aortic valve is replaced with an artificial heart valve. The aortic valve can be affected by a range of diseases; the valve can either become leaky (aortic insufficiency / regurgitation) or partially blocked (aortic stenosis).

Hair transplant is a life-altering decision. If you are worried about hair loss, or consider baldness a hindrance, then you are ready to take the next step. Now the question is what to do next? Obviously, the worst choice would be to do "nothing" at all! Secondly, you could try to preserve your existing hair with medicines, remedies and hair-care products - it might just work for you. Thirdly, you could go for a hair-piece or a wig. But if you're reading this, then the chances are that you're looking for a permanent solution for your hair problem, which can best be provided through a hair transplant -an increasingly popular method of defeating baldness and patchy hair.
http://www.cocoona.ae/hair_transplantation.asp
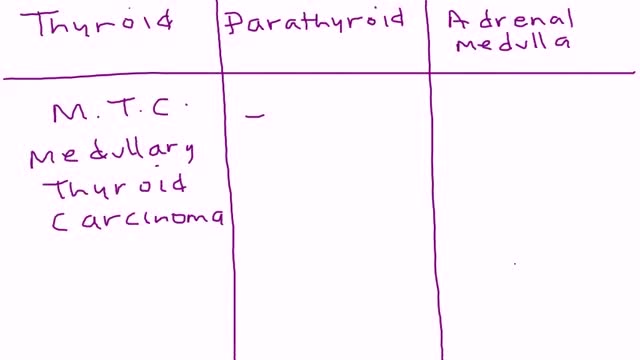
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN2) (also known as "Pheochromocytoma and amyloid producing medullary thyroid carcinoma", "PTC syndrome," and "Sipple syndrome") is a group of medical disorders associated with tumors of the endocrine system. The tumors may be benign or malignant (cancer).
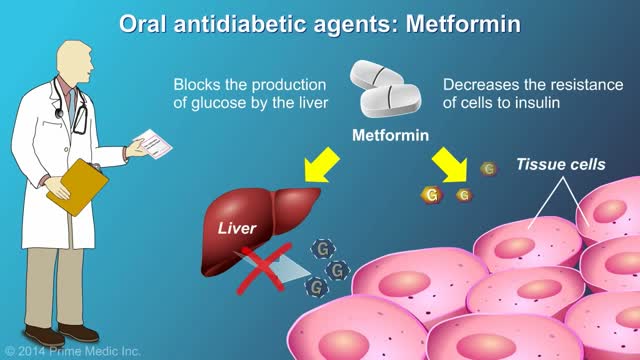
protecting the body from damage caused by hyperglycemia cannot be overstated. In the United States, 57.9% of diabetic patients have one or more diabetes complications, and 14.3% have three or more.1 Strict glycemic control is the primary method of reducing the development and progression of microvascular complications, such as retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy. Aggressive treatment of dyslipidemia and hypertension decreases macrovascular complications.2-4 Glycemic Control There are two primary techniques available for physicians to assess the quality of a patient’s glycemic control: self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and interval measurement of hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c).

Liposuction surgery is used to reduce the extra fat from your body with the very safe surgical process but you must consult with your Surgeon first when deciding about using this surgery to meet your body fat needs.
Vaser Lipo was Rs. 65000 per region. Now at Rs. 50,000 per Region
Offer valid till 31st March only
Vaser Liposuction technology helps to reduce the healing time and increase effective skin contraction, giving you smooth, slim results. With Liposuction there are no stitches, only a single 1cm small incision giving you permanent large result.
For further information, are available visit our website:
http://www.imageclinic.org/liposuction.html
Your Query for Chat and call +91-9818369662, 9958221983 (WhatsApp)

Download Clash of Clans for free for mobile devices. http://supr.cl/ThisArmy
I don't know you, BigBuffetBoy85
But if you think you can humiliate me and take my gold, think again.
Oh, I am coming for you with lots of Barbarians and Dragons. I can't wait to destroy your village, while you beg for mercy, but you will get no mercy. I will have my revenge.
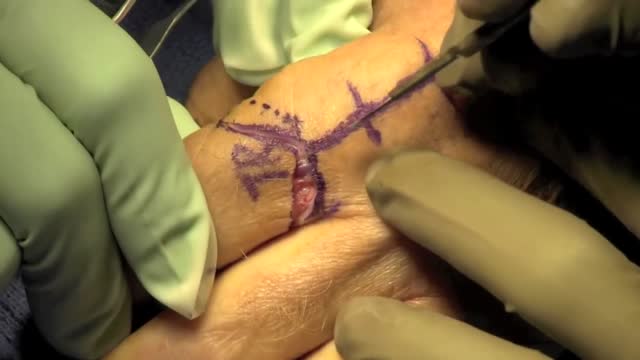
An amputation is the removal of an extremity or appendage from the body. Amputations in the upper extremity can occur as a result of trauma, or they can be performed in the treatment of congenital or acquired conditions. Although successful replantation represents a technical triumph to the surgeon, the patient's best interests should direct the treatment of amputations. The goals involved in the treatment of amputations of the upper extremity include the following : Preservation of functional length Durable coverage Preservation of useful sensibility Prevention of symptomatic neuromas Prevention of adjacent joint contractures Early return to work Early prosthetic fitting These goals apply differently to different levels of amputation. Treatment of amputations can be challenging and rewarding. It is imperative that the surgeon treat the patient with the ultimate goal of optimizing function and rehabilitation and not become absorbed in the enthusiasm of the technical challenge of the replantation, which could result in poorer outcome and greater financial cost due to lost wages, hospitalization, and therapy.
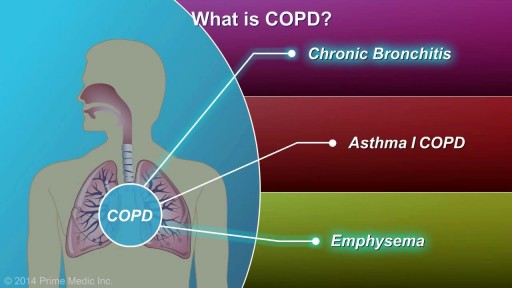
COPD, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, is a progressive disease that makes it hard to breathe. Progressive means the disease gets worse over time. COPD can cause coughing that produces large amounts of a slimy substance called mucus, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and other symptoms. Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of COPD. Most people who have COPD smoke or used to smoke. However, up to 25 percent of people with COPD never smoked. Long-term exposure to other lung irritants—such as air pollution, chemical fumes, or dusts—also may contribute to COPD. A rare genetic condition called alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency can also cause the disease.