Top videos

Dr. Celia Divino, Chief, Division of General Surgery at The Mount Sinai Hospital, performs a laparoscopic appendectomy. Visit the Division of General Surgery at http://bit.ly/18z944M. Click here to learn more about Dr. Celia Divino http://bit.ly/12RF0ee

Join Dr. Parsia Vagefi, Chief of Surgical Transplantation and Dr. Steven Hanish, Surgical Director of Liver Transplantation, as they grant unprecedented access to the OR while performing a #Liver #Transplant #Surgery.
To find out more about UT Southwestern's transplant programs visit:
https://www.utswmed.org/transplant
An aortic dissection is a serious condition in which the inner layer of the aorta, the large blood vessel branching off the heart, tears. Blood surges through the tear, causing the inner and middle layers of the aorta to separate (dissect). If the blood-filled channel ruptures through the outside aortic wall, aortic dissection is often fatal. Aortic dissection is relatively uncommon. The condition most frequently occurs in men in their 60s and 70s. Symptoms of aortic dissection may mimic those of other diseases, often leading to delays in diagnosis. However, when an aortic dissection is detected early and treated promptly, the chance of survival greatly improves.
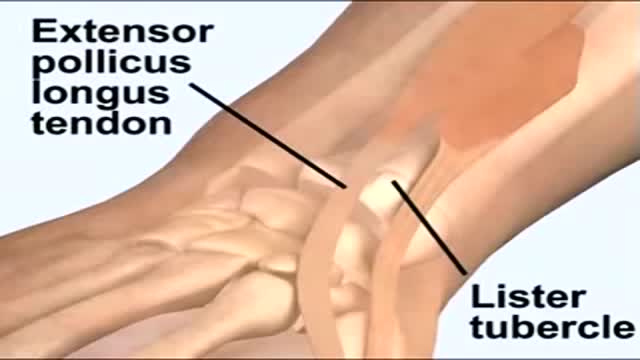
A needle is inserted into a joint for two main indications: aspiration of fluid (arthrocentesis) for diagnosis or for relief of pressure, or injection of medications. In practical terms, most injections into joints consist of a glucocorticoid, a local anesthetic, or a combination of the two. Occasionally saline is injected into the joint to diagnose a joint injury. This topic will review the basic technique of inserting a needle into a joint and the main indications for intraarticular steroid injections. The same techniques apply for injection of the less commonly used hyaluronate viscosupplementation agents into knees, hips, and perhaps shoulders.

Vaginal discharge serves an important housekeeping function in the female reproductive system. Fluid made by glands inside the vagina and cervix carries away dead cells and bacteria. This keeps the vagina clean and helps prevent infection. Most of the time, vaginal discharge is perfectly normal. The amount can vary, as can odor and hue (its color can range from clear to a milky white-ish), depending on the time in your menstrual cycle. For example, there will be more discharge if you are ovulating, breastfeeding, or are sexually aroused. The smell may be different if you are pregnant or you haven't been diligent about your personal hygiene. None of those changes is cause for alarm. However, if the color, smell, or consistency seems significantly unusual, especially if it accompanied by vaginal itching or burning, you could be noticing an infection or other condition. What causes abnormal discharge? Any change in the vagina's balance of normal bacteria can affect the smell, color, or discharge texture. These are a few of the things that can upset that balance:
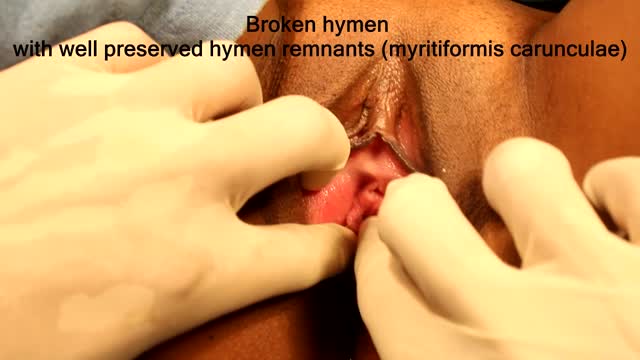
Best and 100% Successful Hymen Repair Surgery in Delhi with Latest Ultrafine Hymen repair Technology. 100% successful , Secure and Private. for more information visit: http://www.olmeccosmeticsurgery.com/best-hymenoplasty-surgery-india-delhi/

White stretch marks are unsightly marks that are found along the thighs, abdomen and upper arms. These are marks that could be due to a recent weight loss, trauma or pregnancy. Stretch marks can affect your confidence if you wear revealing outfits and so you should do all you can to remove them.

Morning erections have colloquially been termed as “morning wood” while scientifically it is called nocturnal penile tumescence. It is a normal and healthy physiological reaction and response that most men experience in their lives. Morning erections are really the ending of a series of erections that happen to men during the night. Healthy men can, on average, have anywhere between three to five erections in a full night of sleep, each of which lasts from 25-35 minutes.

The Epley Maneuver for Vertigo can be very effective at relieving vertigo symptoms, but it’s a procedure that should be performed by a physical therapist or other health care professional. This video is for demonstration purposes only. See Doctor Jo’s blog post about the Epley
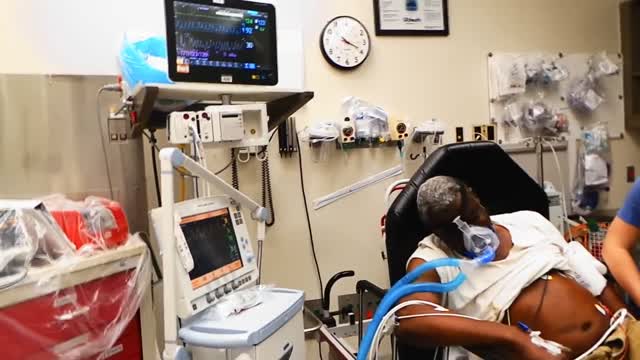
Pulmonary edema is almost always treated in the emergency room or hospital. You may need to be in an intensive care unit (ICU). Oxygen is given through a face mask or tiny plastic tubes are placed in the nose. A breathing tube may be placed into the windpipe (trachea) so you can be connected to a breathing machine (ventilator) if you cannot breathe well on your own. The cause of edema should be identified and treated quickly. For example, if a heart attack has caused the condition, it must be treated right away. Medicines that may be used include: Diuretics that remove excess fluid from the body Medicines that strengthen the heart muscle, control the heartbeat, or relieve pressure on the heart