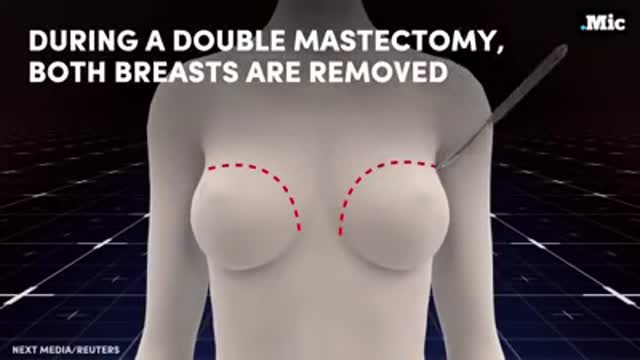
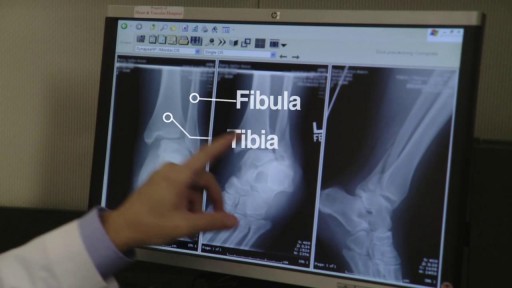
Top videos

http://vaincre-le-diabete.plus101.com
---Traitement Diabete 2. Vous Eliminerez Le Diabète D'Une Fois Pour Toutes!
Laissez de côté les préoccupations des risques de votre maladie.
Ne souffrez plus de votre poids et la privation des aliments préférés.
Ne dépensez plus des milliers d'euros en médicaments qui combattent la maladie de l'extérieur.
Ne vivez plus une vie de restrictions.
Ne souffrez plus!!!
Oubliez de changer constamment de médicaments prescrits, de mesurer le niveau de glucose et de vous injecter l'insuline.
Traitement Diabete 2
http://youtu.be/SvsCAZuKGBo
traitement contre le diabete de type 2,
traitement de diabete type 2,
traitement de diabète de type 2,
traitement diabete type 1,
traitement diabète de type 2,
traitement diabète type 2,
traitement du diabete type 2 par les plantes,
traitement du diabète de type 2,
traitement du diabète par les plantes,
traitement du diabète type 2,
traitement naturel diabete,
traitement pour diabete,
traitement pour le diabète de type 2,
traitements diabète
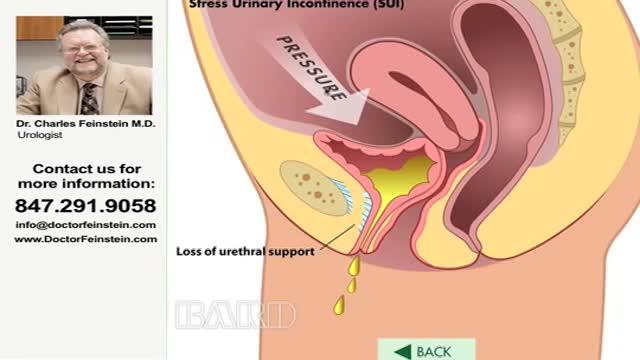
Urinary incontinence — the loss of bladder control — is a common and often embarrassing problem. The severity ranges from occasionally leaking urine when you cough or sneeze to having an urge to urinate that's so sudden and strong you don't get to a toilet in time. If urinary incontinence affects your daily activities, don't hesitate to see your doctor. For most people, simple lifestyle changes or medical treatment can ease discomfort or stop urinary incontinence

