Top videos
Throughout the body, there are several points at which blood vessels unite. The junctions are termed anastomoses. In the simplest sense, an anastomosis is any connection (made surgically or occurring naturally) between tube-like structures. Naturally occurring arterial anastomoses provide an alternative blood supply to target areas in cases where the primary arterial pathway is obstructed. They are most abundant in regions of the body where the blood supply may can be easily damaged or blocked (such as the joints or intestines). This article focuses on the arterial anastomotic networks of the upper limb.
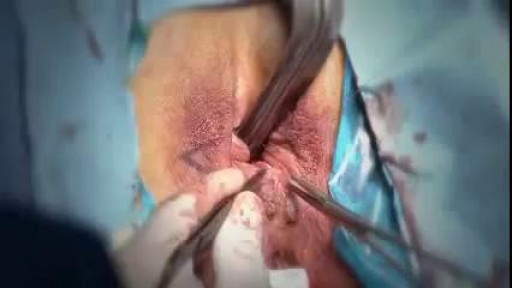
A vaginoplasty is a surgical procedure that tightens the vagina. This is done by removing excess vaginal lining and tightening the surrounding soft tissues and muscles. During delivery of a baby the vagina and surrounding tissues and muscles become stretched. After delivery the vagina may return to a more “normal” size, but it often fails to return to its’ pre pregnancy diameter. Generally, the more vaginal deliveries, the worse the condition gets. Many women will complain of decreased sensation and sexual satisfaction during intercourse. Commonly this is due to a lack of friction. Often their partner may notice a change although he may say nothing. Kegel exercises are often recommended but rarely succeed in restoring vaginal tightness.

Surgical site infections (SSIs) remain a prevalent threat to patient safety. Proper surgical hand scrub or rub techniques are essential to decreasing the incidence of SSIs. This video provides instructions on the anatomical surgical hand scrub procedure using the brushstroke method. Learn more from the Department of Hospital Epidemiology and Infection Control (HEIC) at The Johns Hopkins Hospital: http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/heic
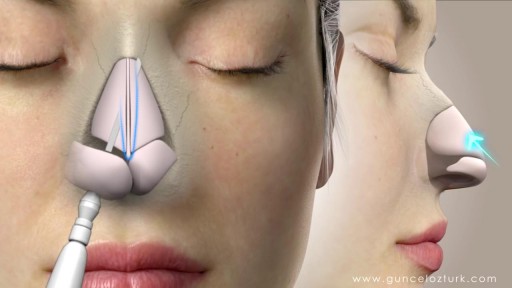
Rhinoplasty, sometimes referred to as a "nose job" or "nose reshaping" by patients, enhances facial harmony and the proportions of your nose. It can also correct impaired breathing caused by structural defects in the nose. What surgical rhinoplasty can treat Nose size in relation to facial balance Nose width at the bridge or in the size and position of the nostrils Nose profile with visible humps or depressions on the bridge Nasal tip that is enlarged or bulbous, drooping, upturned or hooked Nostrils that are large, wide or upturned Nasal asymmetry If you desire a more symmetrical nose, keep in mind that everyone's face is asymmetric to some degree. Results may not be completely symmetric, although the goal is to create facial balance and correct proportion. Rhinoplasty to correct a deviated septum Nose surgery that's done to improve an obstructed airway requires careful evaluation of the nasal structure as it relates to airflow and breathing. Correction of a deviated septum, one of the most common causes of breathing impairment, is achieved by adjusting the nasal structure to produce better alignment.

