Top videos

Identify the anatomy and explain the physiology of the scrotum on diagrams and sonograms.
Describe and demonstrate the protocol for sonographic scanning of the scrotum.
Identify and describe sonographic images of congenital abnormalities of the scrotum.
Identify and describe sonographic images of pathologies of the scrotum.
Identify and describe sonographic images of extratesticular disease processes.
Identify the anatomy and explain the physiology of the prostate on diagrams and sonograms.
Describe and demonstrate the protocol for transabdominal and endorectal sonographic scanning of the prostate.
Identify and describe sonographic images of benign and malignant pathologies of the prostate, including benign hyperplasia, prostatitis, carcinoma, and calculi.
Explain the technique for prostate biopsy.
Define the criteria for an ultrasound appearance of prostate tumor staging.
Explain the technique for radiation seed implantation.
Explain the Patient Privacy Rule (HIPAA) and Patient Safety Act (see reference).

This 3D animation of brain surgery, shows how a ventriculostomy is performed, which is a neurosurgical procedure of creating a hole within a cerebral ventricle for drainage. It is most commonly performed on those with hydrocephalus, an abnormal buildup of fluid in the ventricles (cavities) deep within the brain. It's done by surgically penetrating the skull, dura mater, and brain such that the ventricular system ventricle of the brain is accessed.
When catheter drainage is temporary, it is commonly referred to as an external ventricular drain (EVD). When catheter drainage is permanent, it is usually referred to as a shunt.
There are many catheter-based ventricular shunts that are named for where they terminate, for example, a ventriculi-peritoneal shunt terminates in the peritoneal cavity, a ventriculoarterial shunt terminates within the atrium of the heart, etc. The most common entry point on the skull is called Kocher's point. An EVD ventriculostomy is done primarily to monitor the intracranial pressure as well as to drain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), primarily, or blood to relieve pressure from the central nervous system (CNS).
For more information about custom medical animation, please visit https://www.amerra.com/.
Watch additional medical animations:
Craniectomy brain surgery - 3D animation: https://youtu.be/1RkseDeYS9g
Accessing an implantable port training - 3D animation: https://youtu.be/xSTpxjyv4O4
Open Suctioning with a Tracheostomy Tube - 3D animation: https://youtu.be/wamB7jpWCiQ
Suctioning the endotracheal tube - medical animation: https://youtu.be/pN6-EYoeh3g
Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) - 3D animation: https://youtu.be/qKTRyowwaLA
How to insert a nasogastric tube for NG intubation - 3d animation: https://youtu.be/Abf3Gd6AaZQ
Oral airway insertion - oropharyngeal airway technique - 3D animation: https://youtu.be/caxUdNwjt34
Nasotracheal suctioning (NTS) - 3D animation: https://youtu.be/979jWMsF62c
Learn about hemorrhoids with #3d #animation: https://youtu.be/R6NqlMpsiiY
LASIK eye surgery - 3D animation: https://youtu.be/Bb8bnjnEM00
CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation - 3D animation: https://youtu.be/G87knTZnhks
What are warts (HPV)? - 3D animation: https://youtu.be/guJ1J7rRs1w
How Macular Degeneration Affects Your Vision - 3D animation: https://youtu.be/ozZQIZ_52YY
NeoGraft hair transplant procedure – animation: https://youtu.be/C-eTdH2UPXI
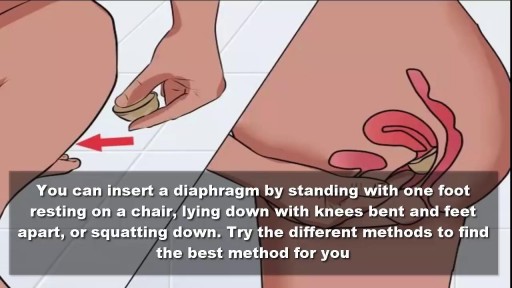
To use the diaphragm, first cover the inside of it with spermicide. Then insert it into your vagina so that it covers your cervix. You can insert the diaphragm up to 6 hours before sex. You should leave it in for at least 6 hours after the last time you have sex.

A patient at a British hospital played Mahler and Gershwin on the violin while surgeons removed a tumor from her brain, so doctors could preserve her ability to play music.
She left the hospital 3 days later and hopes to return to the symphony soon. https://abcn.ws/2SGY9mp
SUBSCRIBE to ABC NEWS: https://www.youtube.com/ABCNews/
Watch More on http://abcnews.go.com/
LIKE ABC News on FACEBOOK
https://www.facebook.com/abcnews
FOLLOW ABC News on TWITTER:
https://twitter.com/abc
GOOD MORNING AMERICA'S HOMEPAGE:
https://www.goodmorningamerica.com/

Website : https://www.udemy.com/course/h....istology/?referralCo
Human Histology is one of the basic subject in a Medical Student career. By learning Histology in a proper way, this will help you to get a Visual memory of the Human body. Using this Visual memory, you can Learn any other subjects with little effort.
This Course is very well organized with lot of Histology images, Line diagrams, simple presentations and clear Explanations. This course has 33 videos, 19 chapters, 6 hours long covering all topics. Every topic is made Simple and Complete. Dr Ram has a great teaching style and has a good experience in teaching medical subjects to students.
After finishing this course, you will be better in your basics, with ability to visualize the human body and this will create an intense thirst to learn more. We give 100% guarantee that you will have a complete and in-depth understanding in short time, You will start to enjoy Learning Medicine because of the visualization of human body you get from this course and you will be ready to face any Medical exams in world.
Course features:
- Complete Histology lectures covering all chapters
- 19 chapters | 33 Videos | 6 Hours
- Clear Histology images
- Line diagrams for easy understanding
- Lot of memory tips
- High quality audio and Videos
- Can be viewed in Pc, or Phones or TV
Course content: ( 19 Chapters, 33 videos )
I The Cell - 3 Lessons
1. Nucleus
2. Cytoplasm
3. Cell Junctions
II Tissues - 11 Lessons
4. Epithelial tissues
5. Connective tissues
6. Muscular tissues
7. Nervous tissues
8. Bones
9. Cartilage
10. Lymphoid tissues
III Organ systems - 19 Lessons
11. Cardiovascular system
12. Respiratory system
13. Gastrointestinal system
14. Liver and Exocrine pancreas
15. Endocrine system
16. Urinary system
17. male reproductive system
18. Female reproductive system
19. The skin
Instructor : Dr Ram , Med Madness

If a fetal lung lesion is causing heart failure, fetal surgery may be performed to remove the CCAM before birth. http://fetalsurgery.chop.edu
N. Scott Adzick, MD, Mark Johnson, MD, and Holly Hedrick, MD, experts from the Center for Fetal Diagnosis and Treatment at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, explain when fetal intervention for CCAM is recommended, the various approaches that may be used to treat the most complex fetal lung lesions before birth, and how these procedures are performed.
One concern with fetal lung lesions is that they take up space in the chest. If the lung mass grows and pushes the heart and other organs out of place, it can lead to complications such as fetal hydrops (heart failure in the fetus). If this happens, a fetal surgery procedure may be performed to remove the CCAM before birth.
In other cases, an EXIT procedure may be performed to partially deliver the baby, so the team can remove the mass before the baby is fully delivered.
In this video series, parents, nurses and doctors from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia’s Center for Fetal Diagnosis and Treatment talk about the different types of fetal lung lesions like congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (CCAM) and bronchopulmonary sequestration (BPS), the importance of accurate diagnosis and monitoring, and the most advanced treatment options currently available. They also discuss follow-up care and long-term outcomes for babies diagnosed with fetal lung lesions.