Come Si Può Rimanere Incinta, Rimanere Incinta A 42 Anni Naturalmente, Settimane Di Gravidanza--- http://come-rimanere-incinta.info-pro.co --- Come rimanere incinta in modo naturale La sterilità può essere generalmente definita come l'incapacità di avere una gravidanza dopo aver provato per almeno un anno senza l'uso di contraccettivi. Nei paesi occidentali la sterilità colpisce circa il 15% della popolazione. Mentre c'è chi cerca di concepire con metodi alternativi come la fecondazione in vitro, altri preferiscono ottimizzare le probabilità di rimanere incinta naturalmente. Cercare di rimanere incinta naturalmente può essere molto importante dal momento che molte coppie o individui con diagnosi di sterilità possono tornare ad essere fertili senza trattamenti (e quindi si dovrebbe parlare di "sub-fertilità" piuttosto che di "sterilità"). Quando si cerca di rimanere incinta naturalmente, il fattore più importante è capire il ciclo mestruale e la tempistica di ovulazione, che porta ad ottimizzare le possibilità di ottenere una gravidanza. Di solito l'ovulazione avviene intorno al quattordicesimo giorno e, di conseguenza, per ottenere una gravidanza naturale la coppia dovrebbe avere più rapporti sessuali possibili tra il dodicesimo e il quindicesimo giorno. Ogni donna ha un ciclo leggermente diverso. Per cui, per migliorare le probabilità di rimanere incinta, è indispensabile studiare i propri cicli e calcolare con esattezza quando si ovula. L'antico Sistema Olistico Cinese In 5-passi Per Rimanere Incita Naturalmente E Avere Bimbi Sani Clicca sul link http://come-rimanere-incinta.info-pro.co

Dr. Salvador pioneered the development of new liposuction techniques. In 2005, he developed Smartlipo Ultra to provide a safer and more effective treatment for removal of unwanted fat. Smartlipo Ultra was the first liposuction treatment to combine ultrasound for fat removal with laser technology to tighten skin.Dr. Salvador now focuses his cosmetic practice exclusively on SafeSculpt Laser Liposuction. He is recognized internationally as an expert on minimally invasive liposuction and tumescent anesthesia.
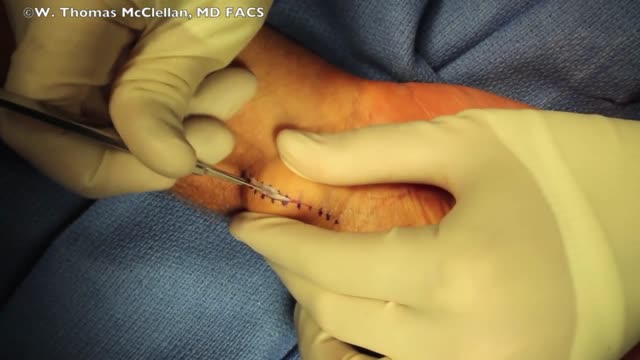
Ganglion Cyst Volar Wrist Removal Ganglion cysts are noncancerous lumps that most commonly develop along the tendons or joints of your wrists or hands. They also may occur in the ankles and feet. Ganglion cysts are typically round or oval and are filled with a jellylike fluid. Small ganglion cysts can be pea-sized, while larger ones can be around an inch (2.5 centimeters) in diameter. Ganglion cysts can be painful if they press on a nearby nerve. Their location can sometimes interfere with joint movement. If your ganglion cyst is causing you problems, your doctor may suggest trying to drain the cyst with a needle. Removing the cyst surgically also is an option. But if you have no symptoms, no treatment is necessary. In many cases, the cysts go away on their own.

Liquid Zeolite is one of best natural Zeolite products which is used to remove the cancer cells and tumor. This is helpful to activate P21 tumor gene to remove the tumor. For more information visit our website at http://www.pureliquidzeolite.com/.

Antiphospholipid (AN-te-fos-fo-LIP-id) syndrome occurs when your immune system attacks some of the normal proteins in your blood. It can cause blood clots in your arteries or veins. And it can cause pregnancy complications, such as miscarriage and stillbirth. Blood clots in your leg veins cause a condition known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Damage from blood clots in your organs, such as your kidneys, lungs or brain, depends on the extent and location of the clot. For instance, a clot in your brain can cause a stroke. There's no cure for antiphospholipid syndrome, but medications can reduce your risk of blood clots.

Proper placement of sutures enhances the precise approximation of the wound edges, which helps minimize and redistribute skin tension. Wound eversion is essential to maximize the likelihood of good epidermal approximation. Eversion is desirable to minimize the risk of scar depression secondary to tissue contraction during healing. Usually, inversion is not desirable, and it probably does not decrease the risk of hypertrophic scarring in an individual with a propensity for hypertrophic scars. The elimination of dead space, the restoration of natural anatomic contours, and the minimization of suture marks are also important to optimize the cosmetic and functional results.

