Top videos

Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects the brain and spinal cord. Early MS symptoms include weakness, tingling, numbness, and blurred vision. Other signs are muscle stiffness, thinking problems, and urinary problems. Treatment can relieve MS symptoms and delay disease progression.

The pain is frequently severe and is described as throbbing or pulsating. Nausea is common, and many migraine patients have a watering eye, a running nose, or congestion. If these symptoms are prominent, they may lead to a misdiagnosis of sinus headaches.

A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder of the sleep patterns of a person or animal. Some sleep disorders are serious enough to interfere with normal physical, mental, social and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests commonly ordered for some sleep disorders.

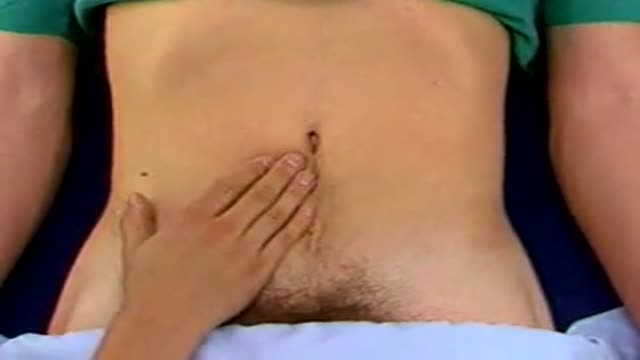
A successful cardiovascular exam includes visual examination, palpation of the apical impulse, auscultation of Erb's point, auscultation of the carotids, and auscultation over the four different heart valve locations (aortic, pulmonic, tricuspid, and mitral). Additionally, the radial pulse is palpated while auscultating to distinguish whether a murmur is diastolic or systolic.
Video Index:
0:13 - Inspection of the thorax
0:29 - Palpation of the apex heart beat
0:59 - Auscultation of the heart
1:16 - Auscultation of the Erb’s point
1:33 - Using Erb’s point to check the heart rate
1:45 - Systolic and diastolic heart sound identification
2:01 - Ascultating individual valves: aortic, pulmonary, tricuspid, mitral
2:41 - Ascultation of the carotids
2:54 - Ascultating the pulmonary and aortic valves
3:04 - Ascultation of the mitral valve
3:16 - Mitral valve murmurs
Subscribe to AMBOSS YouTube for the latest clinical examination videos, medical student interviews, study tips and tricks, and live webinars!
Free 5 Day Trial: https://go.amboss.com/amboss-YT
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/amboss_med/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/AMBOSS.Med/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ambossmed
Blog: https://blog.amboss.com/us
#CardiovascularExamination #AuscultationOfTheHeart #USMLE #AMBOSSMed
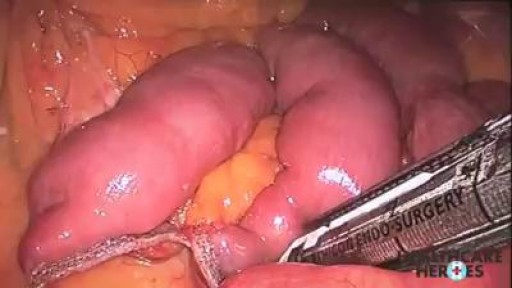
Bariatric surgical procedures cause weight loss by restricting the amount of food the stomach can hold, causing malabsorption of nutrients, or by a combination of both gastric restriction and malabsorption. Bariatric procedures also often cause hormonal changes. Most weight loss surgeries today are performed using minimally invasive techniques (laparoscopic surgery). The most common bariatric surgery procedures are gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, adjustable gastric band, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Each surgery has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Lip augmentation is a cosmetic procedure that can give you fuller, sensual, plumper lips that are now considered aesthetically appealing. Dr. Ajaya Kashyap best cosmetic & plastic surgeon in Delhi at MedSpa Clinic. Learn more about #lipaugmentation at www.bestfacesurgeryindia.com Learn more about #lipenhancement at www.themedspa.us/cosmetic-surgery/lip-enhancement.html Contact us : info@themedspa.us http://www.themedspa.us/contact.html Tag: lipaugmentation, lipenhancement, fullerlips, lipenlargement, lipfullness, nonsurgicalprocedure, fillers, cosmeticsurgery, dermalfiller, plumperlips, lipinjections, plumplips, injectablefillers, lipimplant, lip augmenation cost in delhi, lip augmenation in delhi , lip augmenation cost in India, best lip augmenation cost in delhi
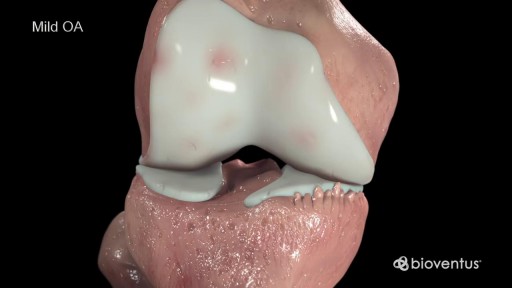
Cartilage is a slippery tissue that provides a smooth surface for joint motion and acts as a cushion between the bones. Synovium is soft, and it lines the joints. It produces fluid, called synovial fluid, for lubrication, and it supplies nutrients and oxygen to the cartilage. As these functions break down, they no longer protect the bones of the knee joint, and bone damage occurs. OA of the knee can cause pain and stiffness. The symptoms worsen over time