The purpose of this video is to help you learn what to expect while you are in hospital, and how to care for yourself after surgery so that you can have the best recovery possible.
----------------------------------
At Horizon Health Network, we are helping people be healthy! Chez le Réseau de santé Horizon, nous aidons les gens à être en santé!
For more information, visit/Pour plus d'information, cliquez-ici:
https://news.horizonnb.ca
Facebook: https://facebook.com/HorizonNB
Twitter: https://twitter.com/HorizonHealthNB
Instagram: https://instagram.com/horizonhealthnb/
Linkedin: https://linkedin.com/company/h....orizon-health-networ
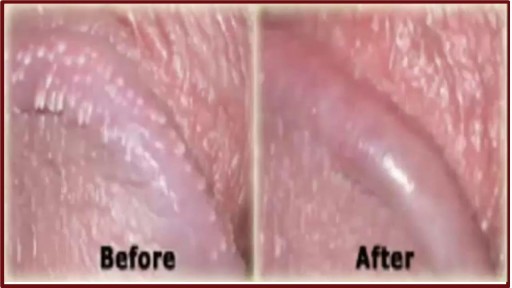
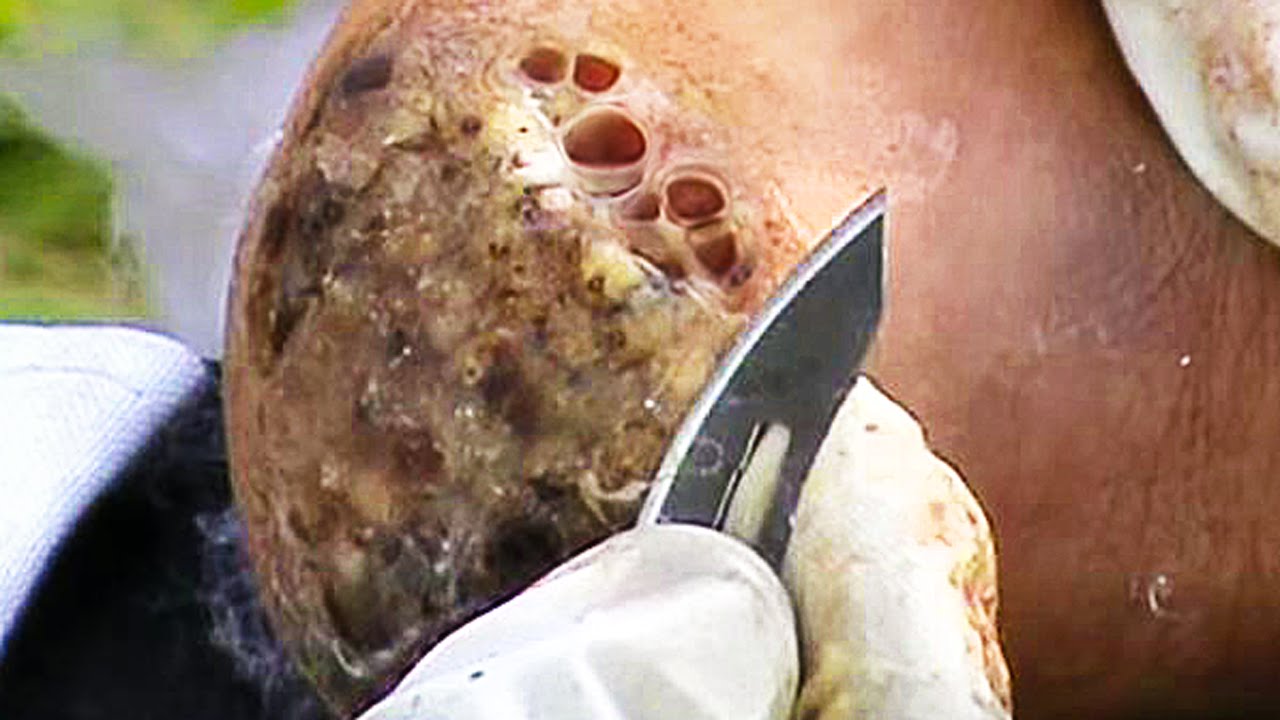
http://penilepapules.plus101.com/ ----- White Spots On Shaft, Pearly Penile Papules Treatment Cream, Single Red Bump On Shaft, Ppp Surgery. Common Home Made Remedies for Pearly Penile Papules. When it comes to treating pearly penile papules many people find it very difficult to reach one of the medical treatments. This is mainly because they are highly expensive and not many people can afford spending large amounts of money on surgery and recovery. In addition to that, these procedures have been reported as being quite risky, which make the men suffering from pearly penile papules think twice before going for one of the available surgeries. This is why, along the time, many homemade, natural treatments have been experienced, so that a cheaper and less risky way of curing pearly penile papules would be found. Some of the methods which have been tried proved to be very less effective, while some did not have any effect at all. Yet, there have also been methods which not only proved to be effective, but they were also considered to be much better than the medical treatment. Most of those who have tried the tea tree oil treatment reported significant diminish of the number of the papules from their penises. In addition to the clearing of the skin, they have also noticed that there were no side effects and the skin remained soft after the papules were removed. As the method was quite simple to put in practice (it requires the application of tea tree oil on the affected area with a cotton swab for three or four times per day), many men decided this was indeed a great solution to their problem.

http://www.amerra.com In this patient education video from Colorectal Surgical Associates in Houston, Texas, learn more about the single incision laparoscopic colectomy procedure. This minimally invasive procedure uses a mini incision that
results in less pain, fewer complications, earlier recovery, and a smaller scar. Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in the United States. For more information please visit our website: www.csamd.com or call (713)-790-0600.