How To Improve Memory Power, How To Improve Concentration And Memory, Foods That Help The Brain---- http://brain-revitalizer.info-pro.co --- Brain Entrainment, For centuries humans have wondered at the connection between specific sound frequencies and the effect it can have on the brain and corresponding moods and emotions. From tribal drums to periodic stimulus tones the human brain taps into dominant external frequencies and when it does the mind can be altered to induce a host of different states including relaxation, sleep, creativity and excitement. The practice of causing brainwave frequencies to match a periodic stimulus to produce an intended state is called brainwave entrainment or brainwave synchronization and it is becoming more popular as life becomes more stressful. The study of sound and light and how it affects the human brain is nothing new. In the 1930's William Grey Walter used EEG equipment and strobe lights to detect the existence of high speed alpha waves and low speed delta waves and how each played a factor in human sleep patterns. In 1973 Gerald Oster published his discovery of binaural beats in Scientific American, a breakthrough article that defined binaural beats as apparent sounds which arise in the brain for specific physical stimuli. Though first discovered in 1839 by Heinrich Wilhelm Dove it wasn't until Oster's research that scientists began to speculate that binaural beats could be used to help induce relaxation, creativity and other desirable mental states. Today brainwave entrainment is gaining rapid popularity with people who feel over-stressed, depressed and unmotivated. With technology growing by leaps and bounds it's not hard to understand how a person can feel overwhelmed by information and sensory overload and instead of taking pills a growing segment of the population is turning to brainwave entrainment to produce a more natural and lasting feeling of relaxation. But YOU can be different! You can use Genius Brain Power to empower your brain so that you come alive with more energy, learn quicker, think more creatively, focus on your work like never before and drastically reduce stress with amazingly deep states of relaxation and meditation. click here: http://brain-revitalizer.info-pro.co
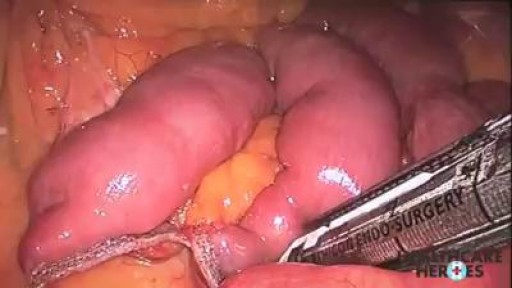
Bariatric surgical procedures cause weight loss by restricting the amount of food the stomach can hold, causing malabsorption of nutrients, or by a combination of both gastric restriction and malabsorption. Bariatric procedures also often cause hormonal changes. Most weight loss surgeries today are performed using minimally invasive techniques (laparoscopic surgery). The most common bariatric surgery procedures are gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, adjustable gastric band, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Each surgery has its own advantages and disadvantages.

Among the many health benefits of sex are: Improved Immunity. People who have sex frequently (one or two times a week) have significantly higher levels of immunoglobulin A (IgA). ... Heart Health. ... Lower Blood Pressure. ... It's a Form of Exercise. ... Pain Relief. ... May Help Reduce Risk of Prostate Cancer. ... Improve Sleep. ... Stress Relief.
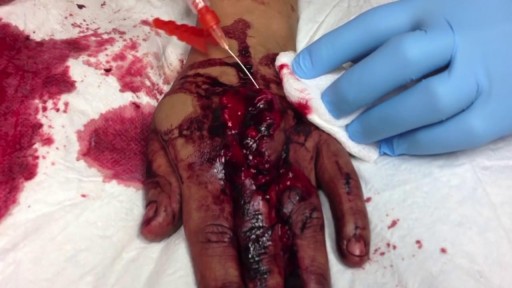
Skin laceration repair is an important skill in family medicine. Sutures, tissue adhesives, staples, and skin-closure tapes are options in the outpatient setting. Physicians should be familiar with various suturing techniques, including simple, running, and half-buried mattress (corner) sutures. Although suturing is the preferred method for laceration repair, tissue adhesives are similar in patient satisfaction, infection rates, and scarring risk in low skin-tension areas and may be more cost-effective. The tissue adhesive hair apposition technique also is effective in repairing scalp lacerations. The sting of local anesthesia injections can be lessened by using smaller gauge needles, administering the injection slowly, and warming or buffering the solution. Studies have shown that tap water is safe to use for irrigation, that white petrolatum ointment is as effective as antibiotic ointment in postprocedure care, and that wetting the wound as early as 12 hours after repair does not increase the risk of infection. Patient education and appropriate procedural coding are important after the repair.