Liquid Zeolite is one of best natural Zeolite products which is used to remove the cancer cells and tumor. This is helpful to activate P21 tumor gene to remove the tumor. For more information visit our website at http://www.pureliquidzeolite.com/.

Weiße Punkte Auf Der Haut, Vitiligo Symptome, Vitiligo Behandlung, Weiße Flecken Haut Pilz--- http://vitiligo-heilung.info-pro.co --- Wie wird Vitiligo diagnostiziert? Der Arzt wird als allererstes nach den offensichtlichsten Anzeichen von Vitiligo suchen, den weißen Hautflecken. Es gibt jedoch auch noch weitere diagnostische Methoden. In manchen Fällen kann Vitiligo vererbt sein. Der Arzt wird also erörtern, ob die Eltern oder andere Familienmitglieder des Patienten an der Hautstörung litten (oder leiden), ob in der Familie Fälle von Autoimmunstören, und ob der Patient bereits ergraute bevor er das Alter von 35 Jahren erreichte. Manchmal wird sich der Arzt auch einer Blutentnahme oder Gewebe-Biopsie bedienen, um durch Laboruntersuchungen abzusichern, dass tatsächlich Vitiligo vorliegt. Behandlung von Vitiligo Die Behandlung von Vitiligo ist in ständiger Weiterentwicklung begriffen. Die gegenwärtig eingesetzten Behandlungsmethoden hängen vor allem vom Schweregrad der Hautstörung ab. Allerdings spielt auch die Krankenversicherung des Patienten eine Rolle, denn die meisten verfügbaren Behandlungsverfahren sind äußerst kostspielig. Dennoch sind sie nicht immer effektiv und können zudem auch noch eine Masse an Nebenwirkungen mit sich bringen. Patienten, die sich die teuren Behandlungen nicht leisten können, bleibt meistens nichts anderes übrig als zu lernen, mit der Erkrankung zu leben. Vitiligo ist zwar nicht lebensbedrohlich, aber sie kann einen schweren Einfluss auf das Selbstwertgefühl und Selbstbewusstsein des Patienten haben. "Gratis-Präsentation enthüllt einen ziemlich ungewöhnlichen Tipp zur Beseitigung von Vitiligo für alle Zeiten und in nur 45-60 Tagen - Garantiert!" http://vitiligo-heilung.info-pro.co

MUSC Children’s Health offers South Carolina’s only Level 1 Children’s Surgery Center, representing excellence in inpatient surgery at MUSC Shawn Jenkins Children’s Hospital, as well as outpatient surgery at R. Keith Summey Medical Pavilion. These two state-of-the-art facilities are equipped with a team of pediatric board-certified providers utilizing pediatric-specific devices and the most technologically advanced tools.